
Lake Saint Pierre is a lake in Quebec, Canada, a widening of the Saint Lawrence River between Sorel-Tracy and Trois-Rivières. It is located downstream, and northeast, of Montreal; and upstream, and southwest, of Quebec City. The end of the lake delimits the beginning of the estuary of Saint Lawrence.

Slovincians, also known as Łeba Kashubians, is a near-extinct ethnic subgroup of the Kashubian people, who originated from the north western Kashubia, located in the Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland, from the area around the lakes of Łebsko and Gardno. In the aftermath of World War II, Slovincians emigrated en masse to Germany, with the last families emigrating there in the 1980s. They originally spoke the Slovincian language, which went extinct in the early 20th century, as well as Kashubian, Polish, and German.

Lake Peipus is the largest trans-boundary lake in Europe, lying on the international border between Estonia and Russia.
UNESCO Biosphere Reserves are environment-protected scientific-research institutions of international status that are created with the intent for conservation in a natural state the most typical natural complexes of biosphere, conducting background ecological monitoring, studying of the surrounding natural environment, its changes under the activity of anthropogenic factors.

Łeba is a seaside town in the Pomeranian Voivodeship of northern Poland. It is located in the region of Gdańsk Pomerania (Pomerelia), near Łebsko Lake and the mouth of the river Łeba on the Slovincian Coast of the Baltic Sea.

Étang Saumâtre, is the largest lake in Haiti It is also known as Lake Azuéi ; its Taíno name was Yainagua.

The Lake Prespa is located on the tripoint of North Macedonia, Albania and Greece. It is a system of two lakes separated by an isthmus: the Great Prespa Lake, divided between the three countries, and the Little Prespa Lake, mostly within Greece. They are the highest tectonic lakes in the Balkans, at an elevation of 853 metres (2,799 ft).

Malham Tarn is a glacial lake near the village of Malham in the Yorkshire Dales, England. The lake is one of only eight upland alkaline lakes in Europe. At an altitude of 377 metres (1,237 ft) above sea level it is the highest marl lake in the United Kingdom. Its geology, flora and fauna have led to it being listed under a number of conservation designations. The site is currently owned by the National Trust, who used to lease part of the site to the Field Studies Council but this closed as a field centre in 2022. The site was the inspiration for Charles Kingsley's 1863 novel The Water-Babies, A Fairy Tale for a Land Baby.

The Łeba, a river in Middle Pomerania (Poland), originates near the village of Borzestowo west of Kartuzy, passes through Łebsko Lake and empties into the Baltic Sea. It is 117 km long with a basin area of 1,801 km².

Giant Mountains National Park is a National Park in the Giant Mountains in the Sudetes in southwestern Poland, along the border with the Czech Republic.

Wigry National Park is a national park in Podlaskie Voivodeship in northeastern Poland. It covers parts of the Masurian Lake District and Augustów Primeval Forest. It is named after Lake Wigry, the largest of the park's many lakes. It is also designated as a Ramsar wetland site, one of 13 such sites in Poland.

Tatra National Park is a national park located in the Tatra Mountains in Tatra County, in the Lesser Poland Voivodeship in central-southern Poland. The park is headquartered in the town of Zakopane.

Gardno is a lake in the Słowińskie Lakeland in Pomeranian Voivodship, Poland. It is the part of Słowiński National Park. Its area is 24.69 km2 (9.53 sq mi). It is 6.8 km long and 4.7 km wide. Maximum depth is 2.6 m.

Łebsko Lake is a brackish coastal lake in the Pomeranian Voivodeship of Poland. It is connected to the Baltic Sea by the Łeba River, which causes saltwater intrusion. It is located within Słowiński National Park. The lake formed when sea winds pushed up a spit of sand that ultimately separated it from the Baltic sea. The town of Łeba sits where the Łeba river meets the sea.

The wildlife of Chad is composed of its flora and fauna. West African lions, buffalo, hippopotamuses, Kordofan giraffes, antelopes, African leopards, cheetahs, hyenas, Bush elephants, and many species of snakes are found there, although most large carnivore populations have been drastically reduced since the early 20th century. Elephant poaching, particularly in the south of the country in areas such as Zakouma National Park, is a severe problem.

Butrint Lagoon is a salt lagoon south of Saranda, Albania, located in direct proximity of the Ionian Sea. It is surrounded by dense forested hills, rocky coast and complemented by saltwater and freshwater marshlands. The lake has a length of 7.1 km (4.4 mi) and a width of 3.3 km (2.1 mi), with a surface area of 16 km2 (6.18 sq mi). The maximum depth of the lake is 24.4 m (80 ft). At the south, the Vivari Channel connects the lagoon to the sea.

Bundala National Park is an internationally important wintering ground for migratory water birds in Sri Lanka. Bundala harbors 197 species of birds, the highlight being the greater flamingo, which migrate in large flocks. Bundala was designated a wildlife sanctuary in 1969 and redesignated to a national park on 4 January 1993. In 1991 Bundala became the first wetland to be declared as a Ramsar site in Sri Lanka. In 2005 the national park was designated as a biosphere reserve by UNESCO, the fourth biosphere reserve in Sri Lanka. The national park is situated 245 kilometres (152 mi) southeast of Colombo.
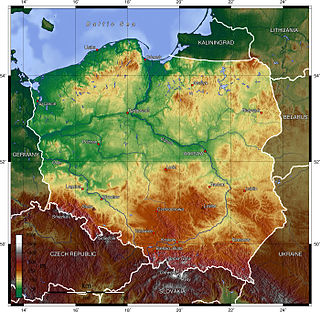
Poland is a country that extends across the North European Plain from the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south to the sandy beaches of the Baltic Sea in the north. Poland is the fifth-most populous country of the European Union and the ninth-largest country in Europe by area. The territory of Poland covers approximately 312,696 km2 (120,733 sq mi), of which 98.52% is land and 1.48% is water. The Polish coastline was estimated at 770 km (478 mi) in length. Poland's highest point is Rysy, at 2,500 m (8,202 ft).

The Slovincian Coast (313.41) is a mesoregion, the northernmost part of the Koszalin Coast, with an area of 1132 km2. The highest hill is Rowokół, at 114,8 metres above sea level. The coast stretches from the west at Kołobrzeg, up to the east at Karwia. The landscape mainly compromises of dunes, marshland and lakes. The region is sparsely populated. The towns of Łeba, Ustka, Darłowo and Mielno are located on the coast. In the region of the Slovincian Coast is the Słowiński National Park, and the spas of Ustka and Dąbki.



































