A period 5 element is one of the chemical elements in the fifth row of the periodic table of the chemical elements. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behaviour of the elements as their atomic number increases: a new row is begun when chemical behaviour begins to repeat, meaning that elements with similar behaviour fall into the same vertical columns. The fifth period contains 18 elements, beginning with rubidium and ending with xenon. As a rule, period 5 elements fill their 5s shells first, then their 4d, and 5p shells, in that order; however, there are exceptions, such as rhodium.

Group 3 is the first group of transition metals in the periodic table. This group is closely related to the rare-earth elements. It contains the four elements scandium (Sc), yttrium (Y), lutetium (Lu), and lawrencium (Lr). The group is also called the scandium group or scandium family after its lightest member.

Yttrium oxide, also known as yttria, is Y2O3. It is an air-stable, white solid substance.
Yttrium oxide may refer to:
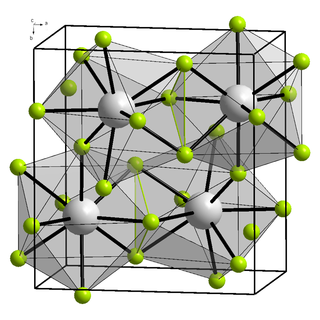
Yttrium(III) fluoride is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula YF3. It is not known naturally in 'pure' form. The fluoride minerals containing essential yttrium include tveitite-(Y) (Y,Na)6Ca6Ca6F42 and gagarinite-(Y) NaCaY(F,Cl)6. Sometimes mineral fluorite contains admixtures of yttrium.

Yttrium(III) chloride is an inorganic compound of yttrium and chloride. It exists in two forms, the hydrate (YCl3(H2O)6) and an anhydrous form (YCl3). Both are colourless solids that are highly soluble in water and deliquescent.
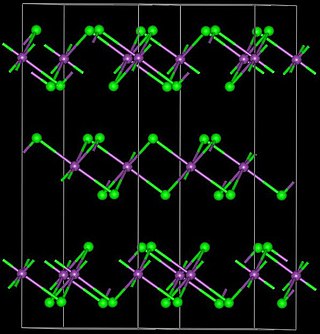
Yttrium(III) bromide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula YBr3. It is a white solid. Anhydrous yttrium(III) bromide can be produced by reacting yttrium oxide or yttrium(III) bromide hydrate and ammonium bromide. The reaction proceeds via the intermediate (NH4)3YBr6. Another method is to react yttrium carbide (YC2) and elemental bromine. Yttrium(III) bromide can be reduced by yttrium metal to YBr or Y2Br3. It can react with osmium to produce Y4Br4Os.

Organoyttrium chemistry is the study of compounds containing carbon-yttrium bonds. These compounds are almost invariably formal Y3+ derivatives, are generally diamagnetic and colorless, a consequence of the closed-shell configuration of the trication. Organoyttrium compounds are mainly of academic interest.

Yttrium is a chemical element with the symbol Y and atomic number 39. It is a silvery-metallic transition metal chemically similar to the lanthanides and has often been classified as a "rare-earth element". Yttrium is almost always found in combination with lanthanide elements in rare-earth minerals, and is never found in nature as a free element. 89Y is the only stable isotope, and the only isotope found in the Earth's crust.

DOTA (also known as tetraxetan) is an organic compound with the formula (CH2CH2NCH2CO2H)4. The molecule consists of a central 12-membered tetraaza (i.e., containing four nitrogen atoms) ring. DOTA is used as a complexing agent, especially for lanthanide ions. Its complexes have medical applications as contrast agents and cancer treatments.
Yttrium hydride is a compound of hydrogen and yttrium. It is considered to be a part of the class of rare-earth metal hydrides. It exists in several forms, the most common being a metallic compound with formula YH2. YH2 has a face-centred cubic structure, and is a metallic compound. Under great pressure, extra hydrogen can combine to yield an insulator with a hexagonal structure, with a formula close to YH3. Hexagonal YH3 has a band gap of 2.6 eV. Under pressure of 12 GPa YH3 transforms to an intermediate state, and when the pressure increases to 22 GPa another metallic face-centred cubic phase is formed.
Yttrium phosphide is an inorganic compound of yttrium and phosphorus with the chemical formula YP. The compound may be also classified as yttrium(III) phosphide.
Yttrium oxyfluoride is an inorganic chemical compound with the formula YOF. Under normal conditions, the compound is a colorless solid.

Yttrium(III) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt with the formula Y(NO3)3. The hexahydrate is the most common form commercially available.
An yttrium compound is a chemical compound containing yttrium. Among these compounds, yttrium generally has a +3 valence. The solubility properties of yttrium compounds are similar to those of the lanthanides. For example oxalates and carbonates are hardly soluble in water, but soluble in excess oxalate or carbonate solutions as complexes are formed. Sulfates and double sulfates are generally soluble. They resemble the "yttrium group" of heavy lanthanide elements.
Yttrium(III) hydroxide is an inorganic compound and an alkali with the chemical formula Y(OH)3.
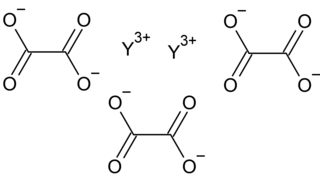
Yttrium oxalate is an inorganic compound, a salt of yttrium and oxalic acid with the chemical formula Y2(C2O4)3. The compound does not dissolve in water and forms crystalline hydrates—colorless crystals.
Yttrium(II) oxide or yttrium monoxide is a chemical compound with the formula YO. This chemical compound was first created in its solid form by pulsed laser deposition, using yttrium(III) oxide as the target at 350 °C. The film was deposited on calcium fluoride using a krypton monofluoride laser. This resulted in a 200nm flim of yttrium monoxide.
Yttrium iodide is a binary inorganic compound, a salt of yttrium and hydroiodic acid with the formula YI
3. The compound forms colorless crystals, soluble in water.











