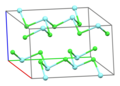
Part of a layer in the crystal structure of YCl3 [1] | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC names Yttrium(III) chloride Yttrium trichloride | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
| ||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.716 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID | |||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| YCl3 | |||
| Molar mass | 195.265 g/mol [2] | ||
| Appearance | white solid | ||
| Density | 2.61 g/cm3 [2] | ||
| Melting point | 721 °C (1,330 °F; 994 K) [2] | ||
| Boiling point | 1,482 °C (2,700 °F; 1,755 K) [2] | ||
| 751 g/L (20 °C) [2] | |||
| Solubility | 601 g/L ethanol (15 °C) 606 g/L pyridine (15 °C) [3] | ||
| Structure [4] | |||
| Monoclinic, mS16 | |||
| C2/m, No. 12 | |||
a = 0.692 nm, b = 1.194 nm, c = 0.644 nm α = 90°, β = 111°, γ = 90° | |||
Formula units (Z) | 4 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
 | |||
| Warning | |||
| H315, H319, H335 | |||
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Other anions | Yttrium(III) fluoride Yttrium(III) bromide Yttrium(III) iodide | ||
Other cations | Scandium(III) chloride Lutetium(III) chloride | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
Yttrium(III) chloride is an inorganic compound of yttrium and chloride. It exists in two forms, the hydrate (YCl3(H2O)6) and an anhydrous form (YCl3). Both are colourless salts that are highly soluble in water and deliquescent.