The actinide or actinoid series encompasses at least the 14 metallic chemical elements in the 5f series, with atomic numbers from 89 to 102, actinium through nobelium. Number 103, lawrencium, is also generally included despite being part of the 6d transition series. The actinide series derives its name from the first element in the series, actinium. The informal chemical symbol An is used in general discussions of actinide chemistry to refer to any actinide.
Berkelium is a synthetic chemical element; it has symbol Bk and atomic number 97. It is a member of the actinide and transuranium element series. It is named after the city of Berkeley, California, the location of the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory where it was discovered in December 1949. Berkelium was the fifth transuranium element discovered after neptunium, plutonium, curium and americium.

Neptunium is a chemical element; it has symbol Np and atomic number 93. A radioactive actinide metal, neptunium is the first transuranic element. It is named after Neptune, the planet beyond Uranus in the Solar System, which uranium is named after. A neptunium atom has 93 protons and 93 electrons, of which seven are valence electrons. Neptunium metal is silvery and tarnishes when exposed to air. The element occurs in three allotropic forms and it normally exhibits five oxidation states, ranging from +3 to +7. Like all actinides, it is radioactive, poisonous, pyrophoric, and capable of accumulating in bones, which makes the handling of neptunium dangerous.

Protactinium is a chemical element; it has symbol Pa and atomic number 91. It is a dense, radioactive, silvery-gray actinide metal which readily reacts with oxygen, water vapor, and inorganic acids. It forms various chemical compounds, in which protactinium is usually present in the oxidation state +5, but it can also assume +4 and even +3 or +2 states. Concentrations of protactinium in the Earth's crust are typically a few parts per trillion, but may reach up to a few parts per million in some uraninite ore deposits. Because of its scarcity, high radioactivity, and high toxicity, there are currently no uses for protactinium outside scientific research, and for this purpose, protactinium is mostly extracted from spent nuclear fuel.

Thorium(IV) chloride describes a family of inorganic compounds with the formula ThCl4(H2O)n. Both the anhydrous and tetrahydrate (n = 4) forms are known. They are hygroscopic, water-soluble white salts.

Organoactinide chemistry is the science exploring the properties, structure, and reactivity of organoactinide compounds, which are organometallic compounds containing a carbon to actinide chemical bond.

Protactinium(V) chloride is the chemical compound composed of protactinium and chlorine with the formula PaCl5. It forms yellow monoclinic crystals and has a unique structure composed of chains of 7 coordinate, pentagonal bipyramidal, protactinium atoms sharing edges.

Niobium(IV) chloride, also known as niobium tetrachloride, is the chemical compound of formula NbCl4. This compound exists as dark violet crystals, is highly sensitive to air and moisture, and disproportiates into niobium(III) chloride and niobium(V) chloride when heated.
Berkelium forms a number of chemical compounds, where it normally exists in an oxidation state of +3 or +4, and behaves similarly to its lanthanide analogue, terbium. Like all actinides, berkelium easily dissolves in various aqueous inorganic acids, liberating gaseous hydrogen and converting into the trivalent oxidation state. This trivalent state is the most stable, especially in aqueous solutions, but tetravalent berkelium compounds are also known. The existence of divalent berkelium salts is uncertain and has only been reported in mixed lanthanum chloride-strontium chloride melts. Aqueous solutions of Bk3+ ions are green in most acids. The color of the Bk4+ ions is yellow in hydrochloric acid and orange-yellow in sulfuric acid. Berkelium does not react rapidly with oxygen at room temperature, possibly due to the formation of a protective oxide surface layer; however, it reacts with molten metals, hydrogen, halogens, chalcogens and pnictogens to form various binary compounds. Berkelium can also form several organometallic compounds.
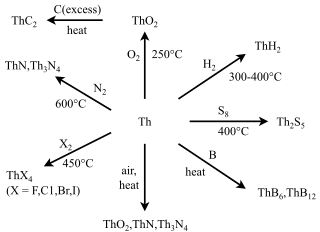
Many compounds of thorium are known: this is because thorium and uranium are the most stable and accessible actinides and are the only actinides that can be studied safely and legally in bulk in a normal laboratory. As such, they have the best-known chemistry of the actinides, along with that of plutonium, as the self-heating and radiation from them is not enough to cause radiolysis of chemical bonds as it is for the other actinides. While the later actinides from americium onwards are predominantly trivalent and behave more similarly to the corresponding lanthanides, as one would expect from periodic trends, the early actinides up to plutonium have relativistically destabilised and hence delocalised 5f and 6d electrons that participate in chemistry in a similar way to the early transition metals of group 3 through 8: thus, all their valence electrons can participate in chemical reactions, although this is not common for neptunium and plutonium.
Curium (Cm) usually forms compounds in the +3 oxidation state, although compounds with curium in the +4, +5 and +6 oxidation states are also known.
Protactinium(V) bromide is an inorganic compound. It is a halide of protactinium, consisting of protactinium and bromine. It is radioactive and has a chemical formula of PaBr5, which is a red crystal of the monoclinic crystal system.
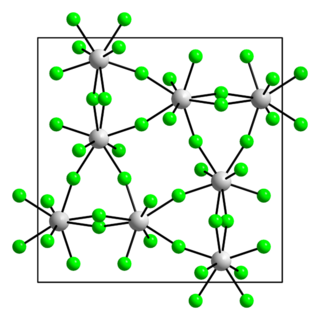
Protactinium(V) fluoride is a fluoride of protactinium with the chemical formula PaF5.

Protactinium(IV) bromide is an inorganic compound. It is an actinide halide, composed of protactinium and bromine. It is radioactive, and has the chemical formula of PaBr4. It may be due to the brown color of bromine that causes the appearance of protactinium(IV) bromide to be brown crystals. Its crystal structure is tetragonal. Protactinium(IV) bromide is sublimed in a vacuum at 400 °C. The protactinium(IV) halide closest in structure to protactinium(IV) bromide is protactinium(IV) chloride.
Protactinium compounds are compounds containing the element protactinium. These compounds usually have protactinium in the +5 oxidation state, although these compounds can also exist in the +2, +3 and +4 oxidation states.
Neptunium compounds are compounds containing the element neptunium (Np). Neptunium has five ionic oxidation states ranging from +3 to +7 when forming chemical compounds, which can be simultaneously observed in solutions. It is the heaviest actinide that can lose all its valence electrons in a stable compound. The most stable state in solution is +5, but the valence +4 is preferred in solid neptunium compounds. Neptunium metal is very reactive. Ions of neptunium are prone to hydrolysis and formation of coordination compounds.
Americium compounds are compounds containing the element americium (Am). These compounds can form in the +2, +3, and +4, although the +3 oxidation state is the most common. The +5, +6 and +7 oxidation states have also been reported.
Thorium(IV) bromide is an inorganic compound, with the chemical formula of ThBr4.

Neptunium tetrachloride is a binary inorganic compound of neptunium metal and chlorine with the chemical formula NpCl4.
Protactinium tetraiodide is a binary inorganic compound of protactinium metal and iodine with the chemical formula PaI4.











