Related Research Articles

Palladium(II) chloride, also known as palladium dichloride and palladous chloride, are the chemical compounds with the formula PdCl2. PdCl2 is a common starting material in palladium chemistry – palladium-based catalysts are of particular value in organic synthesis. It is prepared by the reaction of chlorine with palladium metal at high temperatures.

Sulfur dichloride is the chemical compound with the formula SCl2. This cherry-red liquid is the simplest sulfur chloride and one of the most common, and it is used as a precursor to organosulfur compounds. It is a highly corrosive and toxic substance, and it reacts on contact with water to form chlorine-containing acids.

Vanadium(II) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula VCl2, and is the most reduced vanadium chloride. Vanadium(II) chloride is an apple-green solid that dissolves in water to give purple solutions.

Tritellurium dichloride is the inorganic compound with the formula Te3Cl2. It is one of the more stable lower chlorides of tellurium.
Niobocene dichloride is the organometallic compound with the formula (C5H5)2NbCl2, abbreviated Cp2NbCl2. This paramagnetic brown solid is a starting reagent for the synthesis of other organoniobium compounds. The compound adopts a pseudotetrahedral structure with two cyclopentadienyl and two chloride substituents attached to the metal. A variety of similar compounds are known, including Cp2TiCl2.

(Cymene)ruthenium dichloride dimer is the organometallic compound with the formula [(cymene)RuCl2]2. This red-coloured, diamagnetic solid is a reagent in organometallic chemistry and homogeneous catalysis. The complex is structurally similar to (benzene)ruthenium dichloride dimer.

Germanium dichloride is a chemical compound of germanium and chlorine with the formula GeCl2. It is a yellow solid. Germanium dichloride is an example of a compound featuring germanium in the +2 oxidation state.

Pentamethylcyclopentadienyl iridium dichloride dimer is an organometallic compound with the formula [(C5(CH3)5IrCl2)]2, commonly abbreviated [Cp*IrCl2]2 This bright orange air-stable diamagnetic solid is a reagent in organometallic chemistry.
Selenium monochloride or diselenium dichloride is an inorganic compound with the formula Se2Cl2. Although a common name for the compound is selenium monochloride, reflecting its empirical formula, IUPAC does not recommend that name, instead preferring the more descriptive diselenium dichloride.

Few compounds of californium have been made and studied. The only californium ion that is stable in aqueous solutions is the californium(III) cation. The other two oxidation states are IV (strong oxidizing agents) and II (strong reducing agents). The element forms a water-soluble chloride, nitrate, perchlorate, and sulfate and is precipitated as a fluoride, oxalate or hydroxide. If problems of availability of the element could be overcome, then CfBr2 and CfI2 would likely be stable.

Tellurium dichloride is a chloride of tellurium with the chemical formula TeCl2.

Pentamminechlororhodium dichloride is the dichloride salt of the coordination complex [RhCl(NH3)5]2+. It is a yellow, water-soluble solid. The salt is an intermediate in the purification of rhodium from its ores.

Bis(benzonitrile)palladium dichloride is the coordination complex with the formula PdCl2(NCC6H5)2. It is the adduct of two benzonitrile (PhCN) ligands with palladium(II) chloride. It is a yellow-brown solid that is soluble in organic solvents. The compound is a reagent and a precatalyst for reactions that require soluble Pd(II). A closely related compound is bis(acetonitrile)palladium dichloride.

(Benzene)ruthenium dichloride dimer is the organoruthenium compound with the formula [(C6H6)RuCl2]2. This red-coloured, diamagnetic solid is a reagent in organometallic chemistry and homogeneous catalysis.
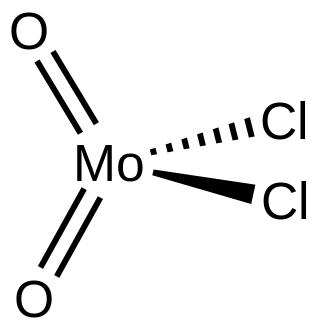
Molybdenum dichloride dioxide is the inorganic compound with the formula MoO2Cl2. It is a yellow diamagnetic solid that is used as a precursor to other molybdenum compounds. Molybdenum dichloride dioxide is one of several oxychlorides of molybdenum.

(Cyclopentadienyl)titanium trichloride is an organotitanium compound with the formula (C5H5)TiCl3. It is a moisture sensitive orange solid. The compound adopts a piano stool geometry.
Dysprosium(II) chloride (DyCl2), also known as dysprosium dichloride, is an ionic chemical compound of dysprosium and chlorine. This salt is a reduced compound, as the normal oxidation state of dysprosium in dysprosium compounds is +3.
Einsteinium(II) chloride is a binary inorganic chemical compound of einsteinium and chlorine with the chemical formula EsCl2.
Californium tetrafluoride is a binary inorganic compound of californium and fluorine with the formula CfF4.
Thorium triiodide is a binary inorganic compound of thorium metal and chloride with the chemical formula ThCl2.
References
- ↑ "WebElements Periodic Table » Californium » californium dichloride". webelements.com. Retrieved 16 April 2024.
- ↑ J.R., Peterson; R.L., Fellows; R.G., Haire; J.P., Young (1977). "Stabilization of californium(II) in the solid state". Radiochemical and Radioanalytical Letters. 31 (4–5). Retrieved 16 April 2024.
- 1 2 Macintyre, Jane E. (23 July 1992). Dictionary of Inorganic Compounds. CRC Press. p. 2825. ISBN 978-0-412-30120-9 . Retrieved 16 April 2024.