Union Square is a neighborhood located in the Sowebo area of Baltimore. It dates to the 1830s and includes a historic district of houses and commerce buildings.

The Margaret Sanger Clinic is a historic building at 17 West 16th Street in Manhattan, New York City. Built in 1846, it is notable as the location of the Clinical Research Bureau, where birth control pioneer Margaret Sanger and her successors provided contraceptive services and conducted research from 1930 to 1973. The building was designated a New York City Landmark in 1976 for its Greek Revival architecture, and was declared a National Historic Landmark in 1993 for its association with Sanger.

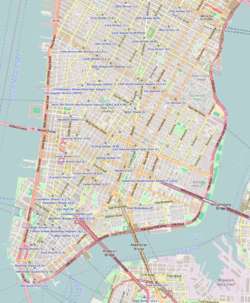
1 Hanover Square is a commercial building on the southwestern edge of Hanover Square in the Financial District of Lower Manhattan in New York City. It was the site of the United States' first cotton futures exchange, the New York Cotton Exchange.

The New York Amsterdam News Building is a historic rowhouse at 2293 Seventh Avenue in the Harlem neighborhood of Manhattan, New York City. It is historically significant as the publishing home of the New York Amsterdam News between 1916 and 1938. During this period, the newspaper became one of the nation's most influential publications covering African-American issues. It was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1976. The Amsterdam News now publishes out of a building at 2340 Frederick Douglass Boulevard.

The General Winfield Scott House is a historic rowhouse at 24 West 12th Street in the Greenwich Village area of Lower Manhattan in New York City. Built in 1851–52, the house was home to General and unsuccessful Whig Presidential candidate Winfield Scott (1786–1866) from 1853 to 1855. Best known as the leader of the United States Army during the Mexican–American War, Scott had a significant effect on the Army for about half a century. The building was declared a National Historic Landmark in 1973.

The Reynolds-Morris House is an historic house which is located at 225 South 8th Street in the Washington Square West neighborhood of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Built between 1786 and 1787 by John and William Reynolds, it is a well-preserved example of a Philadelphia Georgian townhouse.

The Thomas Sully Residence is a historic rowhouse at 530 Spruce Street in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA. It was briefly (1828–29) a home of painter Thomas Sully (1783-1872), who lived in Philadelphia for the last 64 years of his life.

The William H. Welch House is a three-story rowhouse located at 935 St. Paul Street in Baltimore, Maryland. Probably built in the 1880s, it is notable as the residence of William H. Welch (1850-1934) from 1891 to 1908. Welch was one of the "Big Four" founding professors at Johns Hopkins Hospital, and an important conduit of European medical research methods and ideas to the United States. He was also the first dean of the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and the first director of the Johns Hopkins School of Hygiene and Public Health. The house was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1976, and is included in the Baltimore National Heritage Area.

The houses at 208–218 East 78th Street in Manhattan, New York, United States, are a group of six attached brick rowhouses built during the early 1860s, on the south side of the street between Second and Third Avenues. They are the remnant of 15 built along that street as affordable housing when the Upper East Side was just beginning to be developed.

The East 80th Street Houses are a group of four attached rowhouses on that street in the New York City borough of Manhattan. They are built of brick with various stone trims in different versions of the Colonial Revival architectural style.

The East 73rd Street Historic District is a block of that street on the Upper East Side of the New York City borough of Manhattan, on the south side of the street between Lexington and Third Avenues. It is a neighborhood of small rowhouses built from the mid-19th to early 20th centuries.

The W New York Union Square is a 270-room, 21-story boutique hotel operated by W Hotels at the northeast corner of Park Avenue South and 17th Street, across from Union Square in Manhattan, New York. Originally known as the Germania Life Insurance Company Building, it was designed by Albert D'Oench and Joseph W. Yost and built in 1911 in the Beaux-Arts style.

The Benjamin N. Duke House, also the Duke–Semans Mansion and the Benjamin N. and Sarah Duke House, is a mansion at 1009 Fifth Avenue, at the southeast corner with 82nd Street, on the Upper East Side of Manhattan in New York City. It was built between 1899 and 1901 and was designed by the firm of Welch, Smith & Provot. The house, along with three other mansions on the same block, was built speculatively by developers William W. Hall and Thomas M. Hall. The Benjamin N. Duke House is one of a few remaining private mansions along Fifth Avenue. It is a New York City designated landmark and is listed on the National Register of Historic Places.

The William H. Moore House, also known as the Stokes-Moore Mansion and 4 East 54th Street, is a commercial building in the Midtown Manhattan neighborhood of New York City. It is along 54th Street's southern sidewalk between Madison Avenue and Fifth Avenue. The building was designed by McKim, Mead & White and constructed between 1898 and 1900 as a private residence.

The Isaac T. Hopper House is a Greek Revival townhouse at 110 Second Avenue between East 6th and 7th Streets in the East Village neighborhood of Manhattan, New York City. Located just south of the New Middle Collegiate Church, it was built in 1837 and 1838 as a rowhouse. The building was also known as the Ralph and Ann E. Van Wyck Mead House, after its first owner. 110 Second Avenue is the only remaining rowhouse out of a group of four at 106–112 Second Avenue that was used by the Meads' extended family, and was originally known as 108 Second Avenue.

The Walter Merchant House, on Washington Avenue in Albany, New York, United States, is a brick-and-stone townhouse in the Italianate architectural style, with some Renaissance Revival elements. Built in the mid-19th century, it was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2002.

The 12 rowhouses at 322–344 East 69th Street are located on the south side of that street between First and Second avenues on the Upper East Side of the New York City borough of Manhattan. They are Neo-Grec brownstone structures built around 1879, in two sets designed by different architects.

State Street Houses describes 23 Greek Revival and Italianate rowhouses built between 1847 and 1874 and located at 291-299 (odd) and 290-324 (even) State Street between Smith and Hoyt Streets in the Boerum Hill neighborhood of Brooklyn, New York City. The construction of the houses was part of the transformation of the formerly rural area into a fashionable new residential neighborhood.

Langston Hughes House is a historic home located in Harlem, Manhattan, New York City. It is an Italianate style dwelling built in 1869. It is a three story with basement, rowhouse faced in brownstone and measuring 20 feet wide and 45 feet deep. Noted African American poet and author Langston Hughes (1902-1967) occupied the top floor as his workroom from 1947 to 1967.

The Schinasi House is a 12,000-square-foot (1,100 m2), 35-room marble mansion located at 351 Riverside Drive on the Upper West Side of Manhattan in New York City. It was built in 1907 for Sephardic Jewish tobacco baron Morris Schinasi. The mansion was designed by Carnegie Hall architect William Tuthill and reportedly retains almost all of its historic detail, including a Prohibition-era trap door that once extended all the way to the river.