The South Island is the largest of the three major islands of New Zealand in surface area, the other being the smaller but more populous North Island and sparsely populated Stewart Island. It is bordered to the north by Cook Strait, to the west by the Tasman Sea, to the south by the Foveaux Strait and Southern Ocean, and to the east by the Pacific Ocean. The South Island covers 150,437 square kilometres (58,084 sq mi), making it the world's 12th-largest island, constituting 56% of New Zealand's land area. At low altitudes, it has an oceanic climate.

Invercargill is the southernmost and westernmost city in New Zealand, and one of the southernmost cities in the world. It is the commercial centre of the Southland region. The city lies in the heart of the wide expanse of the Southland Plains to the east of the Ōreti or New River some 18 km north of Bluff, which is the southernmost town in the South Island. It sits amid rich farmland that is bordered by large areas of conservation land and marine reserves, including Fiordland National Park covering the south-west corner of the South Island and the Catlins coastal region.

Chatham Island is the largest island of the Chatham Islands group, in the south Pacific Ocean off the eastern coast of New Zealand's South Island. It is said to be "halfway between the equator and the pole, and right on the International Date Line", although that point is 173 miles WSW of the island's westernmost point. The island is called Rekohu in Moriori, and Wharekauri in Māori.

Tasman District is a local government district in the northwest of the South Island of New Zealand. It borders the Canterbury Region, West Coast Region, Marlborough Region and Nelson City. It is administered by the Tasman District Council, a unitary authority, which sits at Richmond, with community boards serving outlying communities in Motueka and Golden Bay / Mohua. The city of Nelson has its own unitary authority separate from Tasman District, and together they comprise a single region in some contexts, but not for local government functions or resource management (planning) functions.

Haast is a small town in the Westland District territorial authority on the West Coast of New Zealand's South Island. The township is beside the Haast River, 3 kilometres (2 mi) south of Haast Junction, on State Highway 6. The Haast region is in Te Wahipounamu – The South West New Zealand World Heritage, a UNESCO World Heritage Site designated in 1990.

The Tweed River is a river situated in the Northern Rivers region of New South Wales, Australia. From the middle reaches of its course, the state boundary between New South Wales and Queensland is located approximately 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) north.

The Catlins comprise an area in the southeastern corner of the South Island of New Zealand. The area lies between Balclutha and Invercargill, straddling the boundary between the Otago and Southland regions. It includes the South Island's southernmost point, Slope Point.
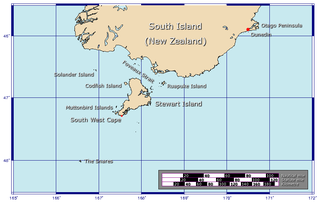
Ruapuke Island is one of the southernmost islands in New Zealand's main chain of islands. It lies 15 kilometres (9.3 mi) to the southeast of Bluff and 32 kilometres (20 mi) northeast of Oban on Stewart Island/Rakiura. It was named "Bench Island" upon its discovery by Captain James Cook in 1770, but has rarely been known by any other name than its Māori name, which means "two hills". Ruapuke Island was called Goulburn Island by Captain John Kent, named after Frederick Goulburn, a Government official in New South Wales, but the whalers generally called it Long Island, or Robuck. The island covers an area of about 16 km2 (6 sq mi). It guards the eastern end of Foveaux Strait.
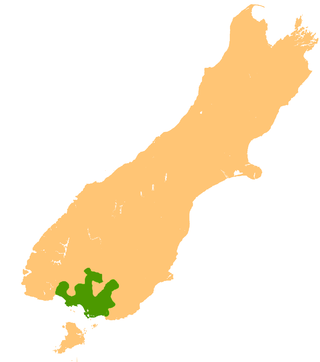
The Southland Plains is a general name given to several areas of low-lying land in the South Island of New Zealand, separated by the rise of the Hokonui Hills in the north. It forms a sizeable area of Southland region and encompasses its two principal settlements the city of Invercargill and the town of Gore. The Southland Plains include some of New Zealand's most fertile farmland.

The Awarua Plain is a large area of wetland to the east of Bluff, New Zealand. Covering an area of around 600 km², the plain stretches for 35 kilometres along the coast of Foveaux Strait. This stretch of coast includes the peninsula of Tiwai Point, Awarua Bay, the Waituna Lagoon, and Toetoes Bay. The Mataura River is the major river responsible for the presence of the Awarua Plain; along with the Ōreti River, it is a remnant of the rivers from the Ice Ages that formed the Southland Plains (Murihiku). In addition, several small streams enter Foveaux Strait along this stretch of coast, mainly via Awarua Bay and Waituna Lagoon.

Toetoes Bay is the easternmost of three large bays lying on the Foveaux Strait coast of Southland, New Zealand, the others being Te Waewae Bay and Oreti Beach. The 240 km Mataura River drains to sea at Toetoes Bay, first passing through the Toetoes Harbour estuary. Thirty kilometres in length, the bay is the southern end of the Awarua Plain, an area of swampy land stretching inland for about fifteen kilometres. The eastern end of the bay is close to Slope Point, the South Island's southernmost point, and the western end of the Catlins.
Awarua Point is located on the southwestern coast of New Zealand's South Island, at the northern end of Big Bay, 40 kilometres (25 mi) north of Milford Sound / Piopiotahi, and 15 kilometres (9.3 mi) north of the mouth of the Hollyford River / Whakatipu Kā Tuka.

Te Awarua-o-Porirua Harbour, commonly known as Porirua Harbour, is a natural inlet in the south-western coast of the North Island of New Zealand.
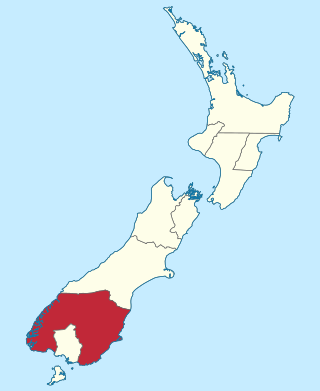
The Otago Province was a province of New Zealand until the abolition of provincial government in 1876. The capital of the province was Dunedin. Southland Province split from Otago in 1861, but became part of the province again in 1870.

Stewart Island is New Zealand's third-largest island, located 30 kilometres south of the South Island, across Foveaux Strait. It is a roughly triangular island with a total land area of 1,746 km2 (674 sq mi). Its 164-kilometre (102 mi) coastline is deeply indented by Paterson Inlet (east), Port Pegasus (south), and Mason Bay (west). The island is generally hilly and densely forested. Flightless birds, including penguins, thrive because there are few introduced predators. Almost all the island is owned by the New Zealand government, and over 80 per cent of the island is set aside as the Rakiura National Park.
The Awarua River is a short river that flows from the Waiuna Lagoon into Big Bay, also known as Awarua Bay, an embayment at the northern end of Fiordland in New Zealand. The river's mouth is at the northern end of Three Mile Beach, the Big Bay beach. One of the rivers that feeds Waiuna Lagoon is the Dry Awarua River.

Southland is New Zealand's southernmost region. It consists of the southwestern portion of the South Island and includes Stewart Island. Southland is bordered by the culturally similar Otago Region to the north and east, and the West Coast Region in the extreme northwest. The region covers over 3.1 million hectares and spans 3,613 km of coastline. As of June 2023, Southland has a population of 103,900, making it the eleventh-most-populous New Zealand region, and the second-most sparsely populated. Approximately half of the region's population lives in Invercargill, Southland's only city.

Nepean Bay is a bay located on the north-east coast of Kangaroo Island in the Australian state of South Australia about 130 kilometres south-south-west of Adelaide. It was named by the British navigator, Matthew Flinders, after Sir Evan Nepean on 21 March 1802.
Waiuna Lagoon is a lake in the Southland Region of New Zealand's South Island, just inland from Big Bay. It is 15 metres above sea level, and is drained by the Awarua River.

A waituna is a freshwater coastal lagoon on a mixed sand and gravel (MSG) beach, formed where a braided river meets a coastline affected by longshore drift. This type of waterbody is neither a true lake, lagoon nor estuary.