A column or pillar in architecture and structural engineering is a structural element that transmits, through compression, the weight of the structure above to other structural elements below. In other words, a column is a compression member. The term column applies especially to a large round support with a capital and a base or pedestal, which is made of stone, or appearing to be so. A small wooden or metal support is typically called a post. Supports with a rectangular or other non-round section are usually called piers.

Worsted is a high-quality type of wool yarn, the fabric made from this yarn, and a yarn weight category. The name derives from Worstead, a village in the English county of Norfolk. That village, together with North Walsham and Aylsham, formed a manufacturing centre for yarn and cloth in the 12th century, when pasture enclosure and liming rendered the East Anglian soil too rich for the older agrarian sheep breeds. In the same period, many weavers from the County of Flanders moved to Norfolk. "Worsted" yarns/fabrics are distinct from woollens : the former is considered stronger, finer, smoother, and harder than the latter.
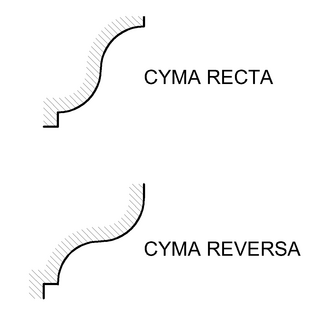
An ogee ( ) is the name given to objects, elements, and curves—often seen in architecture and building trades—that have been variously described as serpentine-, extended S-, or sigmoid-shaped. Ogees consist of a "double curve", the combination of two semicircular curves or arcs that, as a result of a point of inflection from concave to convex or vice versa, have ends of the overall curve that point in opposite directions.

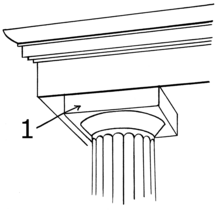
An entablature is the superstructure of moldings and bands which lies horizontally above columns, resting on their capitals. Entablatures are major elements of classical architecture, and are commonly divided into the architrave, the frieze, and the cornice. The Greek and Roman temples are believed to be based on wooden structures, the design transition from wooden to stone structures being called petrification.

Moulding, or molding, also coving, is a strip of material with various profiles used to cover transitions between surfaces or for decoration. It is traditionally made from solid milled wood or plaster, but may be of plastic or reformed wood. In classical architecture and sculpture, the moulding is often carved in marble or other stones. In historic architecture, and some expensive modern buildings, it may be formed in place with plaster.

An astragal is a moulding profile composed of a half-round surface surrounded by two flat planes (fillets). An astragal is sometimes referred to as a miniature torus. It can be an architectural element used at the top or base of a column, but is also employed as a framing device on furniture and woodwork.

A dentil is a small block used as a repeating ornament in the bedmould of a cornice. Dentils are found in ancient Greek and Roman architecture, and also in later styles such as Neoclassical, Federal, Georgian Revival, Greek Revival, Renaissance Revival, Second Empire, and Beaux-Arts architecture. Dentillation refers to use of a course of dentils.

A glazier is a tradesman responsible for cutting, installing, and removing glass. They also refer to blueprints to figure out the size, shape, and location of the glass in the building. They may have to consider the type and size of scaffolding they need to stand on to fit and install the glass. Glaziers may work with glass in various surfaces and settings, such as cutting and installing windows, doors, shower doors, skylights, storefronts, display cases, mirrors, facades, interior walls, ceilings, and tabletops.

Attic base is the term given in architecture to the base of Roman Ionic order columns, consisting of an upper and lower torus, separated by a scotia and fillets.

A baluster is an upright support, often a vertical moulded shaft, square, or lathe-turned form found in stairways, parapets, and other architectural features. In furniture construction it is known as a spindle. Common materials used in its construction are wood, stone, and less frequently metal and ceramic. A group of balusters supporting a handrail, coping, or ornamental detail are known as a balustrade.

The ovolo or echinus is a convex decorative molding profile used in architectural ornamentation. Its profile is a quarter to a half of a more or less flattened circle.
This page is a glossary of architecture.

A cavetto is a concave moulding with a regular curved profile that is part of a circle, widely used in architecture as well as furniture, picture frames, metalwork and other decorative arts. In describing vessels and similar shapes in pottery, metalwork and related fields, "cavetto" may be used of a variety of concave curves running round objects. The word comes from Italian, as a diminutive of cave, from the Latin for "hollow". A vernacular alternative is "cove", most often used where interior walls curve at the top to make a transition to the roof, or for "upside down" cavettos at the bases of elements.

Egg-and-dart, also known as egg-and-tongue, egg-and-anchor, or egg-and-star, is an ornamental device adorning the fundamental quarter-round, convex ovolo profile of moulding, consisting of alternating details on the face of the ovolo—typically an egg-shaped object alternating with a V-shaped element. The device is carved or otherwise fashioned into ovolos composed of wood, stone, plaster, or other materials.

The Lakshmi Narasimha temple was built in 1246 CE by Bommanna Dandanayaka, a commander in the Hoysala Empire during the rule of King Vira Someshwara. It is a good example of 13th-century Hoysala architecture. Located a short distance away in Nuggehalli, and built around the same time is the Sadashiva temple. The town was called Vijaya Somanathapura in ancient times and gained importance as an agrahara during the time of Bommanna Dandanayaka. Nuggehalli,, is a town in Hassan district of Karnataka, India. It is located on the Tiptur-Channarayapatna state highway and is about 50 km from Hassan city. It is well connected by road with Bangalore, the state capital.

The fireplace mantel or mantelpiece, also known as a chimneypiece, originated in medieval times as a hood that projected over a fire grate to catch the smoke. The term has evolved to include the decorative framework around the fireplace, and can include elaborate designs extending to the ceiling. Mantelpiece is now the general term for the jambs, mantel shelf, and external accessories of a fireplace. For many centuries, the chimneypiece was the most ornamental and most artistic feature of a room, but as fireplaces have become smaller, and modern methods of heating have been introduced, its artistic as well as its practical significance has lessened.

Geison is an architectural term of relevance particularly to ancient Greek and Roman buildings, as well as archaeological publications of the same. The geison is the part of the entablature that projects outward from the top of the frieze in the Doric order and from the top of the frieze course of the Ionic and Corinthian orders; it forms the outer edge of the roof on the sides of a structure with a sloped roof. The upper edge of the exterior often had a drip edge formed as a hawksbeak molding to shed water; there were also typically elaborate moldings or other decorative elements, sometimes painted. Above the geison ran the sima. The underside of the geison may be referred to as a soffit. The form of a geison is often used as one element of the argument for the chronology of its building.

A tympanum is the semi-circular or triangular decorative wall surface over an entrance, door or window, which is bounded by a lintel and an arch. It often contains pedimental sculpture or other imagery or ornaments. Many architectural styles include this element.

Fluting in architecture consists of shallow grooves running along a surface.

Millwork is historically any wood mill produced decorative materials used in building construction. Stock profiled and patterned millwork building components fabricated by milling at a planing mill can usually be installed with minimal alteration. Today, millwork may encompass items that are made using alternatives to wood, including synthetics, plastics, and wood-adhesive composites.