
A circular saw or a buzz saw, is a power-saw using a toothed or abrasive disc or blade to cut different materials using a rotary motion spinning around an arbor. A hole saw and ring saw also use a rotary motion but are different from a circular saw. Circular saws may also be loosely used for the blade itself. Circular saws were invented in the late 18th century and were in common use in sawmills in the United States by the middle of the 19th century.

A chisel is a wedged hand tool with a characteristically shaped cutting edge on the end of its blade, for carving or cutting a hard material. The tool can be used by hand, struck with a mallet, or applied with mechanical power. The handle and blade of some types of chisel are made of metal or wood with a sharp edge in it.
A saw is a tool consisting of a tough blade, wire, or chain with a hard toothed edge used to cut through material. Various terms are used to describe toothed and abrasive saws.

Wood carving is a form of woodworking by means of a cutting tool (knife) in one hand or a chisel by two hands or with one hand on a chisel and one hand on a mallet, resulting in a wooden figure or figurine, or in the sculptural ornamentation of a wooden object. The phrase may also refer to the finished product, from individual sculptures to hand-worked mouldings composing part of a tracery.

A table saw is a woodworking tool, consisting of a circular saw blade, mounted on an arbor, that is driven by an electric motor. The drive mechanism is mounted below a table that provides support for the material, usually wood, being cut, with the blade protruding up through the table into the material.

In woodworking, a rip-cut is a type of cut that severs or divides a piece of wood parallel to the grain. The other typical type of cut is a cross-cut, a cut perpendicular to the grain. Unlike cross-cutting, which shears the wood fibers, a rip saw works more like a series of chisels, lifting off small splinters of wood. The nature of the wood grain requires the shape of the saw teeth to be different, thus the need for both rip saws and crosscut saws; however, some circular saw blades are combination blades and can make both types of cuts. A rip cut is the fundamental type of cut made at a sawmill.

A hand plane is a tool for shaping wood using muscle power to force the cutting blade over the wood surface. Some rotary power planers are motorized power tools used for the same types of larger tasks, but are unsuitable for fine-scale planing, where a miniature hand plane is used.

The Japanese saw or nokogiri (鋸) is a type of saw used in woodworking and Japanese carpentry that cuts on the pull stroke, unlike most European saws that cut on the push stroke. Japanese saws are the best known pull saws, but they are also used in China, Iran, Iraq, Korea, Nepal, and Turkey. Among European saws, both coping saws for woodworking and jeweler's saws for metal working also cut on the pull stroke like Japanese saws. Cutting on the pull stroke is claimed to cut more efficiently and leave a narrower cut width. On the other hand, a pull stroke does not easily permit putting one's body weight behind a stroke. This can be readily solved by using a vice or clamping. Another disadvantage, due to the arrangement and form of the teeth, is that Japanese saws do not work as well on hardwoods as European saws do. Japanese saws were originally intended for comparatively soft woods like cypress and pine whereas European saws were intended for hard woods like oak and maple.

A radial arm saw is a cutting machine consisting of a circular saw mounted on a sliding horizontal arm. Invented by Raymond DeWalt in 1922, the radial arm saw was the primary tool used for cutting long pieces of stock to length until the introduction of the power miter saw in the 1970s.

A sickle, bagging hook, reaping-hook or grasshook is a single-handed agricultural tool designed with variously curved blades and typically used for harvesting or reaping grain crops, or cutting succulent forage chiefly for feeding livestock. Falx was a synonym, but was later used to mean any of a number of tools that had a curved blade that was sharp on the inside edge.

A bandsaw is a power saw with a long, sharp blade consisting of a continuous band of toothed metal stretched between two or more wheels to cut material. They are used principally in woodworking, metalworking, and lumbering, but may cut a variety of materials. Advantages include uniform cutting action as a result of an evenly distributed tooth load, and the ability to cut irregular or curved shapes like a jigsaw. The minimum radius of a curve is determined by the width of the band and its kerf. Most bandsaws have two wheels rotating in the same plane, one of which is powered, although some may have three or four to distribute the load. The blade itself can come in a variety of sizes and tooth pitches, which enables the machine to be highly versatile and able to cut a wide variety of materials including wood, metal and plastic. Band saw is recommended for use in cutting metal as it produces much less toxic fumes and particulates when compared with angle grinder and reciprocating saw.

A crosscut saw is any saw designed for cutting wood perpendicular to (across) the wood grain. Crosscut saws may be small or large, with small teeth close together for fine work like woodworking or large for coarse work like log bucking, and can be a hand tool or power tool.
A ripsaw is a wood saw that is specially designed for making a rip cut, a cut made parallel to the direction of the wood grain.

A miter saw or mitre saw is a saw used to make accurate crosscuts and miters in a workpiece by positioning a mounted blade onto a board. A miter saw in its earliest form was composed of a back saw in a miter box, but in modern implementation consists of a powered circular saw that can be positioned at a variety of angles and lowered onto a board positioned against a backstop called the fence.

A backsaw is any hand saw which has a stiffening rib on the edge opposite the cutting edge, enabling better control and more precise cutting than with other types of saws. Backsaws are normally used in woodworking for precise work, such as cutting dovetails, mitres, or tenons in cabinetry and joinery. Because of the stiffening rib, backsaws are limited in the depth to which they can cut. Backsaws usually have relatively closely spaced teeth, often with little or no set.

A bucksaw is a hand-powered frame saw similar to bow saw and generally used with a sawbuck to cut logs or firewood to length (bucking). Modern bucksaws usually have a metal frame and a removable blade with coarse teeth held in tension by the frame. Lightweight portable or foldable models used for camping or back-packing are also available. It is often referred to as a bow saw in the North American hardware market, but that term traditionally refers to a different type of saw with a wooden frame.

Japanese carpentry was developed more than a millennium ago that is known for its ability to create everything from temples to houses to tea houses to furniture by wood with the use of few nails.
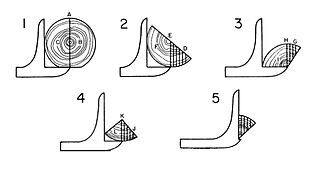
Quarter sawing or quartersawing is a woodworking process that produces quarter-sawn or quarter-cut boards in the rip cutting of logs into lumber. The resulting lumber can also be called radially-sawn or simply quartered. There is widespread confusion between the terms rift sawn and quarter sawn with the terms defined both with opposite meanings and as synonyms.
This glossary of woodworking lists a number of specialized terms and concepts used in woodworking, carpentry, and related disciplines.

A riving knife is a safety device installed on a table saw, circular saw, or radial arm saw used for woodworking. Attached to the saw's arbor, it is fixed relative to the blade and moves with it as blade depth is adjusted.




















