This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

Brodmann area 23 (BA23) is a region in the brain corresponding to some portion of the posterior cingulate cortex. It lies between Brodmann area 30 and Brodmann area 31 and is located on the medial wall of the cingulate gyrus between the callosal sulcus and the cingulate sulcus.
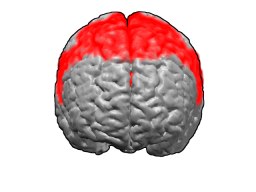
Brodmann area 6 (BA6) part of the frontal cortex in the human brain. Situated just anterior to the primary motor cortex (BA4), it is composed of the premotor cortex and, medially, the supplementary motor area, or SMA. This large area of the frontal cortex is believed to play a role in the planning of complex, coordinated movements.

Brodmann area 5 is one of Brodmann's cytoarchitectural defined regions of the brain. It is involved in somatosensory processing and association.

Brodmann area 20, or BA20, is part of the temporal cortex in the human brain. The region encompasses most of the ventral temporal cortex, a region believed to play a part in high-level visual processing and recognition memory.

Brodmann area 37, or BA37, is part of the temporal cortex in the human brain.

Brodmann area 38, also BA38 or temporopolar area 38 (H), is part of the temporal cortex in the human brain. BA 38 is at the anterior end of the temporal lobe, known as the temporal pole.

Brodmann area 4 refers to the primary motor cortex of the human brain. It is located in the posterior portion of the frontal lobe.

Brodmann area 24 is part of the anterior cingulate in the human brain.

The Brodmann area 32, also known in the human brain as the dorsal anterior cingulate area 32, refers to a subdivision of the cytoarchitecturally defined cingulate cortex. In the human it forms an outer arc around the anterior cingulate gyrus. The cingulate sulcus defines approximately its inner boundary and the superior rostral sulcus (H) its ventral boundary; rostrally it extends almost to the margin of the frontal lobe. Cytoarchitecturally it is bounded internally by the ventral anterior cingulate area 24, externally by medial margins of the agranular frontal area 6, intermediate frontal area 8, granular frontal area 9, frontopolar area 10, and prefrontal area 11-1909. (Brodmann19-09).

Brodmann area 26 is the name for a small part of the brain.

Brodmann area 31, also known as dorsal posterior cingulate area 31, is a subdivision of the cytoarchitecturally defined cingulate region of the cerebral cortex. In the human it occupies portions of the posterior cingulate gyrus and medial aspect of the parietal lobe. Approximate boundaries are the cingulate sulcus dorsally and the parieto-occipital sulcus caudally. It partially surrounds the subparietal sulcus, the ventral continuation of the cingulate sulcus in the parietal lobe. Cytoarchitecturally it is bounded rostrally by the ventral anterior cingulate area 24, ventrally by the ventral posterior cingulate area 23, dorsally by the gigantopyramidal area 4 and preparietal area 5 and caudally by the superior parietal area 7 (H) (Brodmann-1909).
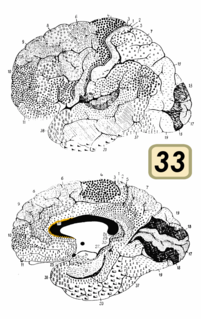
Brodmann area 33, also known as pregenual area 33, is a subdivision of the cytoarchitecturally defined cingulate region of cerebral cortex. It is a narrow band located in the anterior cingulate gyrus adjacent to the supracallosal gyrus in the depth of the callosal sulcus, near the genu of the corpus callosum. Cytoarchitecturally it is bounded by the ventral anterior cingulate area 24 and the supracallosal gyrus (Brodmann-1909).

Brodmann area 29, also known as granular retrolimbic area 29 or granular retrosplenial cortex, is a cytoarchitecturally defined portion of the retrosplenial region of the cerebral cortex. In the human it is a narrow band located in the isthmus of cingulate gyrus. Cytoarchitecturally it is bounded internally by the ectosplenial area 26 and externally by the agranular retrolimbic area 30 (Brodmann-1909).

Brodmann area 30, also known as agranular retrolimbic area 30, is a subdivision of the cytoarchitecturally defined retrosplenial region of the cerebral cortex. In the human it is located in the isthmus of cingulate gyrus. Cytoarchitecturally it is bounded internally by the granular retrolimbic area 29, dorsally by the ventral posterior cingulate area 23 and ventrolaterally by the ectorhinal area 36 (Brodmann-1909).
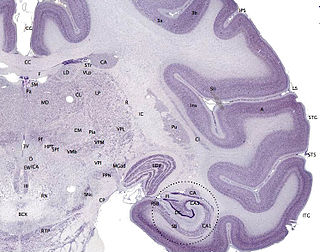
Retrosubicular area 48 is a subdivision of the cytoarchitecturally defined hippocampal region of the cerebral cortex.

Brodmann area 52 (H) or parainsular area, is a subdivision of the cytoarchitecturally defined temporal region of the cerebral cortex in the brain.