
Haryana is an Indian state located in the northern part of the country. It was carved out after the linguistic reorganisation of Punjab on 1 November 1966. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with less than 1.4% of India's land area. The state capital is Chandigarh, which it shares with the neighbouring state of Punjab; the most populous city is Faridabad, a part of the National Capital Region. The city of Gurgaon is among India's largest financial and technology hubs. Haryana has 6 administrative divisions, 22 districts, 72 sub-divisions, 93 revenue tehsils, 50 sub-tehsils, 140 community development blocks, 154 cities and towns, 7,356 villages, and 6,222 villages panchayats.
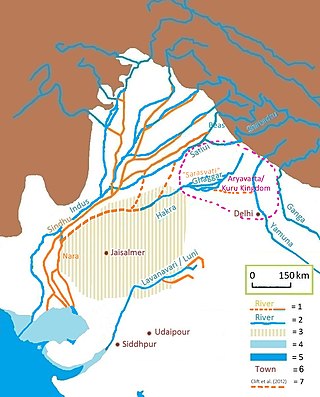
The Sarasvati River is a mythologized and deified ancient river first mentioned in the Rigveda and later in Vedic and post-Vedic texts. It played an important role in the Vedic religion, appearing in all but the fourth book of the Rigveda.

The Chautang is a seasonal river, originating in the Sivalik Hills, in the Indian state of Haryana. The Chautang River is a tributary of the Sarsuti river which in turn is a tributary of the Ghaggar river.

The Ghaggar-Hakra River is an intermittent river in India and Pakistan that flows only during the monsoon season. The river is known as Ghaggar before the Ottu barrage at 29.4875°N 74.8925°E, and as Hakra downstream of the barrage in the Thar Desert. In pre-Harappan times the Ghaggar was a tributary of the Sutlej. It is still connected to this paleochannel of the Sutlej, and possibly the Yamuna, which ended in the Nara River, presently a delta channel of the Indus River joining the sea via Sir Creek.

The Tons is the largest tributary of the Yamuna. It flows through Garhwal region in Uttarakhand, touching Himachal Pradesh. The Tons thrust is named after this river.

Puadh is a historic region in north India that comprises parts of present-day Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh and the U.T. of Chandigarh, India. It has the Sutlej river in its north and covers the regions immediately south of the Ghaggar river. The people of the area are known as Puadhi and speak the Puadhi dialect of Punjabi. The capital cities of Puadh region are Rupnagar, Fatehgarh Sahib, Mohali, Patiala, Sangrur, Mansa Chandigarh, Nalagarh, Panchkula, Baddi, Ambala, Yamunanagar.

Haryana, formed on 1 November 1966, is a state in North India. For the administrative purpose, Haryana is divided into 6 revenue divisions which are further divided into 22 districts. For Law and Order maintenance, it is divided into 5 Police Ranges and 4 Police Commissionerates.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Haryana.

The Sahibi river, also called the Sabi River, is an ephemeral, rain-fed river flowing through Rajasthan, Haryana and Delhi states in India. It originates in the eastern slopes of the Saiwar Protected Forest (PF) hills in Sikar District, enters Jaipur district near the foot of these hills, and after initially flowing southeast and east turns northeastwards near Shahpura and continues further till it exits Rajasthan to enter Haryana and further drains into Yamuna in Delhi, where its channeled course is also called the Najafgarh drain, which also serves as Najafgarh drain bird sanctuary. It flows for 300 km of which 157 km is in Rajasthan 100 km is in Haryana and 40 km in Delhi.

The Kaushalya Dam is an earth-fill embankment dam on the Kaushalya river, which is a tributary of Ghaggar-Hakra River, in Pinjore of Haryana state, India. It was constructed between 2008 and 2012 with the primary purpose of water supply.

The Sarsuti river, originating in Sivalik Hills and flowing through the palaeochannel of Yamuna, is a tributary of Ghaggar river in of Haryana state of India. Its course is dotted with archaeological and religious sites dating back to post-Harrapan Mahabharata sites from Vedic period, such as Kapal Mochan, Kurukshetra, Thanesar, Brahma Sarovar, Jyotisar, Bhor Saidan and Pehowa.
Adi Badri, also Sri Sarasvati Udgam Tirath, is a tourist site of archaeological, religious and ecological significance in a forest area in the foothills of the Sivalik Hills in Bhabar area, situated in northern part of Yamunanagar district, of the north Indian state of Haryana. There are remains of many Buddhist stupas and monasteries, which are about 1500–2000 years old, and there is also a group of Hindu temples from the 9th century. Based on the multiple archaeological excavations undertaken here, archaeologists have sent the proposal to Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) to include this site in the list of protected heritage site. Several popular annual festivals are held here, including the five day long National Saraswati Festival in January, Adi Badri Akha Teej Mela in Vaisakh around April–May, week-long Adi Badri-Kapal Mochan Kartik Purnima religious mela around November.
Tourism in Haryana relates to tourism in the state of Haryana, India. There are 22 tourism hubs created by Haryana Tourism Corporation (HTC), which are located in Ambala, Bhiwani, Faridabad, Fatehabad, Gurgaon, Hisar, Jhajjar, Jind, Kaithal, Karnal, Kaimla, Kurukshetra, Panchkula, Sirsa, Sonipat, Panipat, Rewari, Rohtak, Yamunanagar, Palwal and Mahendergarh.
Western Yamuna Canal is canal in river Yamuna that was dug out and renovated in 1335 CE by Firoz Shah Tughlaq. In 1750 CE, excessive silting caused it to stop flowing. The British raj undertook a three-year renovation in 1817 by Captain GR Blane of the Bengal Engineer Group. In 1832-33 Tajewala Barrage dam at Yamunanagar was also built to regulate the flow of water, and later Pathrala barrage at Dadupur,Yamuna Nagar and Somb river dam downstream of canal were constructed in 1875-76. In 1889-95 the largest branch of the canal Sirsa branch was constructed. The modern Hathni Kund Barrage was built in 1999 to handle the problem of silting to replace the older Tajewala Barrage.

The Kaushalya river, a tributary of Ghaggar river, is a river in Panchkula district of Haryana state of India.

The Markanda is a river in the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh and Haryana. It is a tributary of the Ghaggar river, flowing through Sirmaur District, Ambala district and Shahabad Markanda, a town in Kurukshetra district. The Markanda river's ancient name was Aruna.
The Somb river, also spelled Som river is a tributary of Yamuna in Haryana state of India.
The Indori river, is a rain-fed river originates from Aravalli Range from Sikar district and flows through Alwar district of Rajasthan to Rewari district of Haryana and it is the longest tributary of Sahibi River which stretches to 50 km. In Delhi, it is called the Najafgarh drain or Najafgarh Nallah.
The Krishnavati river, also called Kasaunti, is a rain-fed river originates from Aravalli Range near Dariba copper mines in Rajsamand district of Rajasthan, and flows through Patan in Dausa district and Mothooka in Alwar district and then disappears in Mahendragarh district in Haryana where it used to be a tributary of Sahibi River, which in turn still is a tributary of Yamuna. Several Ochre Coloured Pottery culture sites have been found along the banks of Krishnavati, Sahibi river, Dohan river and Sota River. The drainage pattern for all these rivers is dendritic.
The Dohan river, is a rain-fed river that originates at Mandholi village near Neem Ka Thana in Sikar district of Rajasthan and then disappears in Mahendragarh district in Haryana where it used to be a tributary of Sahibi River, which in turn is a still flowing tributary of Yamuna. Its canalised portion in one of its paleochannel in Haryana is called the "Outfall Drain No 8".















