
The N-methyl-D-aspartatereceptor (also known as the NMDA receptor or NMDAR), is a glutamate receptor and ion channel found in neurons. The NMDA receptor is one of three types of ionotropic glutamate receptors, the other two being AMPA and kainate receptors. Depending on its subunit composition, its ligands are glutamate and glycine (or D-serine). However, the binding of the ligands is typically not sufficient to open the channel as it may be blocked by Mg2+ ions which are only removed when the neuron is sufficiently depolarized. Thus, the channel acts as a “coincidence detector” and only once both of these conditions are met, the channel opens and it allows positively charged ions (cations) to flow through the cell membrane. The NMDA receptor is thought to be very important for controlling synaptic plasticity and mediating learning and memory functions.

Memantine is a medication used to slow the progression of moderate-to-severe Alzheimer's disease. It is taken by mouth.

Dextromethorphan (DXM) is a cough suppressant in over-the-counter cold and cough medicines. It affects NMDA, and sigma-1 receptors in the brain, all of which have been implicated in the pathophysiology of depression. In 2022, the FDA approved a formulation of it combined with bupropion named Auvelity to serve as a rapid acting antidepressant in patients with major depressive disorder.

Acamprosate, sold under the brand name Campral, is a medication used along with counseling to treat alcohol use disorder.
Gepirone, sold under the brand name Exxua, is a medication used for the treatment of major depressive disorder. It is taken orally.

Glutamate [NMDA] receptor subunit epsilon-2, also known as N-methyl D-aspartate receptor subtype 2B, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GRIN2B gene.
Levomilnacipran is an antidepressant which was approved in the United States in 2013 for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD) in adults. It is the levorotatory enantiomer of milnacipran, and has similar effects and pharmacology, acting as a serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI).

Traxoprodil is a drug developed by Pfizer which acts as an NMDA antagonist, selective for the NR2B subunit. It has neuroprotective, analgesic, and anti-Parkinsonian effects in animal studies. Traxoprodil has been researched in humans as a potential treatment to lessen the damage to the brain after stroke, but results from clinical trials showed only modest benefit. The drug was found to cause EKG abnormalities and its clinical development was stopped. More recent animal studies have suggested traxoprodil may exhibit rapid-acting antidepressant effects similar to those of ketamine, although there is some evidence for similar psychoactive side effects and abuse potential at higher doses, which might limit clinical acceptance of traxoprodil for this application.

Brexpiprazole, sold under the brand name Rexulti among others, is a medication used for the treatment of major depressive disorder, schizophrenia, and agitation associated with dementia due to Alzheimer's disease. It is an atypical antipsychotic.

Rapastinel is a novel antidepressant that was under development by Allergan as an adjunctive therapy for the treatment of treatment-resistant depression. It is a centrally active, intravenously administered amidated tetrapeptide that acts as a novel and selective modulator of the NMDA receptor. The drug is a rapid-acting and long-lasting antidepressant as well as robust cognitive enhancer by virtue of its ability to enhance NMDA receptor-mediated signal transduction and synaptic plasticity.

7-Chlorokynurenic acid (7-CKA) is a tool compound that acts as a potent and selective competitive antagonist of the glycine site of the NMDA receptor. It produces ketamine-like rapid antidepressant effects in animal models of depression. However, 7-CKA is unable to cross the blood-brain-barrier, and for this reason, is unsuitable for clinical use. As a result, a centrally-penetrant prodrug of 7-CKA, 4-chlorokynurenine (AV-101), has been developed for use in humans, and is being studied in clinical trials as a potential treatment for major depressive disorder, and anti-nociception. In addition to antagonizing the NMDA receptor, 7-CKA also acts as a potent inhibitor of the reuptake of glutamate into synaptic vesicles, an action that it mediates via competitive blockade of vesicular glutamate transporters.

Esmethadone (INNTooltip International Nonproprietary Name; developmental code name REL-1017), also known as dextromethadone, is the (S)-enantiomer of methadone. It acts as an N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) antagonist, among other actions. Unlike levomethadone, it has low affinity for opioid receptors and lacks significant respiratory depressant action and abuse liability. Esmethadone is under development for the treatment of major depressive disorder. As of August 2022, it is in phase 3 clinical trials for this indication.

Aticaprant, also known by its developmental codes JNJ-67953964, CERC-501, and LY-2456302, is a κ-opioid receptor (KOR) antagonist which is under development for the treatment of major depressive disorder. A regulatory application for approval of the medication is expected to be submitted by 2025. Aticaprant is taken by mouth.

Apimostinel is an investigational antidepressant, acting as a novel and selective modulator of the NMDA receptor. It is currently under development for the acute treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD) by Gate Neurosciences, and previously by Naurex and Allergan. As of February 2015, an intravenous formulation of apimostinel has completed a phase IIa clinical trial for MDD.
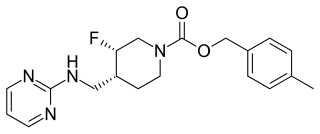
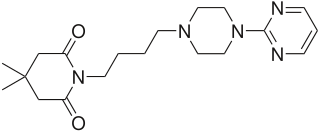
Rislenemdaz is an orally active, selective NMDA receptor subunit 2B (NR2B) antagonist which is under development by Cerecor in the United States as an adjunctive therapy for treatment-resistant depression (TRD). In November 2013, phase II clinical trials were initiated, and in the same month, rislenemdaz received Fast Track Designation from the Food and Drug Administration for TRD.

Basimglurant (INN) is a negative allosteric modulator of the mGlu5 receptor which is under development by Roche and Chugai Pharmaceutical for the treatment of treatment-resistant depression and fragile X syndrome. As of November 2016, it has undergone phase II clinical trials for both of these indications.

Dextromethorphan/bupropion (DXM/BUP), sold under the brand name Auvelity, is a combination medication for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD). Its active components are dextromethorphan (DXM) and bupropion. Patients who stayed on the medication had an average of 11% greater reduction in depressive symptoms than placebo in an FDA approval trial. It is taken as a tablet by mouth.
EVT-103, also known as ENS-103, is an experimental medication which originated from Roche and is under development by Evotec AG for the treatment of major depressive disorder. It acts as an NMDA receptor subunit 2B (NR2B) antagonist. As of November 2017, no recent reports of development for major depressive disorder have been identified. The drug was developed as a follow-up compound to EVT-101. The chemical structure of EVT-103 has not been released.

Zelquistinel is an orally active small-molecule NMDA receptor modulator which is under development for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD) by Gate Neurosciences, and previously by Allergan.

















