A restriction enzyme, restriction endonuclease, or restrictase is an enzyme that cleaves DNA into fragments at or near specific recognition sites within molecules known as restriction sites. Restriction enzymes are one class of the broader endonuclease group of enzymes. Restriction enzymes are commonly classified into five types, which differ in their structure and whether they cut their DNA substrate at their recognition site, or if the recognition and cleavage sites are separate from one another. To cut DNA, all restriction enzymes make two incisions, once through each sugar-phosphate backbone of the DNA double helix.

A nuclease is an enzyme capable of cleaving the phosphodiester bonds between nucleotides of nucleic acids. Nucleases variously effect single and double stranded breaks in their target molecules. In living organisms, they are essential machinery for many aspects of DNA repair. Defects in certain nucleases can cause genetic instability or immunodeficiency. Nucleases are also extensively used in molecular cloning.
dnaQ is the gene encoding the ε subunit of DNA polymerase III in Escherichia coli. The ε subunit is one of three core proteins in the DNA polymerase complex. It functions as a 3’→5’ DNA directed proofreading exonuclease that removes incorrectly incorporated bases during replication. dnaQ may also be referred to as mutD.

RecBCD is an enzyme of the E. coli bacterium that initiates recombinational repair from potentially lethal double strand breaks in DNA which may result from ionizing radiation, replication errors, endonucleases, oxidative damage, and a host of other factors. The RecBCD enzyme is both a helicase that unwinds, or separates the strands of DNA, and a nuclease that makes single-stranded nicks in DNA.

The Klenow fragment is a large protein fragment produced when DNA polymerase I from E. coli is enzymatically cleaved by the protease subtilisin. First reported in 1970, it retains the 5' → 3' polymerase activity and the 3’ → 5’ exonuclease activity for removal of precoding nucleotides and proofreading, but loses its 5' → 3' exonuclease activity.
Endonucleases are enzymes that cleave the phosphodiester bond within a polynucleotide chain. Some, such as deoxyribonuclease I, cut DNA relatively nonspecifically, while many, typically called restriction endonucleases or restriction enzymes, cleave only at very specific nucleotide sequences. Endonucleases differ from exonucleases, which cleave the ends of recognition sequences instead of the middle (endo) portion. Some enzymes known as "exo-endonucleases", however, are not limited to either nuclease function, displaying qualities that are both endo- and exo-like. Evidence suggests that endonuclease activity experiences a lag compared to exonuclease activity.

Exonucleases are enzymes that work by cleaving nucleotides one at a time from the end (exo) of a polynucleotide chain. A hydrolyzing reaction that breaks phosphodiester bonds at either the 3′ or the 5′ end occurs. Its close relative is the endonuclease, which cleaves phosphodiester bonds in the middle (endo) of a polynucleotide chain. Eukaryotes and prokaryotes have three types of exonucleases involved in the normal turnover of mRNA: 5′ to 3′ exonuclease (Xrn1), which is a dependent decapping protein; 3′ to 5′ exonuclease, an independent protein; and poly(A)-specific 3′ to 5′ exonuclease.
Mung bean nuclease is a nuclease derived from sprouts of the mung bean that removes nucleotides in a step-wise manner from single-stranded DNA molecules (ssDNA) and is used in biotechnological applications to remove such ssDNA from a mixture also containing double-stranded DNA (dsDNA). This enzyme is useful for transcript mapping, removal of single-stranded regions in DNA hybrids or single-stranded overhangs produced by restriction enzymes, etc. It has an activity similar to Nuclease S1, but it has higher specificity for single-stranded molecules.
Exodeoxyribonuclease I is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction:

HaeIII is one of many restriction enzymes (endonucleases) a type of prokaryotic DNA that protects organisms from unknown, foreign DNA. It is a restriction enzyme used in molecular biology laboratories. It was the third endonuclease to be isolated from the Haemophilus aegyptius bacteria. The enzyme's recognition site—the place where it cuts DNA molecules—is the GGCC nucleotide sequence which means it cleaves DNA at the site 5′-GG/CC-3. The recognition site is usually around 4-8 bps.This enzyme's gene has been sequenced and cloned. This is done to make DNA fragments in blunt ends. HaeIII is not effective for single stranded DNA cleavage.

EcoRV is a type II restriction endonuclease isolated from certain strains of Escherichia coli. It has the alternative name Eco32I.
Flap endonucleases are a class of nucleolytic enzymes that act as both 5'-3' exonucleases and structure-specific endonucleases on specialised DNA structures that occur during the biological processes of DNA replication, DNA repair, and DNA recombination. Flap endonucleases have been identified in eukaryotes, prokaryotes, archaea, and some viruses. Organisms can have more than one FEN homologue; this redundancy may give an indication of the importance of these enzymes. In prokaryotes, the FEN enzyme is found as an N-terminal domain of DNA polymerase I, but some prokaryotes appear to encode a second homologue.
Deoxyribonuclease IV (phage-T4-induced) is a kind of Endonuclease that catalyzes the degradation nucleotides in DsDNA by attacking the 5'-terminal end.

Endonuclease/Exonuclease/phosphatase family is a structural domain found in the large family of proteins including magnesium dependent endonucleases and many phosphatases involved in intracellular signaling.
Exodeoxyribonuclease III is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Ribonuclease E is a bacterial ribonuclease that participates in the processing of ribosomal RNA and the chemical degradation of bulk cellular RNA.

In molecular biology, ligation is the joining of two nucleic acid fragments through the action of an enzyme. It is an essential laboratory procedure in the molecular cloning of DNA, whereby DNA fragments are joined together to create recombinant DNA molecules (such as when a foreign DNA fragment is inserted into a plasmid). The ends of DNA fragments are joined together by the formation of phosphodiester bonds between the 3'-hydroxyl of one DNA terminus with the 5'-phosphoryl of another. RNA may also be ligated similarly. A co-factor is generally involved in the reaction, and this is usually ATP or NAD+.

Ribonuclease T is a ribonuclease enzyme involved in the maturation of transfer RNA and ribosomal RNA in bacteria, as well as in DNA repair pathways. It is a member of the DnaQ family of exonucleases and non-processively acts on the 3' end of single-stranded nucleic acids. RNase T is capable of cleaving both DNA and RNA, with extreme sequence specificity discriminating against cytosine at the 3' end of the substrate.
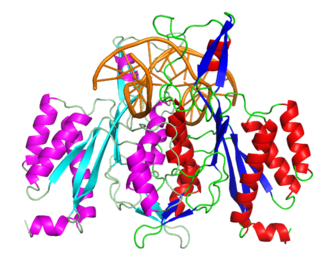
EcoRI is a restriction endonuclease enzyme isolated from species E. coli. It is a restriction enzyme that cleaves DNA double helices into fragments at specific sites, and is also a part of the restriction modification system. The Eco part of the enzyme's name originates from the species from which it was isolated - "E" denotes generic name which is "Escherichia" and "co" denotes species name, "coli" - while the R represents the particular strain, in this case RY13, and the I denotes that it was the first enzyme isolated from this strain.
SCAR-less genome editing Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering (no-SCAR) is an editing method that is able to manipulate the Escherichia coli genome. The system relies on recombineering whereby DNA sequences are combined and manipulated through homologous recombination. No-SCAR is able to manipulate the E. coli genome without the use of the chromosomal markers detailed in previous recombineering methods. Instead, in this method, the λ-Red recombination system facilitates donor DNA integration while Cas9 cleaves double-stranded DNA to counter-select against wild-type cells. Although λ-Red and Cas9 genome editing are widely used technologies, the no-SCAR method is novel in combining the two functions; this technique is able to establish point mutations, gene deletions, and short sequence insertions in several genomic loci with increased efficiency and time sensitivity.










