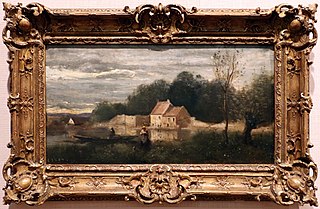In telecommunications, a scrambler is a device that transposes or inverts signals or otherwise encodes a message at the sender's side to make the message unintelligible at a receiver not equipped with an appropriately set descrambling device. Whereas encryption usually refers to operations carried out in the digital domain, scrambling usually refers to operations carried out in the analog domain. Scrambling is accomplished by the addition of components to the original signal or the changing of some important component of the original signal in order to make extraction of the original signal difficult. Examples of the latter might include removing or changing vertical or horizontal sync pulses in television signals; televisions will not be able to display a picture from such a signal. Some modern scramblers are actually encryption devices, the name remaining due to the similarities in use, as opposed to internal operation.

Interlaced video is a technique for doubling the perceived frame rate of a video display without consuming extra bandwidth. The interlaced signal contains two fields of a video frame captured consecutively. This enhances motion perception to the viewer, and reduces flicker by taking advantage of the phi phenomenon.

Telecine is the process of transferring film into video and is performed in a color suite. The term is also used to refer to the equipment used in this post-production process.

A bicycle frame is the main component of a bicycle, onto which wheels and other components are fitted. The modern and most common frame design for an upright bicycle is based on the safety bicycle, and consists of two triangles: a main triangle and a paired rear triangle. This is known as the diamond frame. Frames are required to be strong, stiff and light, which they do by combining different materials and shapes.

Tongue and groove is a method of fitting similar objects together, edge to edge, used mainly with wood, in flooring, parquetry, panelling, and similar constructions. Tongue and groove joints allow two flat pieces to be joined strongly together to make a single flat surface. Before plywood became common, tongue and groove boards were also used for sheathing buildings and to construct concrete formwork.

A tank locomotive or tank engine is a steam locomotive that carries its water in one or more on-board water tanks, instead of a more traditional tender. Most tank engines also have bunkers to hold fuel; in a tender-tank locomotive a tender holds some or all of the fuel, and may hold some water also.

The display resolution or display modes of a digital television, computer monitor or display device is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resolution is controlled by different factors in cathode ray tube (CRT) displays, flat-panel displays and projection displays using fixed picture-element (pixel) arrays.
In the field of video compression a video frame is compressed using different algorithms with different advantages and disadvantages, centered mainly around amount of data compression. These different algorithms for video frames are called picture types or frame types. The three major picture types used in the different video algorithms are I, P and B. They are different in the following characteristics:

Moulding, or molding, also coving, is a strip of material with various profiles used to cover transitions between surfaces or for decoration. It is traditionally made from solid milled wood or plaster, but may be of plastic or reformed wood. In classical architecture and sculpture, the moulding is often carved in marble or other stones. In historic architecture, and some expensive modern buildings, it may be formed in place with plaster.

A chamfer or is a transitional edge between two faces of an object. Sometimes defined as a form of bevel, it is often created at a 45° angle between two adjoining right-angled faces.
In computer science, a call stack is a stack data structure that stores information about the active subroutines of a computer program. This kind of stack is also known as an execution stack, program stack, control stack, run-time stack, or machine stack, and is often shortened to just "the stack". Although maintenance of the call stack is important for the proper functioning of most software, the details are normally hidden and automatic in high-level programming languages. Many computer instruction sets provide special instructions for manipulating stacks.
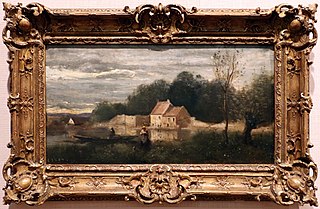
A picture frame is a protective and decorative edging for a picture, such as a painting or photograph. It makes displaying the work safer and easier and both sets the picture apart from its surroundings and aesthetically integrates it with them.

In mechanical engineering, a fillet is a rounding of an interior or exterior corner of a part designed in CAD. An interior or exterior corner, with an angle or type of bevel, is called a "chamfer". Fillet geometry, when on an interior corner is a line of concave function, whereas a fillet on an exterior corner is a line of convex function. Fillets commonly appear on welded, soldered, or brazed joints.
This article discusses moving image capture, transmission and presentation from today's technical and creative points of view; concentrating on aspects of frame rates.

High-speed photography is the science of taking pictures of very fast phenomena. In 1948, the Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE) defined high-speed photography as any set of photographs captured by a camera capable of 69 frames per second or greater, and of at least three consecutive frames. High-speed photography can be considered to be the opposite of time-lapse photography.

3D rendering is the 3D computer graphics process of converting 3D models into 2D images on a computer. 3D renders may include photorealistic effects or non-photorealistic styles.

A skeleton clock is any clock or wristwatch, though typically mechanical in nature, in which the parts that usually conceal the inner workings of the mechanism have been removed or significantly modified so as to display these inner parts.

In the picture framing industry, a mat is a thin, flat piece of paper-based material included within a picture frame, which serves as additional decoration and to perform several other, more practical functions, such as separating the art from the glass. Putting mats in a frame is called matting, a term which can also usually be used interchangeably with mat. The French term, occasionally used in English, is passe-partout. A picture is placed beneath it, with the cutout framing it. The passe-partout serves two purposes: first, to prevent the image from touching the glass, and second, to frame the image and enhance its visual appeal. The cutout in the passe-partout is usually beveled to avoid casting shadows on the picture. The French word may also be used for the tape used to stick the back of the picture to its frame.

The Tejo Power Station is a former coal-fired power station in the Belém district of Lisbon, Portugal that operated from 1908 to 1975.

A lead frame is a metal structure inside a chip package that carries signals from the die to the outside, used in DIP, QFP and other packages where connections to the chip are made on its edges.