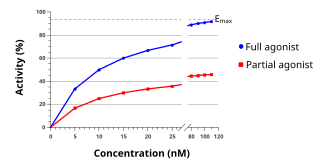
An agonist is a chemical that binds to a receptor and activates the receptor to produce a biological response. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the agonist, while an inverse agonist causes an action opposite to that of the agonist.

The dopamine receptor D4 is a dopamine D2-like G protein-coupled receptor encoded by the DRD4 gene on chromosome 11 at 11p15.5.

Rotigotine, sold under the brand name Neupro among others, is a dopamine agonist of the non-ergoline class of medications indicated for the treatment of Parkinson's disease (PD) and restless legs syndrome (RLS). It is formulated as a once-daily transdermal patch which provides a slow and constant supply of the drug over the course of 24 hours.
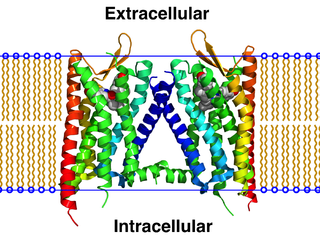
The κ-opioid receptor or kappa opioid receptor, abbreviated KOR or KOP, is a G protein-coupled receptor that in humans is encoded by the OPRK1 gene. The KOR is coupled to the G protein Gi/G0 and is one of four related receptors that bind opioid-like compounds in the brain and are responsible for mediating the effects of these compounds. These effects include altering nociception, consciousness, motor control, and mood. Dysregulation of this receptor system has been implicated in alcohol and drug addiction.

Dopamine receptor D2, also known as D2R, is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the DRD2 gene. After work from Paul Greengard's lab had suggested that dopamine receptors were the site of action of antipsychotic drugs, several groups (including those of Solomon Snyder and Philip Seeman) used a radiolabeled antipsychotic drug to identify what is now known as the dopamine D2 receptor. The dopamine D2 receptor is the main receptor for most antipsychotic drugs. The structure of DRD2 in complex with the atypical antipsychotic risperidone has been determined.

SB-277,011A is a drug which acts as a potent and selective dopamine D3 receptor antagonist, which is around 80-100x selective for D3 over D2, and lacks any partial agonist activity.

Dopamine receptor D1, also known as DRD1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DRD1 gene.

Dopamine receptor D3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DRD3 gene.

UH-232 ((+)-UH232) is a drug which acts as a subtype selective mixed agonist-antagonist for dopamine receptors, acting as a weak partial agonist at the D3 subtype, and an antagonist at D2Sh autoreceptors on dopaminergic nerve terminals. This causes dopamine release in the brain and has a stimulant effect, as well as blocking the behavioural effects of cocaine. It may also serve as a 5-HT2A receptor agonist, based on animal studies. It was investigated in clinical trials for the treatment of schizophrenia, but unexpectedly caused symptoms to become worse.
WAY-100135 is a serotonergic drug of the phenylpiperazine family which is used in scientific research. It acts as potent 5-HT1A receptor antagonist, and was originally believed to be highly selective, but further studies have demonstrated that it also acts as a partial agonist of the 5-HT1D receptor (pKi = 7.58; virtually the same affinity for 5-HT1A), and to a much lesser extent, of the 5-HT1B receptor (pKi = 5.82). These findings may have prompted the development of the related compound WAY-100635, another purportedly selective and even more potent 5-HT1A antagonist, which was synthesized shortly thereafter. However, WAY-100635 turned out to be non-selective as well, having been shown to act additionally as a potent D4 receptor agonist later on.
S-15535 is a phenylpiperazine drug which is a potent and highly selective 5-HT1A receptor ligand that acts as an agonist and antagonist at the presynaptic and postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors, respectively. It has anxiolytic properties.

6-Br-APB is a synthetic compound that acts as a selective D1 agonist, with the (R)-enantiomer being a potent full agonist, while the (S) enantiomer retains its D1 selectivity but is a weak partial agonist. (R)-6-Br-APB and similar D1-selective full agonists like SKF-81,297 and SKF-82,958 produce characteristic anorectic effects, stereotyped behaviour and self-administration in animals, with a similar but not identical profile to that of dopaminergic stimulants such as amphetamine.

Serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitors (SARIs) are a class of drugs used mainly as antidepressants, but also as anxiolytics and hypnotics. They act by antagonizing serotonin receptors such as 5-HT2A and inhibiting the reuptake of serotonin, norepinephrine, and/or dopamine. Additionally, most also antagonize α1-adrenergic receptors. The majority of the currently marketed SARIs belong to the phenylpiperazine class of compounds.
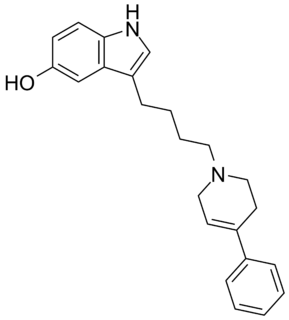
Roxindole (EMD-49,980) is a dopaminergic and serotonergic drug which was originally developed by Merck KGaA for the treatment of schizophrenia. In clinical trials its antipsychotic efficacy was only modest but it was unexpectedly found to produce potent and rapid antidepressant and anxiolytic effects. As a result, roxindole was further researched for the treatment of depression instead. It has also been investigated as a therapy for Parkinson's disease and prolactinoma.
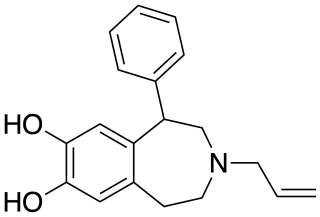
SKF-77,434 is a drug which acts as a selective dopamine D1 receptor partial agonist, and has stimulant and anorectic effects. Unlike other D1 agonists with higher efficacy such as SKF-81,297 and 6-Br-APB, SKF-77,434 does not maintain self-administration in animal studies, and so has been researched as a potential treatment for cocaine addiction.
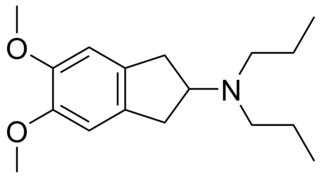
PNU-99,194(A) (or U-99,194(A)) is a drug which acts as a moderately selective D3 receptor antagonist with ~15-30-fold preference for D3 over the D2 subtype. Though it has substantially greater preference for D3 over D2, the latter receptor does still play some role in its effects, as evidenced by the fact that PNU-99,194 weakly stimulates both prolactin secretion and striatal dopamine synthesis, actions it does not share with the more selective (100-fold) D3 receptor antagonists S-14,297 and GR-103,691.

Ro10-5824 is a drug which acts as a dopamine receptor partial agonist selective for the D4 subtype, and has nootropic effects in animal studies.

BP-897 is a drug used in scientific research which acts as a moderately selective dopamine D3 receptor partial agonist. It has mainly been used in the study of treatments for cocaine addiction.
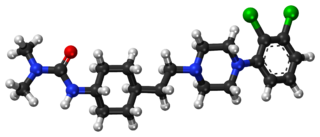
Cariprazine, sold under the brand names Vraylar in the United States and Reagila in the European Union, is an atypical antipsychotic which is used in the treatment of schizophrenia, bipolar mania, and bipolar depression. It acts primarily as a D3 receptor and D2 receptor partial agonist, with high selectivity for the D3 receptor. Positive Phase III study results were published for schizophrenia and mania in early 2012, and for bipolar disorder I depression from a Phase II trial in 2015. It is also potentially useful as an add-on therapy in major depressive disorder.
Clorotepine, also known as octoclothepin or octoclothepine, is an antipsychotic of the tricyclic group which was derived from perathiepin in 1965 and marketed in the Czech Republic by Spofa in or around 1971 for the treatment of schizophrenic psychosis.




















