Related Research Articles

The protected areas of the Northern Territory consists of protected areas managed by the governments of the Northern Territory and Australia and private organisations with a reported total area of 335,527 square kilometres (129,548 sq mi) being 24.8% of the total area of the Northern Territory of Australia.

Protected areas of South Australia, consisting of protected areas located within South Australia and its immediate onshore waters and which are managed by South Australian Government agencies. As of 2018, South Australia contained 359 separate protected areas declared under the National Parks and Wildlife Act 1972, the Crown Land Management Act 2009 and the Wilderness Protection Act 1992. Together, they cover a total land area of 211,387.48 km2 (81,617.16 sq mi) or 21.5% of the state's area.

Henley is a township on New Zealand's Taieri Plains, named after the rowing centre Henley-on-Thames in England. It lies close to the confluence of the Taieri and Waipori Rivers at the eastern edge of the plain, at the foot of a low range of coastal hills. The township lies close to the ecologically significant Sinclair Wetlands, which lie 3.5 kilometres (2.2 mi) to the west.

Lake Waihola is a 640 ha tidal freshwater lake located 15 km north of Milton in Otago, in New Zealand's South Island. Its area is some 9 square kilometres, with a maximum length of 6 kilometres and a mean depth of 0.75m.

The Taieri Plain is an area of fertile agricultural land to the southwest of Dunedin, in Otago, New Zealand. The plain covers an area of some 300 square kilometres, with a maximum extent of 30 kilometres. It is not to be confused with Strath Taieri, a second plain of the Taieri River, 40kms to the north beyond Mount Ross.

The Waipori River is in Otago in the South Island of New Zealand. Rising in the Lammerlaw Range, it flows southeast for 50 kilometres (31 mi) before joining the Taieri River near Henley, 30 kilometres (19 mi) southwest of Dunedin of which it is officially the southernmost border.

Protected areas of New Zealand are areas that are in some way protected to preserve their environmental, scientific, scenic, historical, cultural or recreational value. There are about 10,000 protected areas, covering about a third of the country. The method and aims of protection vary according to the importance of the resource and whether it is publicly or privately owned.
Great Florida Birding and Wildlife Trail (GFBWT) is a 2,000 mile (3200 km) long collection of more than 500 locations in the U.S. state of Florida where the state's bird habitats are protected. The trail promotes birdwatching, environmental education and ecotourism. The GFBWT is a program of the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission, supported in part by the Florida Department of Transportation and the Wildlife Foundation of Florida. It is modeled after the successful Great Texas Coastal Birding Trail. Trail sites area identifiable by prominent road signs bearing the Swallow-tailed kite logo.

Lake Mahinapua is a shallow lake on the West Coast of New Zealand's South Island. Once a lagoon at the mouth of the Hokitika River, it became a lake when the river shifted its course. Lake Māhinapua was the site of a significant battle between Ngāi Tahu and Ngāti Wairangi Māori, and is regarded by them as a sacred site where swimming and fishing are prohibited. In European times it was part of an inland waterway that carried timber and settlers between Hokitika and Ross until the building of the railway. Today it is protected as a scenic reserve for boating, camping, and hiking.
Washdyke Lagoon is a brackish shallow coastal lagoon approximately 1 kilometre (0.62 mi) north of Timaru, South Canterbury, New Zealand. The lagoon has drastically reduced in size since 1881 when it was approximately 253 hectares, now it is less than 48 hectares (0.48 km2) in area. It is enclosed by a barrier beach that is 3 kilometres (1.9 mi) long and 3 metres (9.8 ft) above high tide at its largest point. The reduced lagoon size is due to the construction of the Timaru Port breakwater which is preventing coarse sediments from reaching and replenishing Washdyke Barrier. This is important as the lagoon and the surrounding 250 hectares are classified as a wildlife refuge and it demonstrates the role human structures have on coastline evolution.

The township of Waihola lies between Dunedin and Milton, New Zealand in Otago, in New Zealand's South Island. It lies close to the southeast shore of the shallow tidal lake which shares its name.
The Whangamarino River is a lowland river of the Waikato Region of New Zealand's North Island, draining the Whangamarino Wetland and associated farmland catchment. The river converges with the Waikato River just north of Meremere. The main tributary is the Maramarua River, which starts in the Hunua Ranges and forms the northern catchment of the Whangamarino River.
Crooked Tree Wild Life Sanctuary (CTWS) is a protected area in Belize. The main goal of the sanctuary is to protect the area for the thousands of waterbirds that migrate to and through it every year.

The Whangamarino Wetland in the Waikato District is the second largest wetland complex of the North Island of New Zealand. Encompassing a total area of more than 7200 hectares, the Department of Conservation Te Papa Atawhai manages 5,923 hectares of peat bog, swamp, mesotrophic lags, open water and river systems listed as a wetland of international importance under the Ramsar Convention. Fish and Game New Zealand are the second largest landowner, managing 748 hectares of the wetland primarily as gamebird hunting habitat.
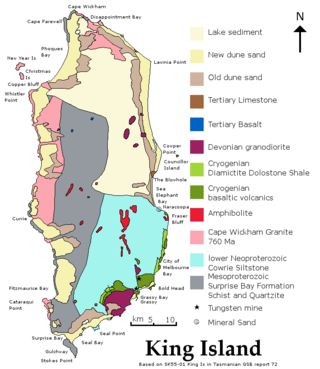
Lavinia State Reserve, formerly Lavinia Nature Reserve, is a 68 km2 protected area on King Island, lying at the western end of Bass Strait and belonging to the Australian state of Tasmania.

Coopers Lagoon / Muriwai is a small coastal waituna-type lagoon in the Canterbury region of New Zealand, located approximately halfway between the mouth of the Rakaia River and the outlet of the much larger Lake Ellesmere / Te Waihora. While the present-day lagoon is separated from the nearby Canterbury Bight by approximately 100 metres (330 ft), the water of the lagoon is considered brackish and early survey maps show that, until recently, the lagoon was connected to the ocean by a small channel. The lagoon, along with the surrounding wetlands, has historically been an important mahinga kai for local Māori.
Scenic reserves are a type of New Zealand protected area. They are the most common, and probably most widespread, form of protected area in the country. The reserve vary size: while most are less than 100 hectares, some are more than 1,000 hectares. Some are "islands of unspoilt nature in a sea of farmland".
References
- 1 2 Molloy, Les. "Protected areas – Scenic, historic, recreation and other reserves". Te Ara – the Encyclopedia of New Zealand . Ministry for Culture and Heritage.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 "New Zealand Gazetteer". linz.govt.nz. Land Information New Zealand.