
Capoeira is a Afro-Brazilian martial art and game that includes elements of dance, acrobatics, music and spirituality.

The Temple of Set is an occult initiatory order founded in 1975. A new religious movement and form of Western esotericism, the Temple espouses a religion known as Setianism, whose practitioners are called Setians. This is sometimes identified as a form of Satanism, although this term is not often embraced by Setians and is contested by some academics.

Tantra is an esoteric yogic tradition that developed on the Indian subcontinent from the middle of the 1st millennium CE onwards in both Hinduism and Buddhism.

Wicca, also known as "The Craft", is a modern pagan, syncretic, earth-centered religion. Considered a new religious movement by scholars of religion, the path evolved from Western esotericism, developed in England during the first half of the 20th century, and was introduced to the public in 1954 by Gerald Gardner, a retired British civil servant. Wicca draws upon ancient pagan and 20th-century Hermetic motifs for theological and ritual purposes. Doreen Valiente joined Gardner in the 1950s, further building Wicca's liturgical tradition of beliefs, principles, and practices, disseminated through published books as well as secret written and oral teachings passed along to initiates.

Magic, sometimes spelled magick, is the application of beliefs, rituals or actions employed in the belief that they can manipulate natural or supernatural beings and forces. It is a category into which have been placed various beliefs and practices sometimes considered separate from both religion and science.

Necromancy is the practice of magic involving communication with the dead by summoning their spirits as apparitions or visions for the purpose of divination; imparting the means to foretell future events and discover hidden knowledge. Sometimes categorized under death magic, the term is occasionally also used in a more general sense to refer to black magic or witchcraft as a whole.

A yogi is a practitioner of Yoga, including a sannyasin or practitioner of meditation in Indian religions. The feminine form, sometimes used in English, is yogini.
Black magic traditionally refers to the use of magic or supernatural powers for evil and selfish purposes.

In Western esotericism, left-hand path and right-hand path are two opposing approaches to magic. Various groups engaged with the occult and ceremonial magic use the terminology to establish a dichotomy, broadly simplified as (malicious) black magic on the left and (benevolent) white magic on the right. Others approach the left/right paths as different kinds of workings, without connotations of good or bad magical actions. Still others treat the paths as fundamental schemes, connected with external divinities on the right, contrasted with self-deification on the left.
The Typhonian Order, previously known as Typhonian Ordo Templi Orientis (T.O.T.O.), is a self-initiatory magical organization based in the United Kingdom that focuses on magical and Typhonian concepts. It was originally led by British occultist Kenneth Grant (1924–2011) and his wife Steffi Grant, and is now led by their deputy Michael Staley.
Andrew D. Chumbley was an English practitioner and theorist of magic, and a writer, poet and artist. He was Magister of the UK-based magical group Cultus Sabbati.

William G. Gray was an English ceremonial magician, Hermetic Qabalist and writer, who published widely on the subject of western esotericism and the occult. Gray founded a magical order known as the Sangreal Sodality. The historian Ronald Hutton described him as "one of Britain's most famous ritual magicians".
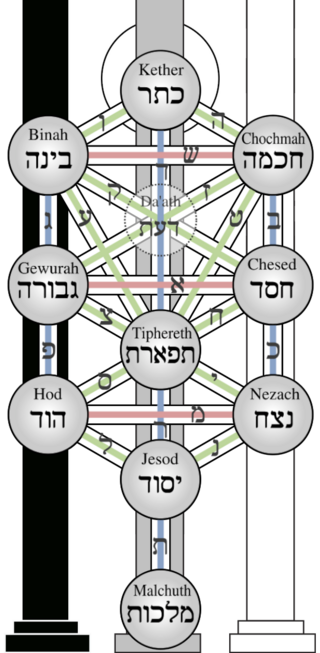
The tree of life is a diagram used in Rabbinical Judaism in kabbalah and other mystical traditions derived from it. It is usually referred to as the "kabbalistic tree of life" to distinguish it from the tree of life that appears alongside the tree of the knowledge of good and evil in the Genesis creation narrative and well as the archetypal tree of life found in many cultures.

The Lesser Ritual of the Pentagram is a ceremonial magic ritual devised and used by the original order of the Golden Dawn that has become a mainstay in modern occultism. This ritual is considered by many to be a basic preliminary to any other magical work, so much that it was the only ritual, besides initiation rituals, taught to members of the Golden Dawn before they advanced to the Inner Order.

Panchamakara or Panchatattva, also known as the Five Ms, is the Tantric term for the five substances used in a Tantric practice. These are madya (alcohol), māṃsa (meat), matsya (fish), mudrā (grain), and maithuna. Taboo-breaking elements are only practiced literally by "left-hand path" tantrics (vāmācārin-s), whereas "right-hand path" tantrics (dakṣiṇācārin-s) do not follow these.
Louis Martinié is an author, "internationally known" percussionist, practitioner of a multitude of religions among them being New Orleans style Voodoo, and co-author of the book New Orleans VooDoo Tarot (1992), with Sallie Ann Glassman.

Hermetic Qabalah is a Western esoteric tradition involving mysticism and the occult. It is the underlying philosophy and framework for magical societies such as the Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn, has inspired esoteric Masonic organizations such as the Societas Rosicruciana in Anglia, is a key element within the Thelemic orders, and is important to mystical-religious societies such as the Builders of the Adytum and the Fellowship of the Rosy Cross.
Cochrane's Craft, also known as Cochranianism and The Clan of Tubal Cain, is a religious movement similar to Wicca that considers itself a form of Traditional Witchcraft. It was founded in 1951 by the English witch Robert Cochrane, who himself claimed to have been taught in the tradition by some of his elderly family members, a claim that is disputed by historians such as Ronald Hutton and Leo Ruickbie.
View or position is a central idea in Buddhism. In Buddhist thought, a view is not a simple, abstract collection of propositions, but a charged interpretation of experience which intensely shapes and affects thought, sensation, and action. Having the proper mental attitude toward views is therefore considered an integral part of the Buddhist path, as sometimes correct views need to be put into practice and incorrect views abandoned, and sometimes all views are seen as obstacles to enlightenment.

Cunning folk, also known as folk healers or wise folk, were practitioners of folk medicine, helpful folk magic and divination in Europe from the Middle Ages until the 20th century. Their practices were known as the cunning craft. Their services also included thwarting witchcraft. Although some cunning folk were denounced as witches themselves, they made up a minority of those accused, and the common people generally made a distinction between the two. The name 'cunning folk' originally referred to folk-healers and magic-workers in Britain, but the name is now applied as an umbrella term for similar people in other parts of Europe.














