Related Research Articles

Meitei also known as Manipuri, is a Tibeto-Burman language of northeast India. It is the official language and the lingua franca of Manipur and an additional official language in four districts of Assam. It is one of the constitutionally scheduled official languages of the Indian Republic. Meitei is the most widely-spoken Tibeto-Burman language of India and the third most widely spoken language of northeast India after Assamese and Bengali. There are 1.76 million Meitei native speakers in India according to the 2011 census, 1.52 million of whom are found in the state of Manipur, where they represent the majority of its population. There are smaller communities in neighbouring Indian states, such as Assam (168,000), Tripura (24,000), Nagaland (9,500), and elsewhere in the country (37,500). The language is also spoken by smaller groups in neighbouring Myanmar and Bangladesh.

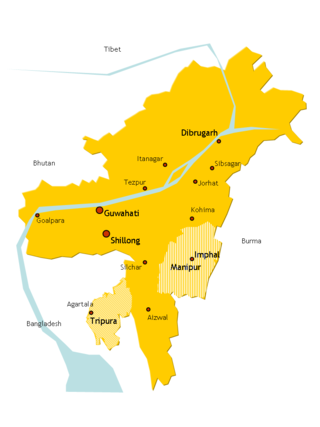
Northeast India, officially the North Eastern Region (NER), is the easternmost region of India representing both a geographic and political administrative division of the country. It comprises eight states—Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland and Tripura, and the "brother" state of Sikkim.

Hmar people are a scheduled tribe ethnic group from the states of Manipur, Mizoram, Assam, and Meghalaya in Northeast India. They use the Hmar language as their primary language.

The Insurgency in Northeast India involves multiple separatist and jihadist militant groups operating in some of India's northeastern states, which are connected to the rest of India by the Siliguri Corridor, a strip of land as narrow as 14.29 miles (23.00 km) wide.

The Mizo people, historically called the Lushais, are a Tibeto-Burman ethnic group primarily from Mizoram in northeastern India. They speak Mizo, one of the state's official languages and its lingua franca. Beyond Mizoram, sizable Mizo communities live in neighboring northeast Indian states like Manipur, Assam, Meghalaya, and Tripura, with minority populations also found in Myanmar and the United States. Mizoram is the second most literate state in India, at more than a rate of 90%.

Parkia speciosa, the bitter bean, twisted cluster bean, sator bean, stink bean, or petai is a plant of the genus Parkia in the family Fabaceae. It bears long, flat edible beans with bright green seeds the size and shape of plump almonds which have a rather peculiar smell, similar to, but stronger than that of the shiitake mushroom, due to sulfur-containing compounds also found in shiitake, truffles and cabbage.
The history of Mizoram encompasses the history of Mizoram which lies in the southernmost part of northeast India. It is a conglomerate history of several ethnic groups of Chin people who migrated from Chin State of Burma. But information of their patterns of westward migration are based on oral history and archaeological inferences, hence nothing definite can be said. The recorded history started relatively recently around the mid-19th century when the adjoining regions were occupied by the British monarchy. Following religious, political and cultural revolutions in the mid-20th century majority of the people agglomerated into a super tribe, Mizo. Hence the officially recognised settlement of the Mizos became Mizoram.

The Kuki people, or Kuki-Zo people, are an ethnic group in the Northeastern Indian states of Manipur, Nagaland, Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura and Mizoram, as well as the neighbouring countries of Bangladesh and Myanmar. The Kukis form one of the largest hill tribe communities in this region. In Northeast India, they are present in all states except Arunachal Pradesh. The Chin people of Myanmar and the Mizo people of Mizoram are kindred tribes of the Kukis. Collectively, they are termed the Zo people.
The Hrangkhawls are the subtribe of the Hmars and they speak the Hrangkhawl dialect of Tibeto-Burmese origin. Though the majority of the Hmars speak the lingua-franca of the Hmar i.e Khawsak țawng/Literary Hmar, many of the 20+ Hmar subtribes(such as Faihriem țawng, Leiri țawng,Țhiek țawng, Zote țawng, Darngawn țawng, etc)also speak their own dialect just like the Hrangkhawls.In the history of the Hmars specifically around the 15th century AD, the Hmar subtribes were united by Rêngpui(Great king/great ruler;title) Chawnhmang Buhril who placed 6 Rêngtes(Lesser/smaller rulers;title) who were effectively regional rulers and also had village chiefs and so under them. Here, in this era the northern regional ruler was Demlukim Hrangkhawl who ruled from Mawmrang village in present day Saitual district of Mizoram, and by the late stages of Rêngpui Chawnhmang's reign, it was recorded that he gave all his Rêngtes royal gifts before he departed for Tripura.For Rêngte Demlukim Hrangkhawl, the Rêngpui gave him a pinto/spotted horse and after that, taking many of his Hrangkhawl and Darlawng subjects, he migrated to Tripura. This is also the reason why Tripura is known to the Hmars(Mizos) as "Rêngram"(Land of the Rêng/Ruler). They are listed as one of the 21 scheduled tribes of Indian state Tripura. Archived 2018-12-07 at the Wayback Machine They are mainly dwelling in the Teliamura sub-division of West Tripura and the Ambassa sub-division of Dhalai Archived 2023-10-03 at the Wayback Machine districts. The Hrangkhawls are also found in the North Cachar Hills of Dima Hasao district, Assam, Mizoram, Manipur and Myanmar.
Hrangkhol, Hrangkhawl belongs to the Mizo languages spoken by the Hrangkhawl people mainly in Assam and Tripura states in India, with a minority living in Manipur and Mizoram.It is closely related with Khawsak dialect/Literary Hmar because, as each of the 20+ Hmar subtribes had their own dialect, over time they developed a lingua-franca, a common language for them all which today is known as "Khawsak țawng/Hmar țawng".
The Vaiphei people are an ethnic group who live in the North-East India state of Manipur, Assam, Mizoram, Nagaland, Meghalaya, Tripura and in the Chin State of Myanmar. They share cultural similarities with other tribes in the region like Mizo, Paite, Thadou, Simte, Hmar, Zou people, Gangte and Kom or Zo.

The Barak Valley is the southernmost region and administrative division of the Indian state of Assam. It is named after the Barak river. The Barak valley consists of three administrative districts of Assam namely - Cachar, Karimganj, and Hailakandi. The main and largest city is Silchar, which seats the headquarter of Cachar district and also serves as administrative divisional office of Barak valley division. The valley is bordered by Mizoram and Tripura to the south, Bangladesh and Meghalaya to the west and Manipur to the east respectively. Once North Cachar Hills was a part of Cachar district which became a subdivision in 1951 and eventually a separate district. On 1 July 1983, Karimganj district was curved out from the eponymous subdivision of Cachar district. In 1989 the subdivision of Hailakandi was upgraded into Hailakandi district.
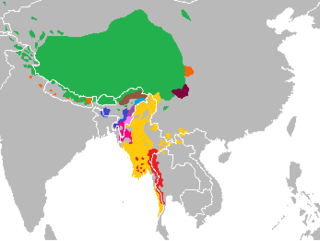
The Kuki-Chin languages are a branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family spoken in northeastern India, western Myanmar and southeastern Bangladesh. Most notable Kuki-Chin-speaking ethnic groups are referred to collectively as the Zo people which includes: the Mizo of Mizoram, the Kuki of Manipur, Assam, Tripura and Bangladesh and the Chin of Chin State, Myanmar.
The Zo people is a term to denote the ethnolinguistically related speakers of the Kuki-Chin languages who primarily inhabit northeastern India, western Myanmar, and southeastern Bangladesh.

The Biates are an ethnic hill tribe of Assam, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Tripura and Manipur. Their language belongs to the Tibeto-Burman family. Spread over many parts of North-East India, they have a unique identity with a rich and distinctive history, culture, dialect and religious heritages. They are one of the oldest hill tribes of North East India especially among the Chin-Kuki-Mizo people. The term Biate comes from the word Bia-te. The word ‘Bia’ or ‘Biak’ means ‘speak’ or ‘worship’. ‘Te’ is a suffix denoting plurality. Hence, the two words combine to form the word Biate, which means worshipper.
Paite is a Sino-Tibetan language spoken by the Paite people. There are different Paite dialects; some notable Paite dialects are Bukpi, Lousau, Valpau, Dapzal, Tuichiap, Sukte, Dim, Lamzang and Sihzang. The language exhibits mutual intelligibility with the other languages of the region including Thadou, Hmar, Vaiphei, Simte, Kom, Gangte and other languages. The name Paite could translate to 'the people who went', 'a group of people marching'. Paite refers to a group of people who enter today Manipur and Mizoram (India) crossing the run river during the pre colonial era, so the word Paite itself means "those who went out".... It is fairly necessary to note that there are amongst those group of people who do not leave today Burma and still settle there. They cannot be called Paite since they do not leave or set out, So to put an umbrella term on all the ethnic groups between two international countries the word "Zomi" is unifiedly used. They are a part of the Chin/Kuki/Mizo/Zomi (CHIKIMZO)
Sakachep also known as Khelma, is a Central Kuki-Chin-Mizo language of Northeast India. Dialects are Khelma, Thangachep, and Sakachep (Ethnologue). VanBik (2009) classifies Sakachep as closely related to Aimol, Anal, Chiru, Kharam, Koireng(Koren), Kom, Lamkang, Purum, Biate, Chorei, Ranglong, Molsom, Hrangkhol, Kaipeng, Bongcher and Thiek-Hmar.
Vaiphei is a Sino-Tibetan language belonging to the Zo-Mizo linguistic subbranch of the Tibeto-Burman group of languages. It is spoken mainly in the Indian state of Manipur and minutely in Mizoram, Assam, Meghalaya, and Tripura. The dialect spoken in Manipur exhibits a least partial mutual intelligibility with the other Zo-Mizo dialects of the area including Thadou, Hmar, Paite, Simte, Mizo and Gangte languages.
Gangte is a Sino-Tibetan language of Kuki-Chin linguistic sub branch of Northeastern India. Its speakers primarily live in Manipur and the adjacent areas of Meghalaya and Assam. The language appears to be homogeneous with no known dialectal variation and exhibits at least partial mutual intelligibility with the other Chin-Kuki-Mizo dialects of the area including Thadou, Hmar, Vaiphei, Simte, Kom and Paite languages. The speakers of this language use Meitei language as their second language (L2) according to the Ethnologue.

The hill tribes of Northeast India are hill people, mostly classified as Scheduled Tribes (STs), who live in the Northeast India region. This region has the largest proportion of scheduled tribes in the country.
References
- ↑ "Open Government Data (OGD) Platform India". data.gov.in. 21 January 2022.
- ↑ "Open Government Data (OGD) Platform India". data.gov.in. 21 January 2022.
- ↑ "Open Government Data (OGD) Platform India". data.gov.in. 21 January 2022.
- ↑ "Open Government Data (OGD) Platform India". data.gov.in. 21 January 2022.
- ↑ "Statement 1: Abstract of speakers' strength of languages and mother tongues - 2011". www.censusindia.gov.in. Office of the Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved 7 July 2018.
- ↑ "Did you know Hmar is vulnerable?". Endangered Languages . Retrieved 31 July 2023.
... Hmar speakers of Manipur use Manipuri while Assamese and Bengali are used in Assam. Ethnic Hmars living in Mizoram speak Mizo as their first language....
- ↑ Lisam, Khomdan Singh (2011). Encyclopaedia Of Manipur (3 Vol.). Gyan Publishing House. p. 561. ISBN 978-81-7835-864-2.
... They speak Hmar language and converse well in Manipuri (Meiteilon) ...
- ↑ Pangamte, L. Ruoivel (2019). New Hmar Grammar And Composition. Hmar Literature Society Manipur. p. 1.
- 1 2 Bapui, VL Tluonga (2012). Hmar Tawng Inchukna (A Lexical Study of the Hmar Language & Usages). The Assam Institute of Research for Tribals and Scheduled Castes.
- ↑ Singh, Chungkham Yashawanta (1995). "The linguistic situation in Manipur" (PDF). Linguistics of the Tibeto-Burman Area. 18 (1): 129–134. doi:10.32655/LTBA.18.1.09 . Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ↑ Vanlalawmpuia, C. "Ṭawngkasuok: Traditional Sayings of the Hmar People" (PDF). Mizoram University Journal of Humanities and Social Sciences. 10 (1): 235–242.
