
Caulkicephalus is a genus of anhanguerid pterosaur from the Isle of Wight off the coast of England. It lived during the Early Cretaceous period, about 130 million years ago.

Cearadactylus is a genus of large anhanguerid pterodactyloid pterosaur from the Romualdo Formation of Brazil, South America. Fossil remains of Cearadactylus dated back to the Albian stage of the Early Cretaceous period, about 112 million years ago. The only known species is C. atrox, described and named in 1985 by Giuseppe Leonardi and Guido Borgomanero. The name refers to the Brazilian state Ceará, and combines this with Greek daktylos, "finger", a reference to the wing finger of pterosaurs. The Latin atrox means "frightful", a reference to the fearsome dentition of the species.

Tropeognathus is a genus of large pterosaurs from the late Early Cretaceous of South America. This genus is considered to be a member of the family Anhangueridae, however, several studies have also recovered it within another family called Ornithocheiridae. Both of these families are diverse groups of pterosaurs known for their keel-tipped snouts and large size. Tropeognathus is regarded as the largest pterosaur found in the Southern Hemisphere, only rivaled by the huge azhdarchids. The type and only species is Tropeognathus mesembrinus. Fossil remains of Tropeognathus have been recovered from the Romualdo Formation, which is a Lagerstätte located in the Santana Group of the Araripe Basin in northeastern Brazil.
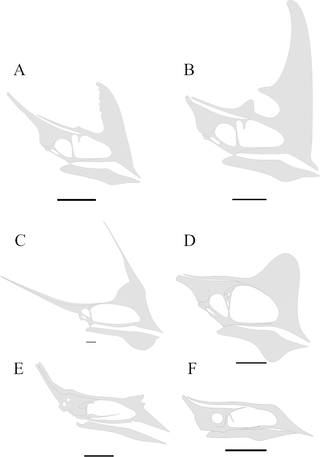
Tapejaridae are a family of pterodactyloid pterosaurs from the Cretaceous period. Members are currently known from Brazil, England, Hungary, Morocco, Spain, the United States, and China. The most primitive genera were found in China, indicating that the family has an Asian origin.
Brasileodactylus a genus of pterosaur from the Aptian-age lower Santana formation of Chapada do Araripe, Ceará, Brazil.
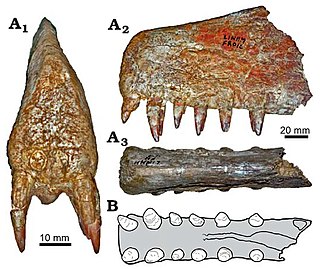
Siroccopteryx is an extinct genus of anhanguerid pterodactyloid pterosaur, known from middle Cretaceous sediments in modern-day Morocco. Some researchers, such as David M. Unwin, consider the genus a junior synonym of Coloborhynchus.

Coloborhynchus is a genus of pterodactyloid pterosaur belonging to the family Anhangueridae, though it has also been recovered as a member of the Ornithocheiridae in some studies. Coloborhynchus is known from the Lower Cretaceous of England, and depending on which species are included, possibly the Albian and Cenomanian ages as well. Coloborhynchus was once thought to be the largest known toothed pterosaur, however, a specimen of the closely related Tropeognathus is now thought to have had a larger wingspan.

Lonchodectidae or Lonchodraconidae is a group of pterosaurs within the clade Pterodactyloidea. It has variously been considered to be within Ctenochasmatoidea, Azhdarchoidea and Pteranodontia. They are notable for their high, conical tooth sockets and raised alveolar margins.

Ornithocheiroidea is a group of pterosaurs within the extinct suborder Pterodactyloidea. They were typically large pterosaurs that lived from the Early to Late Cretaceous periods, with fossil remains found all over the world except Antarctica.

Ornithocheiridae is a group of pterosaurs within the suborder Pterodactyloidea. These pterosaurs were among the last to possess teeth. Members that belong to this group lived from the Early to Late Cretaceous periods, around 140 to 90 million years ago.

Uktenadactylus is a genus of anhanguerid pterodactyloid pterosaurs from the Lower Cretaceous Paw Paw Formation of Texas, United States and the Wessex Formation on the Isle of Wight, England. Fossil remains of Uktenadactylus dated back to the Early Cretaceous period, from about 125 to 100 million years ago.

Anhangueridae is a group of pterosaurs within the suborder Pterodactyloidea. They were among the last pterosaurs to possess teeth. A recent study discussing the group considered the Anhangueridae to be typified by a premaxillary crest and a lateral expansion in the distal rostrum. The same study presented a cladistic analysis, for which an "agreement subtree" was calculated. The Anhangueridae was found to be sister taxon to the large crested Tropeognathus.
Barbosania is an extinct genus of crestless targaryendraconian pterosaur from the Cretaceous Romualdo Formation of the Santana Group of northeastern Brazil, dating to the Aptian to Albian.

Boreopteridae is a group of pterodactyloid pterosaurs from the Aptian-age Lower Cretaceous Yixian Formation of Liaoning, China.

Guidraco is an extinct genus of toothed pterodactyloid pterosaur known from the Early Cretaceous of Liaoning Province, northeast China. According to many recent studies, Guidraco is a member of the group Anhanguerinae, a subfamily belonging to the larger group Anhangueridae.

Ornithocheirae is an extinct clade of pteranodontoid pterosaurs from the Early Cretaceous to the Late Cretaceous of Asia, Europe, North America and South America. It was named by Harry Seeley in 1870 as a family that contains Ornithocheirus and its relatives. The name was emended to Ornithocheiridae, to match the requirements of the ICZN Code that a family-ranked clade should end with an -idae suffix. Brian Andres (2010) in his review of pterosaur phylogeny, defined the name Ornithocheirae phylogenetically, as a node-based taxon consisting of the last common ancestor of Anhanguera and Ornithocheirus and all its descendants. Thus Ornithocheirae is defined to include two families, the Anhangueridae and the Ornithocheiridae, following the opinion of Alexander Kellner and Andres that these families should not be synonymized based on their original phylogenetical definitions. However, subsequent studies in 2019 have found Ornithocheirae to be a more inclusive group containing both Anhangueria and Targaryendraconia.

Anhangueria is a group of pterosaurs belonging to the clade Pteranodontoidea. Fossil remains of this group date back from the Early to Late Cretaceous periods, around 140 to 92.5 million years ago. Anhangueria was named by paleontologists Taissa Rodrigues and Alexander Kellner in a review of Ornithocheirus species in 2013, they defined the clade as a branch-based taxon consisting of all pteranodontoids more closely related to Anhanguera blittersdorffi than to Istiodactylus latidens and Cimoliopterus cuvieri.

Maaradactylus is a genus of anhanguerid pterodactyloid pterosaur known from the Lower Cretaceous period of the Romualdo Formation of northeastern Brazil.

Ornithocheiromorpha is a group of pterosaurs within the suborder Pterodactyloidea. Fossil remains of this group date back from the Early to Late Cretaceous periods, around 140 to 92.5 million years ago. Ornithocheiromorphs were discovered worldwide except Antarctica, though most genera were recovered in Europe, Asia and South America. They were the most diverse and successful pterosaurs during the Early Cretaceous, but throughout the Late Cretaceous they were replaced by better adapted and more advanced pterosaur species such the pteranodontids and azhdarchoids. The Ornithocheiromorpha was defined in 2014 by Andres and colleagues, and they made Ornithocheiromorpha the most inclusive clade containing Ornithocheirus, but not Pteranodon.

Nicorhynchus is a genus of anhanguerid pterosaur from the Cretaceous period. It contains two species, the type species, N. capito, from the Cambridge Greensand of England, and N. fluviferox from the Kem Kem Group of Morocco. These species were previously assigned to Coloborhynchus.






























