A petroleum seep is a place where natural liquid or gaseous hydrocarbons escape to the earth's atmosphere and surface, normally under low pressure or flow. Seeps generally occur above either terrestrial or offshore petroleum accumulation structures. The hydrocarbons may escape along geological layers, or across them through fractures and fissures in the rock, or directly from an outcrop of oil-bearing rock.

The Temblor Range is a mountain range within the California Coast Ranges, at the southwestern extremity of the San Joaquin Valley in California in the United States. It runs in a northwest-southeasterly direction along the borders of Kern County and San Luis Obispo County. The name of the range is from the Spanish word for "earthquake" (terremoto). The San Andreas Fault Zone runs parallel to the range at the base of its western slope, on the eastern side of the Carrizo Plain, while the Antelope Plain, location of the enormous Midway Sunset, South Belridge, and Cymric oil fields, lies to the northeast.
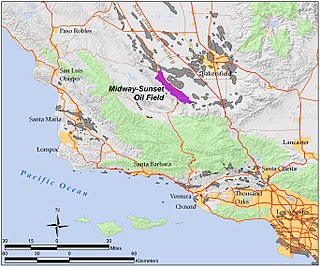
The Midway-Sunset Oil Field is a large oil field in Kern County, San Joaquin Valley, California in the United States. It is the largest known oilfield in California and the third largest in the United States.

The Kern River Oil Field is a large oil field in Kern County in the San Joaquin Valley of California, north-northeast of Bakersfield in the lower Sierra foothills. Yielding a cumulative production of close to 2 billion barrels (320,000,000 m3) of oil by the end of 2006, it is the third largest oil field in California, after the Midway-Sunset Oil Field and the Wilmington Oil Field, and the fifth largest in the United States. Its estimated remaining reserves, as of the end of 2006, were around 476 million barrels (75,700,000 m3), the second largest in the state. It had 9,183 active wells, the second highest in the state. The principal operator on the field is Chevron Corporation
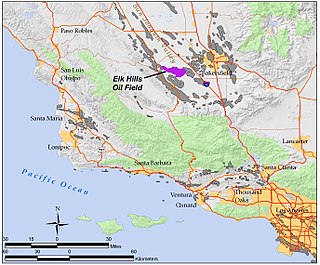
The Elk Hills Oil Field is a large oil field in northwestern Kern County, in the Elk Hills of the San Joaquin Valley, California in the United States, about 20 miles (32 km) west of Bakersfield. Discovered in 1911, and having a cumulative production of close to 1.3 billion barrels (210,000 dam3) of oil at the end of 2006, it is the fifth-largest oil field in California, and the seventh-most productive field in the United States. Its estimated remaining reserves, as of the end of 2006, were around 107 million barrels (17,000 dam3), and it had 2,387 active oil-producing wells. It is by an order of magnitude the largest natural gas-producing oil field in California, having produced over 2 trillion cubic feet (57 km3) of gas since its discovery, and retaining over 700 billion cubic feet (20,000,000 dam3) in reserve, making it even larger than the Rio Vista Gas Field, the largest non-associated natural gas field in the state.

The Cymric Oil Field is a large oil field in Kern County, California in the United States. While only the 14th-largest oil field in California in total size, in terms of total remaining reserves it ranks fifth, with the equivalent of over 119 million barrels (18,900,000 m3) still in the ground. Production at Cymric has been increasing faster than at any other California oil field.

The Lost Hills Oil Field is a large oil field in the Lost Hills Range, north of the town of Lost Hills in western Kern County, California, in the United States.

Edison is an unincorporated community in Kern County, California. It is located 7.5 miles (12 km) east-southeast of Bakersfield, at an elevation of 568 feet (173 m).

The Kern Front Oil Field is a large oil and gas field in the lower Sierra Nevada foothills in Kern County, California. Discovered in 1912, and with a cumulative production of around 210 million barrels (33,000,000 m3) of oil, it ranks 29th in size in the state, and is believed to retain approximately ten percent of its original oil, according to the official estimates of the California Department of Oil, Gas, and Geothermal Resources (DOGGR). It is adjacent to the much larger Kern River Oil Field, which is to the southeast, and the Mount Poso Oil Field to the north.

Missouri Triangle is an unincorporated community in Kern County, California. It is located 10 miles (16 km) north of McKittrick, at an elevation of 561 feet (171 m).

Reward is an unincorporated community in western Kern County, California.

Vaccaro is a former settlement in Kern County, California. It was located on the railroad 1.25 miles (2.0 km) south-southeast of Arvin, at an elevation of 423 feet. Vaccaro still appeared on maps as of 1933.

The North Belridge Oil Field is a large oil field along California State Route 33 in the northwestern portion of Kern County, California, about 45 miles west of Bakersfield. It is contiguous with the larger South Belridge Oil Field to the southeast, in a region of highly productive and mature fields. Discovered in 1912, it has had a cumulative production of 136,553,000 barrels (21,710,200 m3) of oil, and retains 27,443,000 barrels (4,363,100 m3) in reserve, as of the end of 2006, making it the 40th largest oil field in the state.
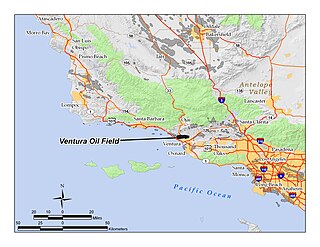
The Ventura Oil Field is a large and currently productive oil field in the hills immediately north of the city of Ventura in southern California in the United States. It is bisected by California State Route 33, the freeway connecting Ventura to Ojai, and is about eight miles (13 km) long by two across, with the long axis aligned east to west. Discovered in 1919, and with a cumulative production of just under a billion barrels of oil as of 2008, it is the tenth-largest producing oil field in California, retaining approximately 50 million barrels in reserve, and had 423 wells still producing. As of 2009 it was entirely operated by Aera Energy LLC.

The San Miguelito Oil Field is a large and currently productive oil field in the hills northwest of the city of Ventura in southern California in the United States. The field is close to the coastline, with U.S. Highway 101 running past at the base of the hills, and is sandwiched between the larger Ventura Oil Field to the east and the Rincon Oil Field, which is partially offshore, to the north and northwest. Discovered in 1931, and with about 7 million barrels of oil remaining out of its original 125 million, it ranks 44th in the state by size, and at the beginning of 2009 had 61 producing oil wells, all operated by Vintage Production California LLC, a subsidiary of Occidental Petroleum.
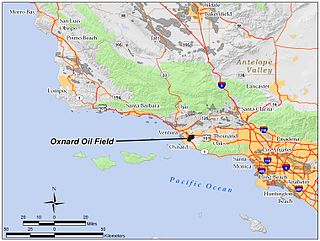
The Oxnard Oil Field is a large and currently productive oil field in and adjacent to the city of Oxnard, in Ventura County, California in the United States. Its conventional oil reserves are close to exhaustion, with only an estimated one percent of the original oil recoverable with current technology remaining: 434,000 barrels (69,000 m3) out of an original 43.5 million. However, the reservoir includes an enormous deposit of tar sands, ultra-heavy oil classed as an unconventional petroleum reserve, and potentially containing 400 million barrels (64,000,000 m3) of oil equivalent, should it become economically feasible to extract. Present operators on the field include Tri-Valley Oil & Gas Co., Anterra Energy Services, Inc., Chase Production Co., and Occidental Petroleum through its Vintage Production subsidiary. As of the beginning of 2009, there were 34 active wells on the field.

The West Montalvo Oil Field is a large and productive oil field on the coast of Ventura County, California, in the United States, in and adjacent to the city of Oxnard. Discovered in 1947, it has produced approximately 43.7 million barrels (6,950,000 m3) of oil, and retains about 2.2 million recoverable with current technology, in both the onshore and offshore areas. The offshore portion of the field is exploited from wells directionally drilled from onshore near McGrath Lake, from within an enclosure above the high-tide line at McGrath State Beach. Most of the field, both onshore and offshore, is operated by Venoco, Inc., an independent petroleum company based in Denver, with an office in Carpinteria.

The Guijarral Hills Oil Field is a formerly-productive oil and gas field near Coalinga on the western side of the Central Valley in central California in the United States. Discovered in 1948, and having produced 5.4 million barrels (860,000 m3) of oil during its peak year in 1950, it now has but one active oil well producing a little over a barrel of oil a day, and is very near to exhaustion, with only 343,000 recoverable barrels of oil remaining throughout its 2,515-acre (10.18 km2) extent according to the official California State Department of Conservation estimate. As of 2010, the only active operator was Longview Production Company.