
A cam is a rotating or sliding piece in a mechanical linkage used especially in transforming rotary motion into linear motion. It is often a part of a rotating wheel or shaft that strikes a lever at one or more points on its circular path. The cam can be a simple tooth, as is used to deliver pulses of power to a steam hammer, for example, or an eccentric disc or other shape that produces a smooth reciprocating motion in the follower, which is a lever making contact with the cam. A cam timer is similar, and were widely used for electric machine control before the advent of inexpensive electronics, microcontrollers, integrated circuits, programmable logic controllers and digital control.

A lathe is a machine tool that rotates a workpiece about an axis of rotation to perform various operations such as cutting, sanding, knurling, drilling, deformation, facing, threading and turning, with tools that are applied to the workpiece to create an object with symmetry about that axis.

Metalworking is the process of shaping and reshaping metals in order to create useful objects, parts, assemblies, and large scale structures. As a term, it covers a wide and diverse range of processes, skills, and tools for producing objects on every scale: from huge ships, buildings, and bridges, down to precise engine parts and delicate jewelry.

Engine turning is a form of ornamental turning. The finishing technique may use lathes or engines to produce a pattern. Aluminium is often the metal chosen to decorate. The technique has been used in various industries, including aircraft and document verification.

Guilloché, or guilloche, is a decorative technique in which a very precise, intricate and repetitive pattern is mechanically engraved into an underlying material via engine turning, which uses a machine of the same name. Engine turning machines may include the rose engine lathe and also the straight-line engine. This mechanical technique improved on more time-consuming designs achieved by hand and allowed for greater delicacy, precision, and closeness of line, as well as greater speed.

Woodturning is the craft of using a wood lathe with hand-held tools to cut a shape that is symmetrical around the axis of rotation. Like the potter's wheel, the wood lathe is a mechanism that can generate a variety of forms. The operator is known as a turner, and the skills needed to use the tools were traditionally known as turnery. In pre-industrial England, these skills were sufficiently difficult to be known as "the mysteries of the turners' guild." The skills to use the tools by hand, without a fixed point of contact with the wood, distinguish woodturning and the wood lathe from the machinist's lathe, or metal-working lathe.

Turning is a machining process in which a cutting tool, typically a non-rotary tool bit, describes a helix toolpath by moving more or less linearly while the workpiece rotates.

A vesta case, or simply a “vesta”, is a small box made to house wax, or "strike anywhere", matches. The first successful friction match appeared in 1826, and in 1832 William Newton patented the "wax vesta" in England. It consisted of a wax stem with embedded cotton threads and a tip of phosphorus. Newton named his matches after Vesta, the Roman goddess of fire and the hearth. Small containers to house these friction matches were introduced shortly afterwards, to guard against accidental combustion. In England these containers took their name from the term Newton used for his invention, and they became known as "vesta cases", "vesta boxes" or simply "vestas". In America the more prosaic yet more descriptive term match safe was chosen.

A geometric lathe was used for making ornamental patterns on the plates used in printing bank notes and postage stamps. It is sometimes called a guilloché lathe.

In machining, a metal lathe or metalworking lathe is a large class of lathes designed for precisely machining relatively hard materials. They were originally designed to machine metals; however, with the advent of plastics and other materials, and with their inherent versatility, they are used in a wide range of applications, and a broad range of materials. In machining jargon, where the larger context is already understood, they are usually simply called lathes, or else referred to by more-specific subtype names. These rigid machine tools remove material from a rotating workpiece via the movements of various cutting tools, such as tool bits and drill bits.

Basse-taille (bahss-tah-ee) is an enamelling technique in which the artist creates a low-relief pattern in metal, usually silver or gold, by engraving or chasing. The entire pattern is created in such a way that its highest point is lower than the surrounding metal. A translucent enamel is then applied to the metal, allowing light to reflect from the relief and creating an artistic effect. It was used in the late Middle Ages, and then again in the 17th century.

The Imperial Coronation egg is a jewelled Fabergé egg made under the supervision of the Russian jeweller Peter Carl Fabergé in 1897 by Fabergé ateliers, Mikhail Perkhin and Henrik Wigstrom. The egg was made to commemorate Tsarina, Empress Alexandra Fyodorovna.
Theo Fabergé was a grandson of Peter Carl Fabergé. His father Nicholas Fabergé, Carl's youngest son, arrived in London in 1906 to help run the only branch of the House of Fabergé outside Russia, on Dover Street in London. After 1917, Nicholas remained in London, and in 1922, his son Theo was born.

Dipped ware is the period term used by potters in late 18th- and 19th-century British potteries for utilitarian earthenware vessels turned on horizontal lathes and decorated with coloured slip; they are thus a type of slipware. The earliest examples have either variegated surfaces or geometric patterns created with the use of a rose and crown engine-turning lathe. By the 1790s mocha decoration began to be used, consisting of dendritic (branching) patterns formed by the reaction of the introduction of an acidic coloring agent to the alkalinity of the wet slip surface. Further decorative motifs were developed in the early 19th century, including common cable, called "earthworm" by collectors, as well as "cat's eyes", "dipped fan", and "twig", all collector terms as no surviving period documents have revealed the terminology used by the manufacturers for such motifs. Much of the factory output was intended for export, with large quantities shipped to North America where bowls, mugs, jugs, and other useful forms were used in households and taverns.
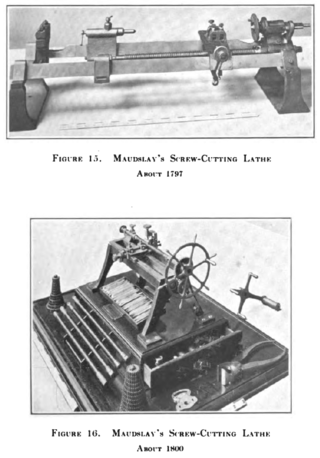
A screw-cutting lathe is a machine capable of cutting very accurate screw threads via single-point screw-cutting, which is the process of guiding the linear motion of the tool bit in a precisely known ratio to the rotating motion of the workpiece. This is accomplished by gearing the leadscrew to the spindle with a certain gear ratio for each thread pitch. Every degree of spindle rotation is matched by a certain distance of linear tool travel, depending on the desired thread pitch.
Ornamental turning is a type of turning, a craft that involves cutting of a work mounted in a lathe. The work can be made of any material that is suitable for being cut in this way, such as wood, bone, ivory or metal. Plain turning is work executed on a lathe where a transverse section through any part of the work comprises a plain circle. Ornamental turning, also called Complex turning, is executed on a lathe with attachments which convert that plain circular section to variants of outline; these range from a simple series of cuts taken at intervals around the work to non-circular movements whereby the whole of the circular shape is removed to give a completely different form. Such shapes are achieved by various means, the principal ones being:
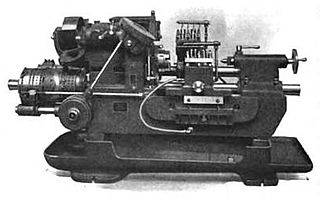
In metalworking and woodworking, an automatic lathe is a lathe with an automatically controlled cutting process. Automatic lathes were first developed in the 1870s and were mechanically controlled. From the advent of NC and CNC in the 1950s, the term automatic lathe has generally been used for only mechanically controlled lathes, although some manufacturers market Swiss-type CNC lathes as 'automatic'.

The copying lathe or duplicating lathe is a lathe that creates shapes identical to the specified pattern.
A straight line engine turning machine is a machine used for engraving decorative patterns on a surface. The engraving may be referred to as Guilloché, which also encompasses patterns created with the rose engine lathe. Where the rose engine is based on a lathe, the straight line engine has more in common with a metal planer machine.
















