
Georgetown is a historic neighborhood and commercial district in Northwest Washington, D.C., situated along the Potomac River. Founded in 1751 as part of the colonial-era Province of Maryland, Georgetown predated the establishment of Washington, D.C. by 40 years. Georgetown was an independent municipality until 1871 when the United States Congress created a new consolidated government for the entire District of Columbia. A separate act, passed in 1895, repealed Georgetown's remaining local ordinances and renamed Georgetown's streets to conform with those in Washington, D.C.

Northwest is the northwestern quadrant of Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States, and is located north of the National Mall and west of North Capitol Street. It is the largest of the four quadrants of the city, and it includes the central business district, the Federal Triangle, and the museums along the northern side of the National Mall, as well as many of the District's historic neighborhoods.

The George Washington Memorial Parkway, colloquially the G.W. Parkway, is a 25-mile-long (40 km) limited-access parkway that runs along the south bank of the Potomac River from Mount Vernon, Virginia, northwest to McLean, Virginia, and is maintained by the National Park Service (NPS). It is located almost entirely in Northern Virginia, except for a short portion of the parkway northwest of the Arlington Memorial Bridge that passes over Columbia Island in Washington, D.C.
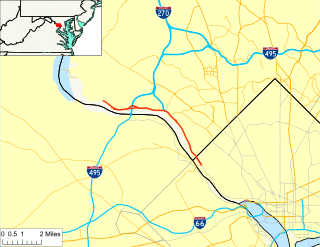
The Clara Barton Parkway is a parkway in the U.S. state of Maryland and the District of Columbia. The highway runs 6.8 miles (10.9 km) from MacArthur Boulevard in Carderock, Maryland, east to Canal Road at the Chain Bridge in Washington. The Clara Barton Parkway is a two- to four-lane parkway that parallels the Potomac River and the Chesapeake and Ohio Canal (C&O) in southwestern Montgomery County, Maryland, and the far western corner of Washington. The parkway provides access to the communities of Cabin John and Glen Echo and several units of the Chesapeake and Ohio Canal National Historical Park. The Maryland portion of the George Washington Memorial Parkway was constructed from Carderock past Interstate 495 (I-495) to Glen Echo in the early to mid-1960s. The parkway was proposed to continue west to Great Falls and east to Georgetown. However, these proposals never came to fruition and the parkway was extended only to the Chain Bridge in the early 1970s. The Maryland portion of the George Washington Memorial Parkway was renamed in 1989 for Clara Barton, the founder of the American Red Cross, and whose original headquarters is located in Glen Echo.

The Washington Aqueduct is an aqueduct that provides the public water supply system serving Washington, D.C., and parts of its suburbs, using water from the Potomac River. One of the first major aqueduct projects in the United States, it was commissioned by the U.S. Congress in 1852, and construction began in 1853 under the supervision of Montgomery C. Meigs and the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. Portions of the aqueduct went online on January 3, 1859, and the full pipeline began operating in 1864.

The Three Sisters are three rocky islands in the Potomac River in Washington, D.C., west of the Key Bridge. A notable landmark in colonial times, the islets are less well known as the Three Sisters Islands and Three Sisters Island.
Dalecarlia Reservoir is the primary storage basin for drinking water in Washington, D.C., and Arlington County, Virginia. The reservoir is fed by an underground aqueduct in turn fed by low dams which divert portions of the Potomac River near Great Falls and Little Falls. The reservoir is located between Spring Valley and the Palisades, two neighborhoods in Northwest Washington, D.C., and Brookmont, a neighborhood in Montgomery County, Maryland.

Streetcars in Washington, D.C. transported people across the city and region from 1862 until 1962.

The Capital Crescent Trail (CCT) is a 7.04-mile (11.33 km), shared-use rail trail that runs from Georgetown in Washington, D.C., to Bethesda, Maryland. An extension of the trail from Bethesda to Silver Spring along a route formerly known as the Georgetown Branch Trail is being built as part of the Purple Line light rail project.

Barney Circle is a small residential neighborhood located between the west bank of the Anacostia River and the eastern edge of Capitol Hill in southeast Washington, D.C., in the United States. The neighborhood is characterized by its sense of community, activism, walkability, and historic feel. The neighborhood's name derives from the eponymous former traffic circle Pennsylvania Avenue SE just before it crosses the John Philip Sousa Bridge over the Anacostia. The traffic circle is named for Commodore Joshua Barney, Commander of the Chesapeake Bay Flotilla in the War of 1812.

Streetcars and interurbans operated in the Maryland suburbs of Washington, D.C., between 1890 and 1962.
Potomac Heights is a neighborhood in Northwest Washington, D.C., overlooking the Potomac River from MacArthur Boulevard westward. Potomac Heights is the part of the Palisades bounded to the north by Loughboro Road and to the south by Chain Bridge and Arizona Avenue NW. It is part of Advisory Neighborhood Commission 3D in Ward 3, the far northwest corner of the Northwest Quadrant just north of Georgetown.

Kent is a neighborhood in Northwest Washington, D.C. in the United States, bounded by Loughboro Road to the north, MacArthur Boulevard to the southwest, and Chain Bridge Road and Battery Kemble Park to the southeast. It is a suburban neighborhood, home to some of the most expensive homes in the city with an average home sales price in 2012 of $1.7 million.

U.S. Route 29 (US 29) enters Washington, D.C., via the Key Bridge from Arlington County, Virginia, and exits at Silver Spring, Maryland. It predominantly follows city surface streets, although the portion of the route from the Key Bridge east to 26th Street Northwest is an elevated highway better known as the Whitehurst Freeway. The freeway, called the city's most ridiculed bridge in 1989, has survived several proposals for its demolition.

The Washington Railway and Electric Company (WRECo) was the larger of the two major streetcar companies in Washington, D.C., and its Maryland suburbs in the early decades of the 20th century.

Little Falls Branch, a 3.8-mile-long (6.1 km) tributary stream of the Potomac River, is located in Montgomery County, Maryland. In the 19th century, the stream was also called Powder Mill Branch. It drains portions of Bethesda, Somerset, Friendship Heights, and Washington, D.C., flows under the Chesapeake and Ohio Canal (C&O), and empties into the Potomac at Little Falls rapids, which marks the upper end of the tidal Potomac.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the District of Columbia:

Battery Kemble Park is a park in Northwest Washington D.C., administered by the National Park Service.
MacArthur Boulevard is a road in Montgomery County, Maryland, and Washington, D.C. The road follows a northwest–southeast route from the Great Falls area of the Chesapeake and Ohio Canal National Historical Park in Potomac, Maryland, to Foxhall Road NW and 44th Street NW in the Foxhall neighborhood of Washington, D.C., near the Georgetown Reservoir. MacArthur Boulevard runs parallel to the Clara Barton Parkway and the C&O Canal for most of its route, passing through the Palisades area of the District. In Cabin John, traffic is reduced to a single alternating lane as it passes over the Union Arch Bridge, the longest span masonry arch bridge in the Western Hemisphere, and which also carries the Washington Aqueduct.
A trio of streetcar companies provided service along a single 10-mile line from the Washington, D.C., neighborhood of Georgetown northward and ultimately to Rockville, Maryland, in the early decades of the 20th century.




















