
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and queer (LGBTQ) movements are social movements that advocate for LGBTQ people in society. Although there is not a primary or an overarching central organization that represents all LGBTQ people and their interests, numerous LGBTQ rights organizations are active worldwide. The first organization to promote LGBTQ rights was the Scientific-Humanitarian Committee, founded in 1897 in Berlin.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) people in South Africa have the same legal rights as non-LGBTQ people. South Africa has a complex and diverse history regarding the human rights of LGBTQ people. The legal and social status of between 400,000 to over 2 million lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and intersex South Africans has been influenced by a combination of traditional South African morals, colonialism, and the lingering effects of apartheid and the human rights movement that contributed to its abolition.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) people in Jamaica face legal and social issues not experienced by heterosexual and gender-conforming people. Consensual sexual intercourse between same-sex partners is legally punishable by up to 10 years of imprisonment in the country.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people living in Lebanon face discrimination and legal difficulties not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Various courts have ruled that Article 534 of the Lebanese Penal Code, which prohibits having sexual relations that "contradict the laws of nature", should not be used to arrest LGBT people. Nonetheless, the law is still being used to harass and persecute LGBT people through occasional police arrests, in which detainees are sometimes subject to intrusive physical examinations.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) people in Botswana face legal issues not experienced by non-LGBTQ citizens. Both female and male same-sex sexual acts have been legal in Botswana since 11 June 2019 after a unanimous ruling by the High Court of Botswana. Despite an appeal by the government, the ruling was upheld by the Botswana Court of Appeal on 29 November 2021.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) people in Bhutan face legal challenges that are not faced by non-LGBTQ people. Bhutan does not provide any anti-discrimination laws for LGBT people, and same-sex unions are not recognised. However, same-sex sexual activity was decriminalised in Bhutan on 17 February 2021.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Myanmar face severe challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Same-sex sexual activity is illegal and section 377 of Myanmar's Penal Code 1861, enacted in 1886, subjects same-sex sexual acts to a term of imprisonment of up to 20 years in prison. Transgender people are subject to police harassment and sexual assault, and their gender identity is not recognized by the state. During the country's long military dictatorship under the authoritarian State Peace and Development Council between 1988 and 2011, it was difficult to obtain accurate information about the legal or social status of LGBT Burmese citizens. Following the 2011–2015 Myanmar political reforms, improvements in media and civil freedoms have allowed LGBTQ people to gain more visibility and support in the country. Despite the 2015 electoral victory of the National League for Democracy, which promised improved human rights and whose leader Aung San Suu Kyi had once called for the decriminalisation of homosexuality, there have been no changes to anti-LGBT laws. Nevertheless, LGBT activists have noted a growing climate of societal acceptance and tolerance toward LGBT people, in line with worldwide trends.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) people in Eswatini have limited legal rights. According to Rock of Hope, a Swati LGBTQ advocacy group, "there is no legislation recognising LGBTIs or protecting the right to a non-heterosexual orientation and gender identity and as a result [LGBTQ people] cannot be open about their orientation or gender identity for fear of rejection and discrimination." Homosexuality is illegal in Eswatini, though this law is in practice unenforced. According to the 2021 Human Rights Practices Report from the US Department of State, "there has never been an arrest or prosecution for consensual same-sex conduct."

Uganda's lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) rights record is considered one of the world's worst. Same-sex sexual activity is illegal for both men and women in Uganda. It was originally criminalised by British colonial laws introduced when Uganda became a British protectorate, and these laws have been retained since the country gained its independence.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) rights in Namibia have expanded in the 21st century, although LGBTQ people still have limited legal protections. Namibia's colonial-era laws criminalising male homosexuality were historically unenforced, and were overturned by the country's High Court in 2024.
This is a list of notable events in the history of LGBT rights that took place in the 1970s.
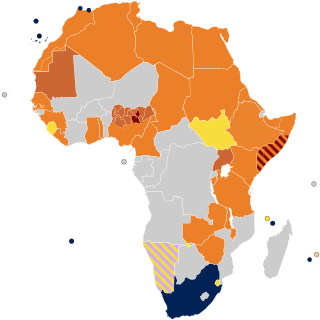
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) rights in Africa are generally poor in comparison to the Americas, Western Europe, and Oceania.

The Lesbian and Gay Equality Project (LGEP), formerly known as the National Coalition for Gay and Lesbian Equality (NCGLE), is a non-profit, non-governmental organization in South Africa that focuses on the expansion of LGBT civil rights in South Africa and other countries in sub-Saharan Africa. It was co-founded by Zackie Achmat in 1994, and successfully lobbied for the inclusion of sexual orientation as a basis for non-discrimination laws in the country after the end of the apartheid period. The organization has continued to operate after South Africa officially legalized same-sex marriage in 2005. Its work includes "law reform, lobbying, litigation, advocacy, employment equity, leadership training and development."

A sodomy law is a law that defines certain sexual acts as crimes. The precise sexual acts meant by the term sodomy are rarely spelled out in the law, but are typically understood and defined by many courts and jurisdictions to include any or all forms of sexual acts that are illegal, illicit, unlawful, unnatural and immoral. Sodomy typically includes anal sex, oral sex, manual sex, and bestiality. In practice, sodomy laws have rarely been enforced to target against sexual activities between individuals of the opposite sex, and have mostly been used to target against sexual activities between individuals of the same sex.
The history of LGBT residents in California, which includes centuries prior to the 20th, has become increasingly visible recently with the successes of the LGBT rights movement. In spite of the strong development of early LGBT villages in the state, pro-LGBT activists in California have campaigned against nearly 170 years of especially harsh prosecutions and punishments toward gays, lesbians, bisexuals, and transgender people.

LGBTQ history in the United States consists of the contributions and struggles of lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and queer (LGBTQ) people, as well as the LGBTQ social movements they have built.

The majority of the countries of the Commonwealth of Nations, formerly known as the British Commonwealth, still criminalise sexual acts between consenting adults of the same sex and other forms of sexual orientation, gender identity and expression. Homosexual activity remains a criminal offence in 29 of the 56 sovereign states of the Commonwealth; and legal in only 27.
This is a timeline of notable events in the history of lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender people in South Africa.

The following is a timeline of lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) history in the 20th century.

The following is a timeline of lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and queer (LGBTQ) history in the 21st century.















