
1756 (MDCCLVI) was a leap year starting on Thursday of the Gregorian calendar and a leap year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar, the 1756th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 756th year of the 2nd millennium, the 56th year of the 18th century, and the 7th year of the 1750s decade. As of the start of 1756, the Gregorian calendar was 11 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which remained in localized use until 1923.

1742 (MDCCXLII) was a common year starting on Monday of the Gregorian calendar and a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar, the 1742nd year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 742nd year of the 2nd millennium, the 42nd year of the 18th century, and the 3rd year of the 1740s decade. As of the start of 1742, the Gregorian calendar was 11 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which remained in localized use until 1923.

The 1740s decade ran from January 1, 1740, to December 31, 1749. Many events during this decade sparked an impetus for the Age of Reason. Military and technological advances brought one of the first instances of a truly global war to take place here, when Maria Theresa of Austria’s struggle to succeed the various crowns of her father King Charles VI led to a war involving nearly all European states in the War of the Austrian Succession, eventually spilling over to North America with the War of Jenkins’ Ear. Capitalism grew robust following the fallout of the South Sea bubble two decades and the subsequent reign of Sir Robert Walpole, whose rule ended in the earlier half of this decade.

1728 (MDCCXXVIII) was a leap year starting on Thursday of the Gregorian calendar and a leap year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar, the 1728th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 728th year of the 2nd millennium, the 28th year of the 18th century, and the 9th year of the 1720s decade. As of the start of 1728, the Gregorian calendar was 11 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which remained in localized use until 1923.

1765 (MDCCLXV) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Gregorian calendar and a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar, the 1765th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 765th year of the 2nd millennium, the 65th year of the 18th century, and the 6th year of the 1760s decade. As of the start of 1765, the Gregorian calendar was 11 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which remained in localized use until 1923.

1720 (MDCCXX) was a leap year starting on Monday of the Gregorian calendar and a leap year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar, the 1720th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 720th year of the 2nd millennium, the 20th year of the 18th century, and the 1st year of the 1720s decade. As of the start of 1720, the Gregorian calendar was 11 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which remained in localized use until 1923.

1813 (MDCCCXIII) was a common year starting on Friday of the Gregorian calendar and a common year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar, the 1813th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 813th year of the 2nd millennium, the 13th year of the 19th century, and the 4th year of the 1810s decade. As of the start of 1813, the Gregorian calendar was 12 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which remained in localized use until 1923.
1762 (MDCCLXII) was a common year starting on Friday of the Gregorian calendar and a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar, the 1762nd year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 762nd year of the 2nd millennium, the 62nd year of the 18th century, and the 3rd year of the 1760s decade. As of the start of 1762, the Gregorian calendar was 11 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which remained in localized use until 1923.

1763 (MDCCLXIII) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Gregorian calendar and a common year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar, the 1763rd year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 763rd year of the 2nd millennium, the 63rd year of the 18th century, and the 4th year of the 1760s decade. As of the start of 1763, the Gregorian calendar was 11 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which remained in localized use until 1923.

1745 (MDCCXLV) was a common year starting on Friday of the Gregorian calendar and a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar, the 1745th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 745th year of the 2nd millennium, the 45th year of the 18th century, and the 6th year of the 1740s decade. As of the start of 1745, the Gregorian calendar was 11 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which remained in localized use until 1923.

1741 (MDCCXLI) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Gregorian calendar and a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar, the 1741st year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 741st year of the 2nd millennium, the 41st year of the 18th century, and the 2nd year of the 1740s decade. As of the start of 1741, the Gregorian calendar was 11 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which remained in localized use until 1923.

1740 (MDCCXL) was a leap year starting on Friday of the Gregorian calendar and a leap year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar, the 1740th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 740th year of the 2nd millennium, the 40th year of the 18th century, and the 1st year of the 1740s decade. As of the start of 1740, the Gregorian calendar was 11 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which remained in localized use until 1923.

1738 (MDCCXXXVIII) was a common year starting on Wednesday of the Gregorian calendar and a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar, the 1738th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 738th year of the 2nd millennium, the 38th year of the 18th century, and the 9th year of the 1730s decade. As of the start of 1738, the Gregorian calendar was 11 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which remained in localized use until 1923.

1731 (MDCCXXXI) was a common year starting on Monday of the Gregorian calendar and a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar, the 1731st year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 731st year of the 2nd millennium, the 31st year of the 18th century, and the 2nd year of the 1730s decade. As of the start of 1731, the Gregorian calendar was 11 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which remained in localized use until 1923.
1727 (MDCCXXVII) was a common year starting on Wednesday of the Gregorian calendar and a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar, the 1727th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 727th year of the 2nd millennium, the 27th year of the 18th century, and the 8th year of the 1720s decade. As of the start of 1727, the Gregorian calendar was 11 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which remained in localized use until 1923.
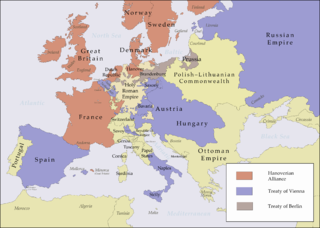
1725 (MDCCXXV) was a common year starting on Monday of the Gregorian calendar and a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar, the 1725th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 725th year of the 2nd millennium, the 25th year of the 18th century, and the 6th year of the 1720s decade. As of the start of 1725, the Gregorian calendar was 11 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which remained in localized use until 1923.

1714 (MDCCXIV) was a common year starting on Monday of the Gregorian calendar and a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar, the 1714th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 714th year of the 2nd millennium, the 14th year of the 18th century, and the 5th year of the 1710s decade. As of the start of 1714, the Gregorian calendar was 11 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which remained in localized use until 1923.

1717 (MDCCXVII) was a common year starting on Friday of the Gregorian calendar and a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar, the 1717th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 717th year of the 2nd millennium, the 17th year of the 18th century, and the 8th year of the 1710s decade. As of the start of 1717, the Gregorian calendar was 11 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which remained in localized use until 1923.

1701 (MDCCI) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Gregorian calendar and a common year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar, the 1701st year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 701st year of the 2nd millennium, the 1st year of the 18th century, and the 2nd year of the 1700s decade. As of the start of 1701, the Gregorian calendar was 11 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which remained in localized use until 1923.

The War of the Austrian Succession was a European conflict fought between 1740 and 1748, primarily in Central Europe, the Austrian Netherlands, Italy, the Atlantic Ocean and Mediterranean Sea. Related conflicts include King George's War in North America, the War of Jenkins' Ear, the First Carnatic War, and the First and Second Silesian Wars.























