The Thermoprotei is a class of the Crenarchaeota.
The Thermodesulfobacteria are a phylum of thermophilic sulfate-reducing bacteria.

Archaeoglobaceae are a family of the Archaeoglobales. All known genera within the Archaeoglobaceae are hyperthermophilic and can be found near undersea hydrothermal vents. Archaeoglobaceae are the only family in the order Archaeoglobales, which is the only order in the class Archaeoglobi.
Rubrobacter is a genus of Actinobacteria, given its own subclass (Rubrobacteridae). It is radiotolerant and may rival Deinococcus radiodurans in this regard.
The Halanaerobiales are an order of bacteria placed within the class Clostridia, and encompassing two families, the Halanaerobiaceae and the Halobacteroidaceae. Originally placed within the highly polyphyletic class Clostridia, according to the NCBI and LPSN, it is now thought to lie outside the Firmicutes. Halanaerobiales are halophilic obligate anaerobes with a fermentative or homoacetogenic metabolism.
The Thermoanaerobacterales is a polyphyletic order of bacteria placed within the polyphyletic class Clostridia, and encompassing four families: the Thermoanaerobacteraceae, the Thermodesulfobiaceae, the Thermoanaerobacterales Family III. Incertae Sedis, and the Thermoanaerobacterales Family IV. Incertae Sedis, and various unplaced genera.
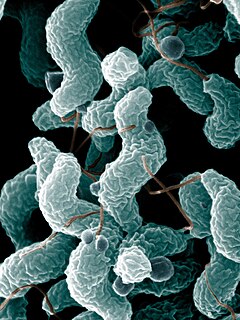
Epsilonproteobacteria are a class of Proteobacteria. All species of this class are, like all Proteobacteria, Gram-negative.

Alphaproteobacteria is a class of bacteria in the phylum Proteobacteria. Its members are highly diverse and possess few commonalities, but nevertheless share a common ancestor. Like all Proteobacteria, its members are gram-negative and some of its intracellular parasitic members lack peptidoglycan and are consequently gram variable.

In the taxonomy of microorganisms, the Methanomicrobia are a class of the Euryarchaeota.
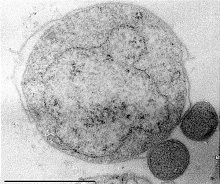
In taxonomy, the Desulfurococcaceae are a family of the disc-shaped anaerobic microorganisms belonging to the order Desulfurococcales, in the domain Archaea. Members of this family are distinguished from the other family (Pyrodictiaceae) in the order Desulfurococcales by having an optimal growth temperature below 100 °C, rather than above 100 °C, and by being more diverse. Several genera of the family have been identified.
In taxonomy, the Methanobacteriaceae are a family of the Methanobacteriales.
The Pyrodictiaceae are a family of disc-shaped anaerobic microorganisms belonging to the order Desulfurococcales, in the domain Archaea. Members of this family are distinguished from the other family (Desulfurococcaceae) in the order Desulfurococcales by having an optimal growth temperature above 100 °C, rather than below 100 °C.
Caldicellulosiruptor is a genus of thermophilic, anaerobic, Gram-positive, non-spore forming bacteria. Originally placed within the highly polyphyletic class Clostridia, order Thermoanaerobacterales and family Thermoanaerobacterales Family III according to the NCBI and LPSN, it is now thought to lie outside of the Firmicutes. Caldicellulosiruptor is known to degrade and ferment complex carbohydrates from plant matter, such as cellulose and hemicellulose, and certain species in the genus have been identified as potential candidates for biofuel production.
Pectinatus is a genus of Firmicutes bacteria classified within the class Negativicutes.
Megamonas is a genus of Firmicutes bacteria classified within the class Negativicutes.
Dialister is a genus of Firmicutes bacteria classified within the class Negativicutes.
The family Thermodesulfobiaceae according to the LPSN is located within the order Thermoanaerobacterales and class Clostridia. However, according to the All-Species Living Tree Project it lies outside the clade Firmicutes and the genus Caldanaerovirga does not belong to the clade, i.e. Thermodesulfobiaceae is polyphyletic.
The Thermaerobacter are an unassigned genus of bacteria placed within the class clostridia. Originally placed within the highly polyphyletic class Clostridia, order Clostridiales and family Clostridiales Family XVII. Incertae Sedis, according to the NCBI and LPSN, it is now thought to lie outside of the Firmicutes.

The Thermoanaerobacteraceae is a highly polyphyletic family of bacteria placed within the class clostridia. Originally placed within the highly polyphyletic class Clostridia and order Thermoanaerobacterales, according to the NCBI and LPSN, it is now thought to be a basal clade of the phylum Firmicutes.
Pelosinus is a genus of Firmicutes bacteria classified within the class Negativicutes.






