Haemophilia A is a blood clotting disorder caused by a genetic deficiency in clotting factor VIII, thereby resulting in significant susceptibility to bleeding, both internally and externally. This condition occurs almost exclusively in males born to carrier mothers due to X-linked recessive inheritance. Nevertheless, rare isolated cases do emerge from de novo (spontaneous) mutations.

Haemophilia B, also spelled hemophilia B, is a blood clotting disorder causing easy bruising and bleeding due to an inherited mutation of the gene for factor IX, and resulting in a deficiency of factor IX. It is less common than factor VIII deficiency.

Von Willebrand disease (VWD) is the most common hereditary blood-clotting disorder in humans. An acquired form can sometimes result from other medical conditions. It arises from a deficiency in the quality or quantity of von Willebrand factor (VWF), a multimeric protein that is required for platelet adhesion. It is known to affect several breeds of dogs as well as humans. The three forms of VWD are hereditary, acquired, and pseudo or platelet type. The three types of hereditary VWD are VWD type 1, VWD type 2, and VWD type 3. Type 2 contains various subtypes. Platelet type VWD is also an inherited condition.

Haemophilia C (also known as plasma thromboplastin antecedent deficiency or Rosenthal syndrome) is a mild form of haemophilia affecting both sexes, due to factor XI deficiency. It predominantly occurs in Ashkenazi Jews. It is the fourth most common coagulation disorder after von Willebrand's disease and haemophilia A and B. In the United States, it is thought to affect 1 in 100,000 of the adult population, making it 10% as common as haemophilia A.

Coagulation factor VIII is an essential blood clotting protein. In humans, it is encoded by F8 gene. Defects in this gene result in hemophilia A, an X-linked bleeding disorder.

In medicine (hematology), bleeding diathesis is an unusual susceptibility to bleed (hemorrhage) mostly due to hypocoagulability, in turn caused by a coagulopathy. Therefore, this may result in the reduction of platelets being produced and leads to excessive bleeding. Several types of coagulopathy are distinguished, ranging from mild to lethal. Coagulopathy can be caused by thinning of the skin, such that the skin is weakened and is bruised easily and frequently without any trauma or injury to the body. Also, coagulopathy can be contributed by impaired wound healing or impaired clot formation.

Factor IX, also known as Christmas factor, is one of the serine proteases involved in coagulation; it belongs to peptidase family S1. Deficiency of this protein causes haemophilia B.

Coagulopathy is a condition in which the blood's ability to coagulate is impaired. This condition can cause a tendency toward prolonged or excessive bleeding, which may occur spontaneously or following an injury or medical and dental procedures.
Congenital afibrinogenemia is a rare, genetically inherited blood fibrinogen disorder in which the blood does not clot normally due to the lack of fibrinogen, a blood protein necessary for coagulation. This disorder is autosomal recessive, meaning that two unaffected parents can have a child with the disorder. The lack of fibrinogen expresses itself with excessive and, at times, uncontrollable bleeding.

Factor VII deficiency is a bleeding disorder characterized by a lack in the production of Factor VII (FVII) (proconvertin), a protein that causes blood to clot in the coagulation cascade. After a trauma factor VII initiates the process of coagulation in conjunction with tissue factor in the extrinsic pathway.
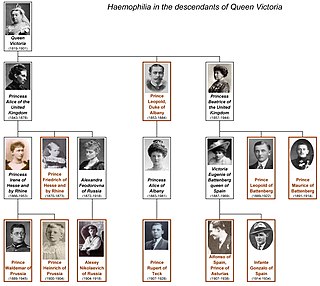
Haemophilia figured prominently in the history of European royalty in the 19th and 20th centuries. Queen Victoria and her husband, Prince Albert, of the United Kingdom, through two of their five daughters – Princess Alice and Princess Beatrice – passed the mutation to various royal houses across the continent, including the royal families of Spain, Germany, and Russia. Victoria's youngest son, Prince Leopold, Duke of Albany, also had the disease, though none of her three elder sons did. Tests on the remains of the Romanov imperial family show that the specific form of haemophilia passed down by Queen Victoria was probably the relatively rare haemophilia B. The presence of haemophilia B within the European royal families was well-known, with the condition once popularly known as "the royal disease".
The dysfibrinogenemias consist of three types of fibrinogen disorders in which a critical blood clotting factor, fibrinogen, circulates at normal levels but is dysfunctional. Congenital dysfibrinogenemia is an inherited disorder in which one of the parental genes produces an abnormal fibrinogen. This fibrinogen interferes with normal blood clotting and/or lysis of blood clots. The condition therefore may cause pathological bleeding and/or thrombosis. Acquired dysfibrinogenemia is a non-hereditary disorder in which fibrinogen is dysfunctional due to the presence of liver disease, autoimmune disease, a plasma cell dyscrasias, or certain cancers. It is associated primarily with pathological bleeding. Hereditary fibrinogen Aα-Chain amyloidosis is a sub-category of congenital dysfibrinogenemia in which the dysfunctional fibrinogen does not cause bleeding or thrombosis but rather gradually accumulates in, and disrupts the function of, the kidney.
An obligate carrier is an individual who may be clinically unaffected but who must carry a gene mutation based on analysis of the family history; usually applies to disorders inherited in an autosomal recessive and X-linked recessive manner.
From the 1970s to the early 1990s, tens of thousands of people were infected with hepatitis C and HIV as a result of receiving infected blood or infected clotting factor products in the United Kingdom. Many of the products were imported from the United States, and distributed to patients by the National Health Service. Most recipients had haemophilia or had received a blood transfusion following childbirth or surgery. It has been estimated that more than 30,000 patients received contaminated blood, resulting in the deaths of at least 3,000 people. In July 2017, Prime Minister Theresa May announced an independent public inquiry into the scandal, for which she was widely praised as successive governments going back to the 1980s had refused such an inquiry. May stated that "the victims and their families who have suffered so much pain and hardship deserve answers as to how this could possibly have happened." The final report was published in seven volumes on 20 May 2024, concluding that the scandal could have been largely avoided, patients were knowingly exposed to "unacceptable risks", and that doctors, the government and NHS tried to cover up what happened by "hiding the truth".
Recombinant factor VIIa (rfVIIa) is a form of blood factor VII that has been manufactured via recombinant technology. It is administered via an injection into a vein. It is used to treat bleeding episodes in people who have acquired haemophilia, among other indications. There are several disimilar forms, and biosimilars for each. All forms are activated.

Jeanne Marie Lusher, M.D. was an American physician, pediatric hematologist/oncologist, and a researcher in the field of bleeding disorders of childhood, and has served as the director of Hemostasis Program at the Children's Hospital of Michigan until her retirement on June 28, 2013.

X-linked thrombocytopenia, also referred to as XLT or thrombocytopenia 1, is an inherited clotting disorder that primarily affects males. It is a WAS-related disorder, meaning it is caused by a mutation in the Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome (WAS) gene, which is located on the short arm of the X chromosome. WAS-related disorders include Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome, XLT, and X-linked congenital neutropenia (XLN). Of the WAS-related disorders, X-linked thrombocytopenia is considered to be the milder phenotype. Between 1 and 10 per million males worldwide are affected with this disorder. Females may be affected with this disorder but this is very rare since females have two X chromosomes and are therefore typically carriers of the mutation.
Factor XII deficiency is a deficiency in the production of factor XII (FXII), a plasma glycoprotein and clotting factor that participates in the coagulation cascade and activates factor XI. FXII appears to be not essential for blood clotting, as individuals with this condition are usually asymptomatic and form blood clots in vivo. FXII deficiency tends to be identified during presurgical laboratory screening for bleeding disorders.
Congenital hypofibrinogenemia is a rare disorder in which one of the three genes responsible for producing fibrinogen, a critical blood clotting factor, is unable to make a functional fibrinogen glycoprotein because of an inherited mutation. In consequence, liver cells, the normal site of fibrinogen production, make small amounts of this critical coagulation protein, blood levels of fibrinogen are low, and individuals with the disorder may develop a coagulopathy, i.e. a diathesis or propensity to experience episodes of abnormal bleeding. However, individuals with congenital hypofibrinogenemia may also have episodes of abnormal blood clot formation, i.e. thrombosis. This seemingly paradoxical propensity to develop thrombosis in a disorder causing a decrease in a critical protein for blood clotting may be due to the function of fibrin to promote the lysis or disintegration of blood clots. Lower levels of fibrin may reduce the lysis of early fibrin strand depositions and thereby allow these depositions to develop into clots.
An X-linked genetic disease is a disease inherited through a genetic defect on the X chromosome. In human cells, there is a pair of non-matching sex chromosomes, labelled X and Y. Females carry two X chromosomes, whereas males have one X and one Y chromosome. A disease or trait determined by a gene on the X chromosome demonstrates X-linked inheritance, which can be divided into dominant and recessive patterns.


















