The Queen Elizabeth Way (QEW) is a 400-series highway in the Canadian province of Ontario linking Toronto with the Niagara Peninsula and Buffalo, New York. The highway begins at the Canada–United States border on the Peace Bridge in Fort Erie and travels 139.1 kilometres (86.4 mi) around the western end of Lake Ontario, ending at Highway 427 as the physical highway continues as the Gardiner Expressway into downtown Toronto. The QEW is one of Ontario's busiest highways, with an average of close to 250,000 vehicles per day on some sections.

King's Highway 3, commonly referred to as Highway 3, is a provincially maintained highway in the Canadian province of Ontario which travels parallel to the northern shoreline of Lake Erie. It has three segments, the first of which travels from the Ambassador Bridge in Windsor to Highway 77 in Leamington. The second portion begins at Talbotville Royal outside of St. Thomas at Highway 4, and travels to the western city limits of Port Colborne. The road is regionally maintained within Port Colborne as Niagara Regional Road 3, but regains its provincial designation at Highway 140. Its third and final terminus is at Edgewood Park, within the Fort Erie town limits. From there, the road continues as Niagara Regional Road 3 to the Peace Bridge, where drivers can cross to the United States. The total length of Highway 3 is 258.2 km (160.4 mi), consisting of 49.2 km (30.6 mi) from Windsor to Leamington, 187.9 km (116.8 mi) from Talbotville Royal to Port Colborne and 21.1 km (13.1 mi) from Port Colborne to Edgewood Park.
A decommissioned highway is a highway that has been removed from service by being shut down, or has had its authorization as a national, provincial or state highway removed, the latter also referred to as downloading. Decommissioning can include the complete or partial demolition or abandonment of an old highway structure because the old roadway has lost its utility, but such is not always the norm. Where the old highway has continuing value, it likely remains as a local road offering access to properties denied access to the new road or for use by slow vehicles such as farm equipment and horse-drawn vehicles denied use of the newer highway.
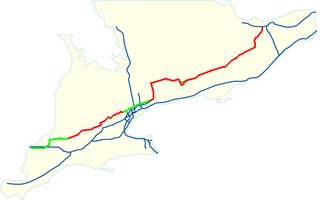
King's Highway 7, commonly referred to as Highway 7 and historically as the Northern Highway, is a provincially maintained highway in the Canadian province of Ontario. At its peak, Highway 7 measured 716 km (445 mi) in length, stretching from Highway 40 east of Sarnia in Southwestern Ontario to Highway 17 west of Ottawa in Eastern Ontario. However, due in part to the construction of Highways 402 and 407, the province transferred the sections of Highway 7 west of London and through the Greater Toronto Area to county and regional jurisdiction. The highway is now 535.7 km (332.9 mi) long; the western segment begins at Highway 4 north of London and extends 154.1 km (95.8 mi) to Georgetown, while the eastern segment begins at Donald Cousens Parkway in Markham and extends 381.6 km (237.1 mi) to Highway 417 in Ottawa.
King's Highway 27, commonly referred to as Highway 27, is a provincially maintained highway in the Canadian province of Ontario. The Ministry of Transportation of Ontario was once responsible for the length of the route, when it ran from Long Branch to Highway 93 in Waverley. Highway 27 followed a mostly straight route throughout its length, as it passed through the suburbs of Toronto, then north of Kleinburg the vast majority of the highway was surrounded by rural farmland. Today, only the southernmost 1.6 km (1 mi) from Highway 427 north to Mimico Creek is under provincial jurisdiction, the remainder of the route is maintained by the city of Toronto, York Region and Simcoe County.

King's Highway 2A, commonly referred to as Highway 2A, was the designation of five separate provincially maintained highways in the Canadian province of Ontario. Highway 2A was an alternate route to Highway 2 in Chatham, London and Cornwall; these routes were all eventually redesignated. Highway 2A was also a highway that extended from Windsor to Tilbury, which was redesignated as Highway 98 in 1938.
King's Highway 20, commonly referred to as Highway 20, is a provincially maintained highway in the Canadian province of Ontario. Presently, it is a short 1.9 km (1.2 mi) stub between Highway 58 and Niagara Regional Road 70 in the City of Thorold, but until 1997 it connected Hamilton to Niagara Falls, serving several towns atop the Niagara Escarpment en route.
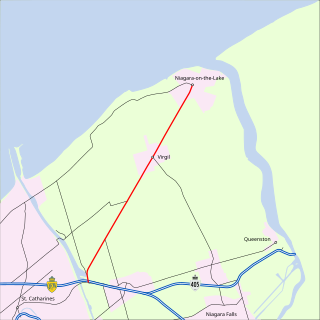
King's Highway 55, commonly referred to as Highway 55 and historically as the Niagara Stone Road and Black Swamp Road, was a provincially maintained highway in the Canadian province of Ontario, which connected the Queen Elizabeth Way (QEW) with Niagara-on-the-Lake, following Niagara Stone Road. The route divided a swath of wineries at the foot of the Niagara Escarpment, passing at an oblique angle to the concession road grid.
King's Highway 28, commonly referred to as Highway 28, is a provincially maintained highway in the Canadian province of Ontario. The southwest–northeast route extends from Highway 7 east of Peterborough, to Highway 41 in Denbigh. The route passes over undulating hills before entering the Canadian Shield near Burleigh Falls, and gradually turns eastward.
King's Highway 62, commonly referred to as Highway 62, is a provincially maintained highway in the Canadian province of Ontario. The highway travels south–north from Highway 33 at Bloomfield in Prince Edward County, through Belleville, Madoc and Bancroft, to Maynooth, where it ends at a junction with Highway 127. Prior to 1997, the route continued north and east of Maynooth through Combermere, Barry's Bay, Killaloe, Round Lake and Bonnechere to Highway 17 in Pembroke. This section of highway was redesignated Hastings Highlands Municipal Road 62, Renfrew County Road 62, and Renfrew County Road 58.
King's Highway 15, commonly referred to as Highway 15, is a provincially maintained highway in the Canadian province of Ontario. It travels north from an interchange with Highway 401 in Kingston to Highway 7 in Carleton Place, a distance of 114.7 kilometres (71.3 mi). In addition to Kingston and Carleton Place, the highway provides access to the Eastern Ontario communities of Joyceville, Seeley's Bay, Morton, Elgin, Crosby, Portland, Lombardy and Franktown. Prior to 1998, Highway 15 continued north from Carleton Place, passed Almonte and through Pakenham, to Highway 17 in Arnprior.
King's Highway 19, commonly referred to as Highway 19, is a provincially maintained highway in the Canadian province of Ontario, connecting Highway 3 in Tillsonburg with Highway 401 southeast of Ingersoll. The highway began as the Plank and Gravel Road, a toll road formed by the Ingersoll and Port Burwell Road Company. It was first assigned in 1930. Several extensions in the early 1930s took the route north to Highway 86 at Tralee. However, a significant amount of Highway 19 was decommissioned and turned over to local and county governments in 1997 and 1998.
King's Highway 169, commonly referred to as Highway 169, was a provincially maintained highway in the Canadian province of Ontario. The highway connected Highway 12 at Brechin, southeast of Orillia, with Highway 69 at Foot's Bay. The 91.40 km (56.79 mi) route included an 18.20 km (11.31 mi) concurrency with Highway 11 between Washago and Gravenhurst. Located within Simcoe County and the District Municipality of Muskoka, the highway also provided access to the community of Bala.
King's Highway 38, commonly referred to as Highway 38, was a provincially maintained highway in the Canadian province of Ontario. The 66.9-kilometre (41.6 mi) road connected Highway 2 and Highway 401 in Kingston with Highway 7 west of Perth. It was designated in 1934 and remained relatively unchanged throughout its existence, aside from some minor diversions and a rerouting through Kingston as a result of the construction of Highway 401 in the mid-1950s. At the beginning of 1998, the entire highway was transferred to the municipalities of Frontenac County through which it travelled: Kingston, South Frontenac and Central Frontenac. Today the former highway is named Road 38 and Gardiners Road, but is still referred to as Highway 38 by locals.
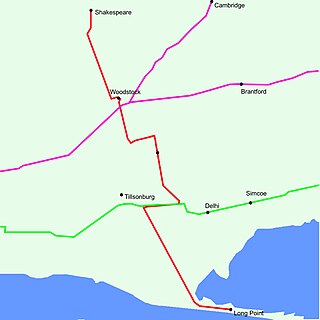
King's Highway 59, commonly referred to as Highway 59, was a provincially maintained highway in the Canadian province of Ontario. It connected Long Point Provincial Park in Norfolk County to the town of Shakespeare in Perth County, passing through the city of Woodstock in Oxford County en route. Several smaller towns also lined the highway, notably Courtland, Delhi, Norwich and Tavistock. Highway 59 featured junctions with Highway 3, Highway 2, Norfolk County Highway 24 and the concurrent routes of Highway 7 and Highway 8. Highway 59 also had an interchange with Highway 401.
King's Highway 36, commonly referred to as Highway 36, was a provincially maintained highway in the Canadian province of Ontario. The highway connected Highway 7 and Highway 35 in Lindsay with Highway 28 in Burleigh Falls, providing access to recreational cottages along the northern shore of several of the Kawartha lakes as well as to multiple communities, including Bobcaygeon. Today it is known as Kawartha Lakes City Road 36 and Peterborough County Road 36.
Highway 7B is the designation for seven former business routes of Highway 7 in the Canadian province of Ontario. All but one was the original route of Highway 7 through the town or city that it served, and was subsequently given the 7B designation when a newer bypass route was constructed to reduce traffic pressure on the urban street network.
King's Highway 25, commonly referred to as Highway 25, was a highway in the Canadian province of Ontario. The north–south route connected several towns on its route northward from Burlington. The first section of Highway 25, designated in 1925, travelled north from Highway 5 to Milton. In 1928, the route was extended south into Burlington, following portions of Lower Middle Road to Highway 2. The highway was extended north to Highway 7 in 1937. That same year, a portion of Highway 25 was made concurrent with The Middle Road, which would be renamed as the Queen Elizabeth Way (QEW) two years later. The route remained relatively unchanged for two decades, save for the southern end being truncated at the QEW in 1946. In 1963 it was extended north to Ospringe to meet Highway 24. Another extension was added in 1974 to bring the route to Highway 89 near Shelburne. The entire route was decommissioned in 1997 and 1998 as part of a province-wide downloading of highways deemed to be of regional importance.
King's Highway 29, commonly referred to as Highway 29, was a provincially maintained highway in the Canadian province of Ontario. The 52.29-kilometre (32.49 mi) route connected Highway 2 in downtown Brockville with Highway 15 south of Smiths Falls. Between those larger settlements, it provided access to the communities of Forthton, Addison, Frankville, Toledo and Newbliss.

Ontario Highway 549, commonly referred to as Highway 549, was a provincially maintained secondary highway in the Canadian province of Ontario. This highway connected former Highway 17 in Whitefish to Lake Panache. The route was assumed along with many other secondary highways in 1956 and remained unchanged until the early 1980s, when it was decommissioned as a provincial highway and transferred to the newly formed Regional Municipality of Sudbury. Today it is known as Greater Sudbury Road 10.










