
Chicano or Chicana is an ethnic identity for Mexican Americans that emerged from the Chicano Movement. Chicano was originally a classist and racist slur used toward low-income Mexicans that was reclaimed in the 1940s among youth who belonged to the Pachuco and Pachuca subculture.
The masculine term Latino, along with its feminine form Latina, is a noun and adjective, often used in English, Spanish, and Portuguese, that most commonly refers to United States inhabitants who have cultural ties to Latin America.

Spanish is the second most spoken language in the United States. Over 43.4 million people aged five or older speak Spanish at home (13.7%). Spanish is also the most learned language other than English, with about 8 million students. Estimates count up to 58.9 million native speakers, heritage language speakers, and second-language speakers. There is an Academy of the Spanish Language located in the United States as well.
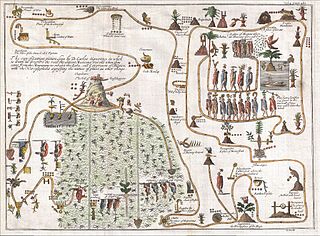
Aztlán is the ancestral home of the Aztec peoples. The word "Aztec" was derived from the Nahuatl aztecah, meaning "people from Aztlán." Aztlán is mentioned in several ethnohistorical sources dating from the colonial period, and while each cites varying lists of the different tribal groups who participated in the migration from Aztlán to central Mexico, the Mexica who later founded Mexico-Tenochtitlan are mentioned in all of the accounts.

M.E.Ch.A. is a US-based organization that seeks to promote Chicano unity and empowerment through political action.

The Plan Espiritual de Aztlán was a pro-indigenist manifesto advocating Chicano nationalism and self-determination for Mexican Americans. It was adopted by the First National Chicano Youth Liberation Conference, a March 1969 convention hosted by Rodolfo Gonzales's Crusade for Justice in Denver, Colorado.

Hispanic and Latino Americans are Americans of full or partial Spanish and/or Latin American background, culture, or family origin. These demographics include all Americans who identify as Hispanic or Latino regardless of race. As of 2020, the Census Bureau estimated that there were almost 65.3 million Hispanics and Latinos living in the United States and its territories.

The Chicano Moratorium, formally known as the National Chicano Moratorium Committee Against The Vietnam War, was a movement of Chicano anti-war activists that built a broad-based coalition of Mexican-American groups to organize opposition to the Vietnam War. Led by activists from local colleges and members of the Brown Berets, a group with roots in the high school student movement that staged walkouts in 1968, the coalition peaked with an August 29, 1970 march in East Los Angeles that drew 30,000 demonstrators. The march was described by scholar Lorena Oropeza as "one of the largest assemblages of Mexican Americans ever." It was the largest anti-war action taken by any single ethnic group in the USA. It was second in size only to the massive U.S. immigration reform protests of 2006.

Rodolfo "Corky" Gonzales was a Mexican-American boxer, poet, political organizer, and activist. He was one of many leaders for the Crusade for Justice in Denver, Colorado. The Crusade for Justice was an urban rights and Chicano cultural urban movement during the 1960s focusing on social, political, and economic justice for Chicanos. Gonzales convened the first-ever Chicano Youth Liberation Conference in 1968, which was poorly attended due to timing and weather conditions. He tried again in March 1969, and established what is commonly known as the First Chicano Youth Liberation Conference. This conference was attended by many future Chicano activists and artists. It also birthed the Plan Espiritual de Aztlán, a pro-indigenist manifesto advocating revolutionary Chicano nationalism and self-determination for all Chicanos. Through the Crusade for Justice, Gonzales organized the Mexican American people of Denver to fight for their cultural, political, and economic rights, leaving his mark on history. He was honored with a Google Doodle in continued celebration of National Hispanic Heritage Month in the United States on October 1, 2021.

Chicanismo emerged as the cultural consciousness behind the Chicano Movement. The central aspect of Chicanismo is the identification of Chicanos with their Indigenous American roots to create an affinity with the notion that they are native to the land rather than immigrants. Chicanismo brought a new sense of nationalism for Chicanos that extended the notion of family to all Chicano people. Barrios, or working-class neighborhoods, became the cultural hubs for the people. It created a symbolic connection to the ancestral ties of Mesoamerica and the Nahuatl language through the situating of Aztlán, the ancestral home of the Aztecs, in the southwestern United States. Chicanismo also rejected Americanization and assimilation as a form of cultural destruction of the Chicano people, fostering notions of Brown Pride. Xicanisma has been referred to as an extension of Chicanismo.
José Angel Gutiérrez, is an attorney and professor at the University of Texas at Arlington in the United States. He was a founding member of the Mexican American Youth Organization (MAYO) in San Antonio in 1967, and a founding member and past president of the Raza Unida Party, a Mexican-American third party movement that supported candidates for elective office in Texas, California, and other areas of the Southwestern and Midwestern United States.

The Chicano Movement, also referred to as El Movimiento, was a social and political movement in the United States that worked to embrace a Chicano/a identity and worldview that combated structural racism, encouraged cultural revitalization, and achieved community empowerment by rejecting assimilation. Chicanos also expressed solidarity and defined their culture through the development of Chicano art during El Movimiento, and stood firm in preserving their religion.
Chicano nationalism is the pro-indigenist ethnic nationalist ideology of Chicanos.

Octaviano Ambrosio Larrazolo Corral was a Republican politician who served as the fourth governor of New Mexico and a United States senator.

The Chicano Art Movement represents groundbreaking movements by Mexican-American artists to establish a unique artistic identity in the United States. Much of the art and the artists creating Chicano Art were heavily influenced by Chicano Movement which began in the 1960s.

The Hispanos of New Mexico, also known as Neomexicanos or Nuevomexicanos, are Hispanic residents originating in the historical region of Santa Fe de Nuevo México, today the US state of New Mexico, southern Colorado, and other parts of the Southwestern United States including Arizona, Nevada, Texas, and Utah. They are descended from Oasisamerica groups and the settlers of the Viceroyalty of New Spain, the First Mexican Empire and Republic, the Centralist Republic of Mexico, and the New Mexico Territory.
This is a Mexican American bibliography. This list consists of books, and journal articles, about Mexican Americans, Chicanos, and their history and culture. The list includes works of literature whose subject matter is significantly about Mexican Americans and the Chicano/a experience. This list does not include works by Mexican American writers which do not address the topic, such as science texts by Mexican American writers.

Mexican-American folklore refers to the tales and history of Chicano people who live in the United States.

A Mexican American is a resident of the United States who is of Mexican descent. Mexican American-related topics include the following:













