Rheumatology is a branch of medicine devoted to the diagnosis and therapy of rheumatic diseases. Physicians who have undergone formal training in rheumatology are called rheumatologists. Rheumatologists deal mainly with immune-mediated disorders of the musculoskeletal system, soft tissues, autoimmune diseases, vasculitides, and heritable connective tissue disorders.

De Quervain syndrome is inflammation of two tendons that control movement of the thumb and their tendon sheath. This results in pain at the outside of the wrist. Pain is typically increased with gripping or rotating the wrist. The thumb may also be difficult to move smoothly. Onset of symptoms is gradual.
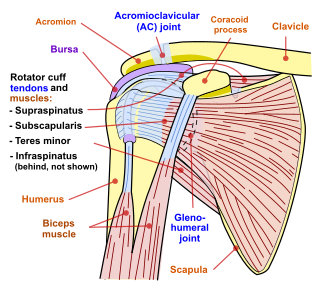
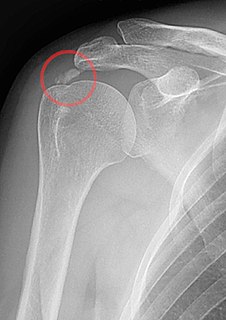
Shoulder problems including pain, are one of the more common reasons for physician visits for musculoskeletal symptoms. The shoulder is the most movable joint in the body. However, it is an unstable joint because of the range of motion allowed. This instability increases the likelihood of joint injury, often leading to a degenerative process in which tissues break down and no longer function well.
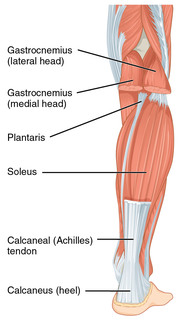
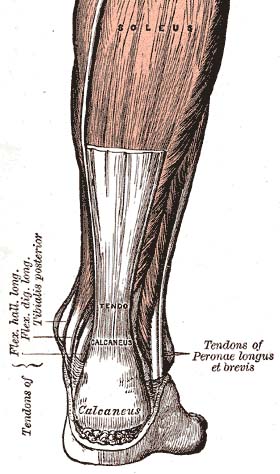
The Achilles tendon or heel cord, also known as the calcaneal tendon, is a tendon of the back of the leg, and the thickest in the human body. It serves to attach the plantaris, gastrocnemius (calf) and soleus muscles to the calcaneus (heel) bone. These muscles, acting via the tendon, cause plantar flexion of the foot at the ankle, and flexion at the knee.
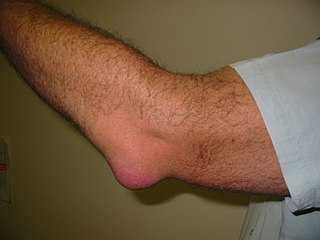
Bursitis is the inflammation of one or more bursae of synovial fluid in the body. They are lined with a synovial membrane that secretes a lubricating synovial fluid. There are more than 150 bursae in the human body. The bursae rest at the points where internal functionaries, such as muscles and tendons, slide across bone. Healthy bursae create a smooth, almost frictionless functional gliding surface making normal movement painless. When bursitis occurs, however, movement relying on the inflamed bursa becomes difficult and painful. Moreover, movement of tendons and muscles over the inflamed bursa aggravates its inflammation, perpetuating the problem. Muscle can also be stiffened.

Plantar fasciitis is a disorder of the connective tissue which supports the arch of the foot. It results in pain in the heel and bottom of the foot that is usually most severe with the first steps of the day or following a period of rest. Pain is also frequently brought on by bending the foot and toes up towards the shin. The pain typically comes on gradually, and it affects both feet in about one third of cases.

Tennis elbow, also known as lateral epicondylitis, is a condition in which the outer part of the elbow becomes painful and tender. The pain may also extend into the back of the forearm and grip strength may be weak. Onset of symptoms is generally gradual. Golfer's elbow is a similar condition that affects the inside of the elbow.

A rotator cuff tear is an injury of one or more of the tendons or muscles of the rotator cuff of the shoulder. Symptoms may include shoulder pain, which is often worse with movement, or weakness. This may limit peoples’ ability to brush their hair or put on clothing. Clicking may also occur with movement of the arm.

Adhesive capsulitis is a painful and disabling disorder of unclear cause in which the shoulder capsule, the connective tissue surrounding the glenohumeral joint of the shoulder, becomes inflamed and stiff, greatly restricting motion and causing chronic pain. Pain is usually constant, worse at night, and with cold weather. Certain movements or bumps can provoke episodes of tremendous pain and cramping. The condition is thought to be caused by injury or trauma to the area and may have an autoimmune component.
Prolotherapy, also called proliferation therapy is an injection-based treatment used in chronic musculoskeletal conditions. It has been characterised as an alternative medicine practice.

Achilles tendon rupture is when the Achilles tendon, at the back of the ankle, breaks. Symptoms include the sudden onset of sharp pain in the heel. A snapping sound may be heard as the tendon breaks and walking becomes difficult.
Synovitis is the medical term for inflammation of the synovial membrane. This membrane lines joints that possess cavities, known as synovial joints. The condition is usually painful, particularly when the joint is moved. The joint usually swells due to synovial fluid collection.
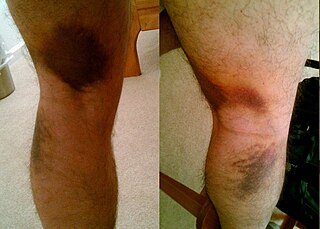
A strain is an acute or chronic soft tissue injury that occurs to a muscle, tendon, or both. The equivalent injury to a ligament is a sprain.

Subacromial bursitis is a condition caused by inflammation of the bursa that separates the superior surface of the supraspinatus tendon from the overlying coraco-acromial ligament, acromion, and coracoid and from the deep surface of the deltoid muscle. The subacromial bursa helps the motion of the supraspinatus tendon of the rotator cuff in activities such as overhead work.

Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) is a treatment mostly used to treat kidney stones and in physical therapy and orthopedics.
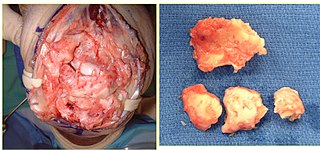
Post-traumatic arthritis (PTA) is a form of osteoarthritis following an injury to a joint.