The 1986 United States Senate elections were elections for the United States Senate. Held on November 4, in the middle of Ronald Reagan's second presidential term, the 34 seats of Class 3 were contested in regular elections. The Republicans had to defend an unusually large number of freshman Senate incumbents who had been elected on President Ronald Reagan's coattails in 1980. Democrats won a net of eight seats, defeating seven freshman incumbents, picking up two Republican-held open seats, and regaining control of the Senate for the first time since January 1981. This remains the most recent midterm election cycle in which the sitting president's party suffered net losses while still flipping a Senate seat.

The 1980 United States Senate elections were held on November 4, coinciding with Ronald Reagan's victory in the presidential election. The 34 Senate seats of Class 3 were contested in regular elections. Reagan's large margin of victory over incumbent Jimmy Carter gave a huge boost to Republican Senate candidates, allowing them to flip 12 Democratic seats and win control of the chamber for the first time since the end of the 83rd Congress in January 1955.

The 1978 United States Senate elections were held on November 7, in the middle of Democratic President Jimmy Carter's term. The 33 seats of Class 2 were contested in regular elections. Special elections were also held to fill vacancies.

The 1970 United States Senate elections was an election for the United States Senate. It took place on November 3, with the 33 seats of Class 1 contested in regular elections. Special elections were also held to fill vacancies. These races occurred in the middle of Richard Nixon's first term as president. The Democrats lost a net of three seats, while the Republicans and the Conservative Party of New York picked up one net seat each, and former Democrat Harry F. Byrd Jr. was re-elected as an independent.
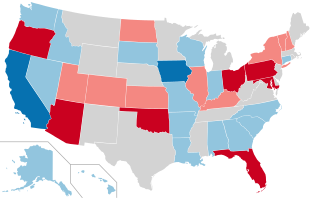
The 1968 United States Senate elections were elections for the United States Senate. Held on November 5, the 34 seats of Class 3 were contested in regular elections. They coincided with the presidential election of the same year. The Republicans picked up five net seats in the Senate. This saw Republicans win a Senate seat in Florida for the first time since Reconstruction.

The 1984 United States House of Representatives elections was an election for the United States House of Representatives on November 6, 1984, to elect members to serve in the 99th United States Congress. They coincided with the re-election of President Ronald Reagan in a landslide. This victory also yielded gains for Reagan's Republican Party in the House, where they picked up a net of sixteen seats from the Democratic Party. Despite Reagan's extremely large electoral victory, the Democrats nonetheless retained a commanding majority in the House and actually gained seats in the Senate. These elections were the last until 2020 when a member of a political party other than the Democrats, Republicans, or an independent had one or more seats in the chamber.
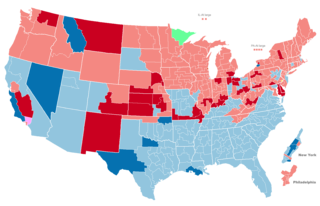
The 1918 United States House of Representatives elections were elections for the United States House of Representatives to elect members to serve in the 66th United States Congress. They were held for the most part on November 5, 1918, while Maine held theirs on September 9. They occurred in the middle of President Woodrow Wilson's second term.

The 2006 United States Senate election in West Virginia was held November 7, 2006. Incumbent Democrat Robert Byrd won re-election to a ninth term. He was sworn in on January 3, 2007. However, he died in office on June 28, 2010, before the end of his term. This was Byrd's closest re-election.

The 1796–97 United States House of Representatives elections took place in the various states took place between August 12, 1796, and October 15, 1797. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives. The size of the House increased to 106 seats after Tennessee became the 16th state to join the union. The first session of the 5th United States Congress was convened on May 15, 1797, at the proclamation of the new President of the United States, John Adams. Since Kentucky and Tennessee had not yet voted, they were unrepresented until the second session began on November 13, 1797.

The 1994 United States elections were held on November 8, 1994. The elections occurred in the middle of Democratic President Bill Clinton's first term in office, and elected the members of 104th United States Congress. The elections have been described as the "Republican Revolution" because the Republican Party captured unified control of Congress for the first time since 1952. Republicans picked up eight seats in the Senate and won a net of 54 seats in the House of Representatives. Republicans also picked up a net of ten governorships and took control of many state legislative chambers. This is the first midterm election since 1946 in which the Republicans ended unified Democratic control of Congress in a midterm election under a Democratic president.

The 2004 United States House of Representatives elections in Texas occurred on November 2, 2004, to elect the members of the state of Texas's delegation to the United States House of Representatives. Texas had thirty-two seats in the House, apportioned according to the 2000 United States census.

A general election was held in the U.S. state of Arkansas on November 4, 2014. All of Arkansas' executive officers were up for election as well as a United States Senate seat, and all of Arkansas' four seats in the United States House of Representatives. Primary elections were held on May 20, 2014, for offices that need to nominate candidates. Primary runoffs, necessary if no candidate wins a majority of the vote, were held on June 10, 2014.

The 1988 United States House of Representatives election in Vermont was held on November 8, 1988. Republican nominee Peter Plympton Smith defeated independent candidate Bernie Sanders and Democratic nominee Paul N. Poirier.

The 2018 United States House of Representatives elections in Alabama were held on November 6, 2018, to elect the seven U.S. representatives from the state of Alabama, one from each of the state's seven congressional districts. The elections coincided with other elections to the House of Representatives, as well as elections to the United States Senate and various state and local elections. The primaries were held on June 5, with all choosing a nominee except the Republican primary in the 2nd district, which went to a July 17 runoff. The 2018 general election saw no change in Alabama's representation, remaining at a 6–1 GOP advantage, even though Democrats won over 40% of the statewide vote.

The 1896 United States presidential election in Iowa took place on November 3, 1896. All contemporary 45 states were part of the 1896 United States presidential election. Voters chose 13 electors to the Electoral College, which selected the president and vice president.

The 2018 Alabama House of Representatives elections were held on November 6, 2018, as part of the biennial United States elections. All 105 of Alabama's state representatives were up for reelection. In Alabama, members of both the House of Representatives and the Senate serve four year terms, running in years corresponding with presidential midterm elections.

The 2022 Wisconsin fall general election was held in the U.S. state of Wisconsin on November 8, 2022. All of Wisconsin's partisan executive and administrative offices were up for election, as well as one of Wisconsin's U.S. Senate seats, Wisconsin's eight seats in the United States House of Representatives, the seventeen odd-numbered seats in the Wisconsin State Senate, and all 99 seats in the Wisconsin State Assembly. The 2022 Wisconsin fall primary was held on August 9, 2022.

The 2022 Texas House of Representatives elections were held on November 8, 2022, to elect representatives from all 150 House of Representatives districts across the U.S. state of Texas. It was held alongside numerous other federal, state, and local elections, including the 2022 Texas State Senate election. The winners of this election served in the 88th Texas Legislature, with seats apportioned according to the 2020 United States census.
The 1944 Massachusetts general election was held on November 7, 1944, throughout Massachusetts. Primary elections took place on July 11.

The 2022 Vermont House of Representatives election took place on November 8, 2022, as part of the biennial United States elections. The election coincided with elections for other offices including the U.S. Senate, U.S. House, Governor, and State Senate. Vermont voters elected all 150 state representatives from 109 districts, with each district electing between one and two representatives. State representatives served two-year terms. A primary election was held on August 9, 2022, and it determined which candidates appear on the November 8 general election ballot. All the members elected would serve in the Vermont General Assembly. This election was the first to use new districts adopted by the Vermont General Assembly to allocate for population changes across the state after the 2020 census.