
1914 United States House of Representatives elections were held in the middle of President Woodrow Wilson's first term.

The 1890 United States House of Representatives elections were held in the middle of President Benjamin Harrison's term.
The 1878–79 United States House of Representatives elections were held in 1878 and 1879, in the middle of President Rutherford B. Hayes's term.
The 1860–61 United States House of Representatives elections were held at various dates in different states from August 1860 to October 1861.

The 1852–53 United States House of Representatives elections were held at various dates in different states from August 1852 to November 1853.
The 1850–51 United States House of Representatives elections were held at various dates in different states from August 1850 to November 1851. The Democrats gained 17 seats, increasing their majority relative to the rival Whigs, who lost 22 seats.
The 1844–45 United States House of Representatives elections were held at various dates in different states from July 1844 to November 1845.
The 1842–43 United States House of Representatives elections were held during President John Tyler's term at various dates in different states between August 1842 and February 1844.
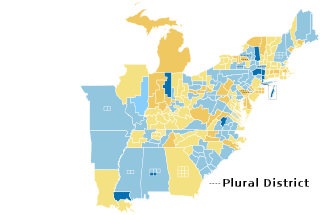
The 1840–41 United States House of Representatives elections were held at various dates in different states from July 1840 to November 1841.
The 1838–39 United States House of Representatives elections were held during President Martin Van Buren's term at various dates in different states from July 1838 to November 1839.
The 1836–37 United States House of Representatives elections were held at various dates in different states from July 1836 to November 1837.

The 1834–35 United States House of Representatives elections were held during President Andrew Jackson's second term.
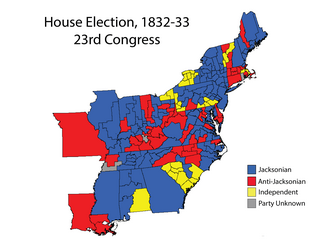
The 1832–33 United States House of Representatives elections were held concurrently with the 1832 presidential election, in which Democrat Andrew Jackson was re-elected.

In the 1830–31 United States House of Representatives elections, the supporters of President Andrew Jackson lost ten seats during his first term, but managed to maintain control of the chamber amidst the growth of two new opposition movements.

In the 1828–29 United States House of Representatives elections, while Jacksonians soundly took control of the presidency, with Andrew Jackson's victory, they greatly increased their majority in Congress. Outgoing President John Quincy Adams's unpopularity played a major role in the Jacksonian pick-up, as did the perception of the Anti-Jacksonian Party as urban and elitist. Major increases in suffrage also heightened Jacksonian wins, as newly enfranchised voters tended to associate with Jacksonian principles. The Anti-Masonic Party, a single issue faction based on distrust of Freemasonry, became the first third party in American history to garner seats in the House.
The 1802–03 United States House of Representatives elections were held at various dates in each state, from April 26, 1802 to December 14, 1803 during President Thomas Jefferson's first term in office. It was common in the early years of the United Congress for some states to elect representatives to a Congress after it had already convened. In the case of the 8th Congress, the representatives from New Jersey were only elected after its first meeting on October 17, 1803.
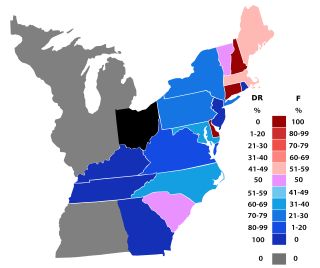
The 1800–01 United States House of Representatives elections were held at the same time as the 1800 presidential election, in which Vice President Thomas Jefferson, a Democratic Republican, defeated incumbent President John Adams, a Federalist.

Vermont elected its members September 2, 1828. Vermont required a majority vote for election, so the 3rd district district election was settled on the second ballot on November 11, 1828 and the 5th district district election was settled on the eighth ballot on November 2, 1829.

The 2020 United States Senate election in Maine was held on November 3, 2020, to elect a member of the United States Senate to represent the State of Maine, concurrently with the 2020 U.S. presidential election, as well as other elections to the United States Senate, elections to the United States House of Representatives and various state and local elections. This was Maine's first election for its Class 2 seat to use its ranked choice voting system. Because the first round of the general election saw a majority (51%), the instant runoff tabulation of more than 800,000 ballots was not carried out.

The 2018 United States House of Representatives elections in Maine were held on November 6, 2018, to elect the two U.S. representatives from the state of Maine, one from each of the state's two congressional districts. The elections coincided with the elections of other offices, including a gubernatorial election, other elections to the House of Representatives, elections to the United States Senate, and various state and local elections.












