
Morphine, formerly also called morphia, is an opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin produced by drying the latex of opium poppies. It is mainly used as an analgesic. There are numerous methods used to administer morphine: orally; administered under the tongue; via inhalation; injection into a vein, injection into a muscle, injection under the skin, or injection into the spinal cord area; transdermal; or via administered into the rectal canal suppository. It acts directly on the central nervous system (CNS) to induce analgesia and alter perception and emotional response to pain. Physical and psychological dependence and tolerance may develop with repeated administration. It can be taken for both acute pain and chronic pain and is frequently used for pain from myocardial infarction, kidney stones, and during labor. Its maximum effect is reached after about 20 minutes when administered intravenously and 60 minutes when administered by mouth, while the duration of its effect is 3–7 hours. Long-acting formulations of morphine are sold under the brand names MS Contin and Kadian, among others. Generic long-acting formulations are also available.
Oxycodone, sold under the brand name Roxicodone and OxyContin among others, is a semi-synthetic opioid used medically for the treatment of moderate to severe pain. It is highly addictive and is a commonly abused drug. It is usually taken by mouth, and is available in immediate-release and controlled-release formulations. Onset of pain relief typically begins within fifteen minutes and lasts for up to six hours with the immediate-release formulation. In the United Kingdom, it is available by injection. Combination products are also available with paracetamol (acetaminophen), ibuprofen, naloxone, naltrexone, and aspirin.

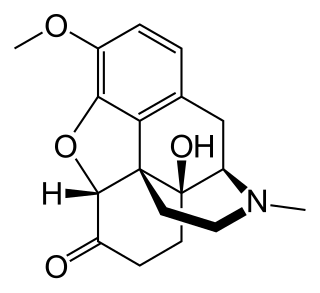
Thebaine (paramorphine), also known as codeine methyl enol ether, is an opiate alkaloid, its name coming from the Greek Θῆβαι, Thēbai (Thebes), an ancient city in Upper Egypt. A minor constituent of opium, thebaine is chemically similar to both morphine and codeine, but has stimulatory rather than depressant effects. At high doses, it causes convulsions similar to strychnine poisoning. The synthetic enantiomer (+)-thebaine does show analgesic effects apparently mediated through opioid receptors, unlike the inactive natural enantiomer (−)-thebaine. While thebaine is not used therapeutically, it is the main alkaloid extracted from Papaver bracteatum and can be converted industrially into a variety of compounds, including hydrocodone, hydromorphone, oxycodone, oxymorphone, nalbuphine, naloxone, naltrexone, buprenorphine, butorphanol and etorphine.

The term narcotic originally referred medically to any psychoactive compound with numbing or paralyzing properties. In the United States, it has since become associated with opiates and opioids, commonly morphine and heroin, as well as derivatives of many of the compounds found within raw opium latex. The primary three are morphine, codeine, and thebaine.

Pentazocine, sold under the brand name Talwin among others, is a painkiller used to treat moderate to severe pain. It is believed to work by activating (agonizing) κ-opioid receptors (KOR) and μ-opioid receptors (MOR). As such it is called an opioid as it delivers its effects on pain by interacting with the opioid receptors. It shares many of the side effects of other opioids like constipation, nausea, itching, drowsiness and respiratory depression, but unlike most other opioids it fairly frequently causes hallucinations, nightmares and delusions. It is also, unlike most other opioids, subject to a ceiling effect, which is when at a certain dose no more pain relief is obtained by increasing the dose any further.

Pethidine, also known as meperidine and sold under the brand name Demerol among others, is a fully synthetic opioid pain medication of the phenylpiperidine class. Synthesized in 1938 as a potential anticholinergic agent by the German chemist Otto Eisleb, its analgesic properties were first recognized by Otto Schaumann while working for IG Farben, in Germany. Pethidine is the prototype of a large family of analgesics including the pethidine 4-phenylpiperidines, the prodines, bemidones, and others more distant, including diphenoxylate and analogues.

The Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, 1961 is an international treaty that controls activities involving specific narcotic drugs and lays down a system of regulations for their medical and scientific uses, concluded under the auspices of the United Nations. The Convention also establishes the International Narcotics Control Board.
Diphenoxylate is a centrally active opioid drug of the phenylpiperidine series that is used as a combination drug with atropine for the treatment of diarrhea. Diphenoxylate is an opioid and acts by slowing intestinal contractions; the atropine is present to prevent drug abuse and overdose. It should not be given to children due to the risk that they will stop breathing and should not be used in people with Clostridioides difficile infection.

Levorphanol is an opioid medication used to treat moderate to severe pain. It is the levorotatory enantiomer of the compound racemorphan. Its dextrorotatory counterpart is dextrorphan.

Levomethorphan (LVM) (INN, BAN) is an opioid analgesic of the morphinan family that has never been marketed. It is the L-stereoisomer of racemethorphan (methorphan). The effects of the two isomers of racemethorphan are quite different, with dextromethorphan (DXM) being an antitussive at low doses and a dissociative hallucinogen at much higher doses. Levomethorphan is about five times stronger than morphine.
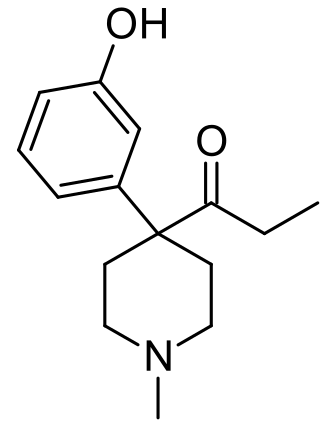
Ketobemidone, sold under the brand name Ketogan among others, is a powerful synthetic opioid painkiller. Its effectiveness against pain is in the same range as morphine, and it also has some NMDA-antagonist properties imparted, in part, by its metabolite norketobemidone. This may make it useful for some types of pain that do not respond well to other opioids. It is marketed in Denmark, Iceland, Norway. Until 2024 it was available in, but is now withdrawn in Sweden. It is used for severe pain.

Piritramide(R-3365, trade names Dipidolor, Piridolan, Pirium and others) is a synthetic opioid analgesic that is marketed in certain European countries including: Austria, Belgium, Czech Republic, Slovenia, Germany and the Netherlands. It comes in free form, is about 0.75x times as potent as morphine and is given parenterally for the treatment of severe pain. Nausea, vomiting, respiratory depression and constipation are believed to be less frequent with piritramide than with morphine, and it produces more rapid-onset analgesia when compared to morphine and pethidine. After intravenous administration the onset of analgesia is as little as 1–2 minutes, which may be related to its great lipophilicity. The analgesic and sedative effects of piritramide are believed to be potentiated with phenothiazines and its emetic (nausea/vomiting-inducing) effects are suppressed. The volume of distribution is 0.7-1 L/kg after a single dose, 4.7-6 L/kg after steady-state concentrations are achieved and up to 11.1 L/kg after prolonged dosing.
Phenadoxone is an opioid analgesic of the open chain class invented in Germany by Hoechst in 1947. It is one of a handful of useful synthetic analgesics which were used in the United States for various lengths of time in the 20 or so years after the end of the Second World War but which were withdrawn from the market for various or no known reason and which now are mostly in Schedule I of the United States' Controlled Substances Act of 1970, or in Schedule II but not produced or marketed in the US. Others on this list are ketobemidone (Ketogin), dextromoramide, phenazocine, dipipanone, piminodine (Alvodine), propiram (Algeril), anileridine (Leritine) and alphaprodine (Nisentil).

Hydroxypethidine (Bemidone) is an opioid analgesic that is an analogue of the more commonly used pethidine (meperidine). Hydroxypethidine is slightly more potent than meperidine as an analgesic, 1.5x meperidine in potency, and it also has NMDA antagonist properties like its close relative ketobemidone.

Oripavine is an opioid and the major metabolite of thebaine. It is the precursor to the semi-synthetic compounds etorphine and buprenorphine. Although this chemical compound has analgesic potency comparable to morphine, it is not used clinically due to severe adverse effects and a low therapeutic index. Being a precursor to a series of extremely strong opioids, oripavine is a controlled substance in some jurisdictions.
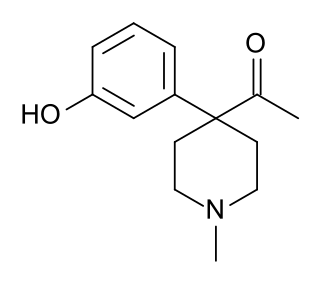
Methylketobemidone is an opioid analgesic that is an analogue of ketobemidone. It was developed in the 1950s during research into analogues of pethidine and was assessed by the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime but was not included on the list of drugs under international control, probably because it was not used in medicine or widely available.
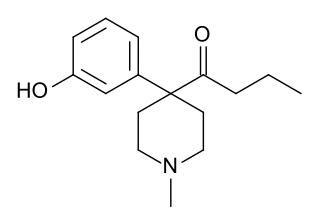
Propylketobemidone is an opioid analgesic that is an analogue of ketobemidone. It was developed in the 1950s during research into analogues of pethidine and was assessed by the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime but was not included on the list of drugs under international control, probably because it was not used in medicine or widely available.

Phenazocine is an opioid analgesic drug, which is related to pentazocine and has a similar profile of effects.

Butyrfentanyl or butyrylfentanyl is a potent short-acting synthetic opioid analgesic drug. It is an analog of fentanyl with around one quarter of its potency. One of the first mentions of this drug can be found in document written by The College on Problem of Drug Dependence, where it is mentioned as N-butyramide fentanyl analog. This document also states that the article describing its clinical effects was published in 1987. It is an agonist for the μ-opioid receptors.

Acetoxymethylketobemidone (O-AMKD), is an opioid designer drug related to ketobemidone, with around the same potency as morphine. It was first identified in Germany in October 2020.




















