
The River Hull is a navigable river in the East Riding of Yorkshire in Northern England. It rises from a series of springs to the west of Driffield, and enters the Humber Estuary at Kingston upon Hull. Following a period when the Archbishops of York charged tolls for its use, it became a free navigation. The upper reaches became part of the Driffield Navigation from 1770, after which they were again subject to tolls, and the section within the city of Hull came under the jurisdiction of the Port of Hull, with the same result.

Arram Beck is a small stream in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England, running through high embankments and flowing eastwards from the village of Arram to join the River Hull. Depths are variable due to the tidal nature of the Hull. It provides habitat for a variety of fish species and chub have also been stocked here too.

The Leven Canal runs for 3.18 miles (5.1 km) from the River Hull to the village of Leven, East Riding of Yorkshire, England. It was built for Mrs Charlotta Bethell in 1805, and remained in use until 1935. It is now a Site of Special Scientific Interest.

The Driffield Navigation is an 11-mile (18-kilometre) waterway, through the heart of the Holderness Plain to the market town of Driffield, East Riding of Yorkshire, England. The northern section of it is a canal, and the southern section is part of the River Hull. Construction was authorised in 1767, and it was fully open in 1770. Early use of the navigation was hampered by a small bridge at Hull Bridge, which was maintained by Beverley Corporation. After protracted negotiation, it was finally replaced in 1804, and a new lock was built to improve water levels at the same time. One curious feature of the new works were that they were managed quite separately for many years, with the original navigation called the Old Navigation, and the new works called the New Navigation. They were not fully amalgamated until 1888.

Aike is a hamlet and former civil parish, now in the parish of Lockington, in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England. The hamlet is centred around a single developed street, which lies to the east of the Yorkshire Wolds. Aike is approximately 4 miles (6 km) north of Beverley and approximately 0.4 miles (1 km) from the west bank of the River Hull. It is approached by a 2.5-mile (4 km) lane which is a no-through road that does not continue beyond the village, although a farm track continues as far as a bridge across the Beverley and Barmston Drain. In 1931 the parish had a population of 48.

The Market Weighton Canal ran 9.5 miles (15.3 km) from the Humber Estuary to its terminus near Market Weighton. It gained its Act of Parliament in 1772 and opened in 1782. The 3.5 miles (5.6 km) closest to Market Weighton was abandoned in 1900 and the right of navigation through Weighton lock was lost in 1971. However, as of 2002 the lock was passable and the canal usable up to the junction with the River Foulness where silt has made it impassable. Also there is no right of navigation under the M62 motorway bridge to the north of Newport.
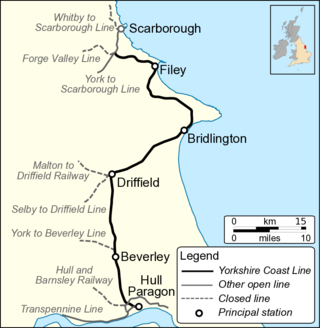
The Hull–Scarborough line, also known as the Yorkshire Coast Line, is a railway line in Yorkshire, England that is used primarily for passenger traffic. It runs northwards from Hull Paragon via Beverley and Driffield to Bridlington, joining the York–Scarborough line at a junction near Seamer before terminating at Scarborough railway station.

Wilfholme Landing is located on the Driffield Navigation in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England. The navigation is still tidal at this point, and is often considered to still be the River Hull, although technically the Navigation starts at the point where the Aike Beck used to join the river, a little further downstream. It is 0.9 miles (1.4 km) from the hamlet of Wilfholme, and its main features are boat moorings, a farm and a pumping station. It is a popular spot for fishing, with anglers targeting resident roach, bream and perch.

West Beck is the common name given to the upper section of the old River Hull, as it rises in the foothills of the Yorkshire Wolds. After reaching Frodingham Beck at Emmotland, it becomes called the River Hull. It is noteworthy for being the most northerly chalk stream in England. It provides fly fishing for wild brown trout and grayling.

The Stainforth and Keadby Canal is a navigable canal in South Yorkshire and Lincolnshire, England. It connects the River Don Navigation at Bramwith to the River Trent at Keadby, by way of Stainforth, Thorne and Ealand, near Crowle. It opened in 1802, passed into the control of the River Don Navigation in 1849, and within a year was controlled by the first of several railway companies. It became part of the Sheffield and South Yorkshire Navigation, an attempt to remove several canals from railway control, in 1895. There were plans to upgrade it to take larger barges and to improve the port facilities at Keadby, but the completion of the New Junction Canal in 1905 made this unnecessary, as Goole could easily be reached and was already a thriving port.
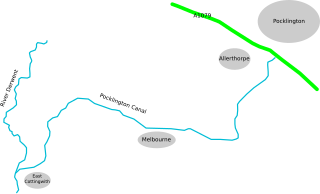
The Pocklington Canal is a broad canal which runs for 9.5 miles (15.3 km) through nine locks from the Canal Head near Pocklington in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England, to the River Derwent which it joins near East Cottingwith. Most of it lies within a designated Site of Special Scientific Interest.

The Oakham Canal ran from Oakham, Rutland to Melton Mowbray, Leicestershire in the East Midlands of England. It opened in 1802, but it was never a financial success, and it suffered from the lack of an adequate water supply. It closed after 45 years, when it was bought by the Midland Railway to allow the Syston and Peterborough Railway to be built, partly along its course. Most of it is infilled, although much of its route can still be seen in the landscape, and there are short sections which still hold water.

The Greasbrough Canal was a private canal built by the Marquess of Rockingham to serve his coal mining interests in and around the village of Greasbrough, near Rotherham, South Yorkshire, England. It opened in 1780, and the Newbiggin branch was built some time later. The main line to Greasbrough closed in 1840 with the coming of the Sheffield and Rotherham Railway, and the canal ceased to carry commercial traffic during the First World War. Most of it has been filled in, but a small section near the River Don Navigation remains in water.

Hull Bridge is a village in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England. It is situated approximately 1.5 miles (2.4 km) north-east of Beverley town centre. It lies south of the A1035 road and straddles the Beverley and Barmston Drain and the River Hull from which it takes its name.

Foston on the Wolds is a village and civil parish in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England. It is situated approximately 8 miles (13 km) south-west of Bridlington town centre and 2 miles (3 km) north of the village of North Frodingham.

Beverley Beck is a short canal in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England. The beck runs from Grovehill Lock on the River Hull at Beverley west for about 0.8 miles (1.3 km) into the town of Beverley. Until 1802, the beck was tidal, but the Beverley and Barmston Drain needed to pass under it, and the lock was constructed to maintain water levels over its tunnel. In 1898, a steam engine was installed, which could be used to top up the water levels in the beck by pumping water from the River Hull. A multimillion-pound refurbishment of the area concluded in 2007, with the refurbishment of the lock gates and pumping engine.

The River Sow Navigation was a short river navigation in Staffordshire, England, which connected the Staffordshire and Worcestershire Canal to the centre of Stafford. There was a coal wharf in Stafford, and a single lock to connect it to the canal. It opened in 1816, and closed in the 1920s. There are proposals to restore the navigation as the Stafford Riverway Link.

Holderness Drain is the main feature of a Land Drainage scheme for the area of Holderness to the east of the River Hull in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England. Construction began in 1764, and several notable civil engineers were involved with the scheme over the years. Despite the high costs of the initial scheme, it was not particularly successful, because of the refusal of the ship owners of Hull to allow an outlet at Marfleet. They insisted that the water be discharged into the River Hull to keep the channel free of silt. Following a period of agricultural depression and the building of new docks in the early 1800s, an outlet at Marfleet was finally authorised in 1832. A high level system still fed upland water to the Hull, but the low level system discharged into the Humber, where levels were considerably lower. Following the success of steam pumping on the Beverley and Barmston Drain, the trustees looked at such a possibility for the Holderness Drain, but the development of the Alexandra Dock in the 1880s and then the King George V Dock in 1913 provided a solution, as the docks were topped up with water pumped from the drain, to lessen the ingress of silt-laden water.

The Beverley and Barmston Drain is the main feature of a land drainage scheme authorised in 1798 to the west of the River Hull in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England. The area consisted of salt marshes to the south and carrs to the north, fed with water from the higher wolds which lay to the north, and from inundation by tidal water passing up the river from the Humber. Some attempts to reduce the flooding by building embankments had been made by the fourteenth century, and windpumps appeared in the seventeenth century. The Holderness Drainage scheme, which protected the area to the east of the river, was completed in 1772, and attention was then given to resolving flooding of the carrs.

Hedon Haven is a waterway that connected the Humber Estuary with the port of Hedon, in Holderness, East Riding of Yorkshire, England. The waterway allowed ships to unload at the port in Hedon, which was also known as Hedon Haven and had, at its peak, three canalised arms that stretched into the town. The port at Hedon was the main port for south Holderness between the 12th and 13th centuries, and was the busiest port in Holderness before the docks at Hull were built.




















