Tipu Sultan, commonly referred to as Sher-e-Mysore or "Tiger of Mysore", was a ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore based in South India. He was a pioneer of rocket artillery. He expanded the iron-cased Mysorean rockets and commissioned the military manual Fathul Mujahidin. He deployed the rockets against advances of British forces and their allies during the Anglo-Mysore Wars, including the Battle of Pollilur and Siege of Srirangapatna.

Hyder Ali was the Sultan and de facto ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore in southern India. Born as Hyder Ali, he distinguished himself as a soldier, eventually drawing the attention of Mysore's rulers. Rising to the post of Dalavayi (commander-in-chief) to Krishnaraja Wodeyar II, he came to dominate the titular monarch and the Mysore government. He became the de facto ruler, King of Mysore as Sarvadhikari by 1761. During intermittent conflicts against the East India Company during the First and Second Anglo–Mysore Wars, Hyder Ali was the military leader.

Srirangapatna is a town and headquarters of one of the seven Taluks of Mandya district, in the Indian State of Karnataka. It gets its name from the Ranganthaswamy temple consecrated around 984 CE. Later, under the British rule, the city was renamed to Seringapatam. Located near the city of Mandya, it is of religious, cultural and historic importance.

The Battle of Pollilur, also known as the Battle of Polilore or Battle of Perambakam, took place on 10 September 1780 at Pollilur near Conjeevaram, the city of Kanchipuram in present-day Tamil Nadu state, India, as part of the Second Anglo-Mysore War. It was fought between an army commanded by King Tipu Sultan of the Kingdom of Mysore, and a British East India Company force led by William Baillie. The EIC force suffered a high number of casualties before surrendering. It was the worst loss the East India Company suffered on the subcontinent until Chillianwala. Benoît de Boigne, a French officer in the service of 6th Regiment of Madras Native Infantry, wrote, "There is not in India an example of a similar defeat".

The Wadiyar dynasty,(Kannada:[ oɖejɐru]) also referred to as the Wadiyars of Mysore, is a late-medieval Indian royal family of former maharajas of Mysore from the Urs clan originally based in Mysore city.
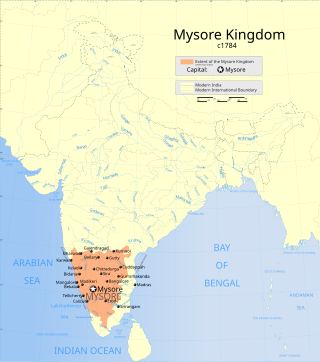
The Kingdom of Mysore was a geopolitical realm in southern India founded in around 1399 in the vicinity of the modern-day city of Mysore and prevailed until 1950. The territorial boundaries and the form of government transmuted substantially throughout the kingdom's lifetime. While originally a feudal vassal under the Vijayanagara Empire, it became a princely state in British India from 1799 to 1947, marked in-between by major political changes.

The Second Anglo-Mysore War was a conflict between the Kingdom of Mysore and the British East India Company from 1780 to 1784. At the time, Mysore was a key French ally in India, and the conflict between Britain against the French and Dutch in the American Revolutionary War influenced Anglo-Mysorean hostilities in India. The great majority of soldiers on the company side were raised, trained, paid and commanded by the company, not the British government. However, the company's operations were also bolstered by Crown troops sent from Great Britain, and by troops from Hanover, which was also ruled by Great Britain's King George III.

The First Anglo-Mysore War (1767–1769) was a conflict in India between the Sultanate of Mysore and the East India Company. The war was instigated in part by the machinations of Asaf Jah II, the Nizam of Hyderabad, who sought to divert the company's resources from attempts to gain control over the Northern Circars.
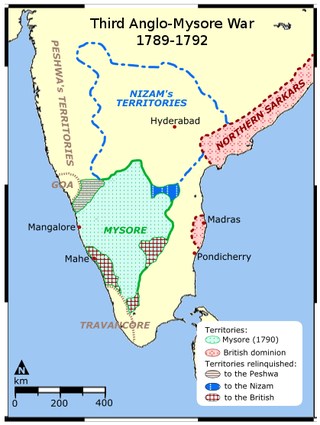
The Third Anglo-Mysore War (1790–1792) was a conflict in South India between the Kingdom of Mysore and the British East India Company, the Kingdom of Travancore, the Maratha Confederacy, and the Nizam of Hyderabad. It was the third of four Anglo-Mysore Wars.

The Fourth Anglo-Mysore War was a conflict in South India between the Kingdom of Mysore against the British East India Company and the Hyderabad Deccan in 1798–99.

The siege of Seringapatam was the final confrontation of the Fourth Anglo-Mysore War between the British East India Company and the Kingdom of Mysore. The British, with the allied Nizam Ali Khan, 2nd Nizam of Hyderabad and Marathas, achieved a decisive victory after breaching the walls of the fortress at Seringapatam and storming the citadel. The leader of the British troops was Major General David Baird, among the lesser known allies were the Portuguese in Goa and Damaon. Tipu Sultan, the ruler after the death of his father, was killed in the action. The British restored the Wodeyar dynasty back to power after the victory through a treaty of subsidiary alliance and Krishnaraja Wodeyar III was crowned the King of Mysore. However, they retained indirect control of the kingdom's external affairs.
The Treaty of Mangalore was signed between Tipu Sultan and the British East India Company on 11 March 1784. It was signed in Mangalore and brought an end to the Second Anglo-Mysore War.

KrishnacharyaPurnaiah, popularly known as DewanPurnaiah, was an Indian administrator, statesman, and military strategist who served as the first dewan of Mysore from 1782 to 1811. He was instrumental in the restoration of the rule of the Kingdom of Mysore to the Wadiyar dynasty. After the death of Tipu, he continued to advice Lakshmi Devi, the queen regent to the newly installed monarch Krishnaraja Wodeyar III.

The 1792 siege of Seringapatam was a battle and siege of the Mysorean capital city of Seringapatam (Srirangapatna) at the end of the Third Anglo-Mysore War. An army led by Charles, Earl Cornwallis, consisting of British East India Company and British Army forces, along with allied forces from the Maratha Empire and the Nizam of Hyderabad, arrived at Seringapatam on 5 February 1792, and after less than three weeks of battle and siege, forced Tipu Sultan to capitulate. With his agreement to the Treaty of Seringapatam on 18 March 1792, the war came to an end.
The Maratha–Mysore wars were a conflict in the 18th century India between the Maratha Confederacy and the Kingdom of Mysore. Though initial hostilities between the sides started in 1760s, the last battle began in February 1785 and ended in 1787.

The Mysorean invasion of Malabar (1766–1792) was the military invasion of the Malabar region of Kerala, including the territories of the Zamorin of Calicut, by the then-de facto ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore, Hyder Ali. After the invasion, the Kingdom of Cochin to the south of Malabar became a tributary state of Mysore.
Mysorean rockets were an Indian military weapon. The iron-cased rockets were successfully deployed for military use. They were the first successful iron-cased rockets, developed in the late 18th century in the Kingdom of Mysore under the rule of King Hyder Ali. The Mysorean army, under King Hyder Ali and his son King Tipu Sultan, used the rockets effectively against the British East India Company during the 1780s and 1790s. According to James Forbes Marathas also used iron-encased rockets in their battles. Their conflicts with the company exposed the British to this technology further, which was then used to advance European rocketry with the development of the Congreve rocket in 1805.

Srirangapatna Fort is a historical fort located in Srirangapatna, the historical capital city of the Kingdom of Mysore in present-day South Indian state of Karnataka. Built by the Timmanna Nayaka in 1454, the fort was modified by King Haider Ali & King Tipu Sultan and fully fortified in the late 18th century with the help of French architects. King Tipu Sultan wanted to protect it against British invaders associated with the East India Company.

Masjid-i-Ala is a mosque located inside the Srirangapatna Fort in Srirangapatna in Mandya District in Karnataka. It was built in 1786–87, during the rule of Tipu Sultan.

Obelisk Monument, also known as the Siege Monument, is a commemorative edifice built in Srirangapatna in the Indian state of Karnataka. It marks the memory of the British officers and native soldiers who lost their lives during the siege of Srirangapatna on 4 May 1799 during the last Fourth Anglo-Mysore war fought during 1798-99 between the British army and the forces of the Mysore Kingdom led by Tipu Sultan. The British army was led by the British General Harris. The memorial was built during the reign of Krishna Raja Wadiyar IV in 1907 as a mark of gratitude by the Wadiyars for getting back their throne from the Sultans.