
King of Italy was the title given to the ruler of the Kingdom of Italy after the fall of the Western Roman Empire. The first to take the title was Odoacer, a barbarian warlord, in the late 5th century, followed by the Ostrogothic kings up to the mid-6th century. With the Frankish conquest of Italy in the 8th century, the Carolingians assumed the title, which was maintained by subsequent Holy Roman Emperors throughout the Middle Ages. The last Emperor to claim the title was Charles V in the 16th century. During this period, the holders of the title were crowned with the Iron Crown of Lombardy.

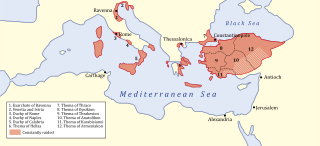
The Exarchate of Ravenna, also known as the Exarchate of Italy, was an administrative district of the Byzantine Empire comprising, between the 6th and 8th centuries, the territories under the jurisdiction of the exarch of Italy resident in Ravenna. The term is used in historiography in a double sense: "exarchate" in the strict sense denotes the territory under the direct jurisdiction of the exarch, i.e. the area of the capital Ravenna, but the term is mainly used to designate all the Byzantine territories in continental and peninsular Italy. According to the legal sources of the time, these territories constituted the so-called Provincia Italiae, on the basis of the fact that they too, until at least the end of the 7th century, fell under the jurisdiction of the exarch and were governed by duces or magistri militum under him.
The history of Italy in the Middle Ages can be roughly defined as the time between the collapse of the Western Roman Empire and the Italian Renaissance. Late antiquity in Italy lingered on into the 7th century under the Ostrogothic Kingdom and the Byzantine Empire under the Justinian dynasty, the Byzantine Papacy until the mid 8th century. The "Middle Ages" proper begin as the Byzantine Empire was weakening under the pressure of the Muslim conquests, and most of the Exarchate of Ravenna finally fell under Lombard rule in 751. From this period, former states that were part of the Exarchate and were not conquered by the Lombard Kingdom, such as the Duchy of Naples, became de facto independent states, having less and less interference from the Eastern Roman Empire.

The Duchy of Benevento was the southernmost Lombard duchy in the Italian Peninsula that was centred on Benevento, a city in Southern Italy. Lombard dukes ruled Benevento from 571 to 1077, when it was conquered by the Normans for four years before it was given to the Pope. Being cut off from the rest of the Lombard possessions by the papal Duchy of Rome, Benevento was practically independent from the start. Only during the reigns of Grimoald and the kings from Liutprand on was the duchy closely tied to the Kingdom of the Lombards. After the fall of the kingdom in 774, the duchy became the sole Lombard territory which continued to exist as a rump state, maintaining its de facto independence for nearly 300 years, although it was divided after 849. Benevento dwindled in size in the early 11th century, and was completely captured by the Norman Robert Guiscard in 1053.

The Catepanateof Italy was a province of the Byzantine Empire from 965 until 1071. At its greatest extent, it comprised mainland Italy south of a line drawn from Monte Gargano to the Gulf of Salerno. North of that line, Amalfi and Naples also maintained allegiance to Constantinople through the catepan. The Italian region of Capitanata derives its name from katepanikion.

Longobardia was a Byzantine term for the territories controlled by the Lombards in the Italian Peninsula. In the ninth and tenth centuries, it was also the name of a Byzantine military-civilian province known as the Theme of Longobardia located in southeastern Italy.

The Kingdom of the Lombards, also known as the Lombard Kingdom and later as the Kingdom of all Italy, was an early medieval state established by the Lombards, a Germanic people, on the Italian Peninsula in the latter part of the 6th century. The king was traditionally elected by the very highest-ranking aristocrats, the dukes, as several attempts to establish a hereditary dynasty failed. The kingdom was subdivided into a varying number of duchies, ruled by semi-autonomous dukes, which were in turn subdivided into gastaldates at the municipal level. The capital of the kingdom and the center of its political life was Pavia in the modern northern Italian region of Lombardy.

The Duchy of Friuli was a Lombard duchy in present-day Friuli, the first to be established after the conquest of the Italian peninsula in 568. It was one of the largest domains in Langobardia Major and an important buffer between the Lombard kingdom and the Slavs, Avars, and the Byzantine Empire. The original chief city in the province was Roman Aquileia, but the Lombard capital of Friuli was Forum Julii, modern Cividale.

The Judicate of Cagliari was one of the four kingdoms or judicates into which Sardinia was divided during the Middle Ages.

The County of Sicily was a Norman state comprising the islands of Sicily and Malta and part of Calabria from 1071 until 1130. The county began to form during the Norman conquest of Sicily (1061–91) from the Muslim Emirate, established by conquest in 965. The county is thus a transitional period in the history of Sicily. After the Muslims had been defeated and either forced out or incorporated into the Norman military, a further period of transition took place for the county and the Sicilians.

The Kingdom of Sardinia, also referred to as the Kingdom ofSardinia-Piedmont, Sardegna and Corsica or Piedmont–Sardinia as a composite state during the Savoyard period, was a country in Southern Europe from the late 13th until the mid-19th century; officially 1297 to 1768 for the Corsican part of this kingdom.
Sicily was a Byzantine province (theme) existing from the late 7th to the 10th century, encompassing the islands of Sicily and Malta, and the region of Calabria in the Italian mainland. Following the Muslim conquest of Sicily, from 902 the theme was limited to Calabria, but retained its original name until the middle of the 10th century.
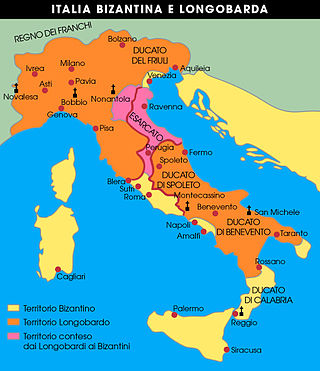
The Duchy of Perugia was a duchy in the Italian part of the Byzantine Empire. Its civil and military administration was overseen by a duke (dux) appointed by and under the authority originally of the Praetorian Prefect of Italy (554–584) and later of the Exarch of Ravenna (584–751). Its chief city and namesake was Perugia (Perusia), located at its centre. It was a band of territory connecting the Duchy of the Pentapolis to its northeast with the Duchy of Rome to its southwest, and separating the duchies of Tuscia and Spoleto, both parts of the Lombard Kingdom of Italy. It was of great strategic significance to the Byzantines since it provided communication between Rome, the city of the Popes, and Ravenna, the capital of the Exarchate. Since it cut off the Duke of Spoleto from his nominal overlord, the king ruling from Pavia, it also disturbed the Lombard kingdom, which was a constant thorn in the Byzantines' side. This strategic importance meant that many Lombard and Byzantine armies passed through it.

The Theme of Sebasteia was a military-civilian province of the Byzantine Empire located in northeastern Cappadocia and Armenia Minor, in modern Turkey. It was established as a theme in 911 and endured until its fall to the Seljuk Turks in the aftermath of the Battle of Manzikert in 1071.

The monarchy of Italy was the system of government in which a hereditary constitutional monarch was the sovereign of the Kingdom of Italy from 1861 to 1946.
Byzantine Syrmia may refer to:
The foreign relations of the Eastern Roman Empire were conducted by the emperor. Preferring diplomacy over war, the emperor would use alliances, treaty's and diplomatic tactics to achieve goals. Military confrontations also occurred, with Dimitri Obolensky calling it as a form of "defensive imperialism". The conduct of its foreign relations is a large factor to the Empire's longevity of 1,123 years.














