
The stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF1), also known as C-X-C motif chemokine 12 (CXCL12), is a chemokine protein that in humans is encoded by the CXCL12 gene on chromosome 10. It is ubiquitously expressed in many tissues and cell types. Stromal cell-derived factors 1-alpha and 1-beta are small cytokines that belong to the chemokine family, members of which activate leukocytes and are often induced by proinflammatory stimuli such as lipopolysaccharide, TNF, or IL1. The chemokines are characterized by the presence of 4 conserved cysteines that form 2 disulfide bonds. They can be classified into 2 subfamilies. In the CC subfamily, the cysteine residues are adjacent to each other. In the CXC subfamily, they are separated by an intervening amino acid. The SDF1 proteins belong to the latter group. CXCL12 signaling has been observed in several cancers. The CXCL12 gene also contains one of 27 SNPs associated with increased risk of coronary artery disease.

C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR-4) also known as fusin or CD184 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CXCR4 gene. The protein is a CXC chemokine receptor.

Interleukin 8 is a chemokine produced by macrophages and other cell types such as epithelial cells, airway smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells. Endothelial cells store IL-8 in their storage vesicles, the Weibel-Palade bodies. In humans, the interleukin-8 protein is encoded by the CXCL8 gene. IL-8 is initially produced as a precursor peptide of 99 amino acids which then undergoes cleavage to create several active IL-8 isoforms. In culture, a 72 amino acid peptide is the major form secreted by macrophages.

Platelet factor 4 (PF4) is a small cytokine belonging to the CXC chemokine family that is also known as chemokine ligand 4 (CXCL4). This chemokine is released from alpha-granules of activated platelets during platelet aggregation, and promotes blood coagulation by moderating the effects of heparin-like molecules. Due to these roles, it is predicted to play a role in wound repair and inflammation. It is usually found in a complex with proteoglycan.

Chemokine ligand 7 (CCL7) is a small cytokine that was previously called monocyte-chemotactic protein 3 (MCP3). CCL7 is a small protein that belongs to the CC chemokine family and is most closely related to CCL2.

Chemokine ligand 8 (CCL8), also known as monocyte chemoattractant protein 2 (MCP2), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCL8 gene.

Chemokine ligand 9 (CXCL9) is a small cytokine belonging to the CXC chemokine family that is also known as monokine induced by gamma interferon (MIG). The CXCL9 is one of the chemokine which plays role to induce chemotaxis, promote differentiation and multiplication of leukocytes, and cause tissue extravasation.

C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10 (CXCL10) also known as Interferon gamma-induced protein 10 (IP-10) or small-inducible cytokine B10 is an 8.7 kDa protein that in humans is encoded by the CXCL10 gene. C-X-C motif chemokine 10 is a small cytokine belonging to the CXC chemokine family.

C-X-C motif chemokine 11 (CXCL11) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CXCL11 gene.

The chemokine ligand 1 (CXCL1) is a small peptide belonging to the CXC chemokine family that acts as a chemoattractant for several immune cells, especially neutrophils or other non-hematopoietic cells to the site of injury or infection and plays an important role in regulation of immune and inflammatory responses. It was previously called GRO1 oncogene, GROα, neutrophil-activating protein 3 (NAP-3) and melanoma growth stimulating activity, alpha (MGSA-α). It's also known as keratinocytes-derived chemokine (KC) in mice or cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant type-1 (CINC-1) in rats. In humans, this protein is encoded by the gene Cxcl1 and is located on human chromosome 4 among genes for other CXC chemokines.

Chemokine ligand 2 (CXCL2) is a small cytokine belonging to the CXC chemokine family that is also called macrophage inflammatory protein 2-alpha (MIP2-alpha), Growth-regulated protein beta (Gro-beta) and Gro oncogene-2 (Gro-2). CXCL2 is 90% identical in amino acid sequence as a related chemokine, CXCL1. This chemokine is secreted by monocytes and macrophages and is chemotactic for polymorphonuclear leukocytes and hematopoietic stem cells. The gene for CXCL2 is located on human chromosome 4 in a cluster of other CXC chemokines. CXCL2 mobilizes cells by interacting with a cell surface chemokine receptor called CXCR2.

Chemokine ligand 3 (CXCL3) is a small cytokine belonging to the CXC chemokine family that is also known as GRO3 oncogene (GRO3), GRO protein gamma (GROg) and macrophage inflammatory protein-2-beta (MIP2b). CXCL3 controls migration and adhesion of monocytes and mediates its effects on its target cell by interacting with a cell surface chemokine receptor called CXCR2. More recently, it has been shown that Cxcl3 regulates cell autonomously the migration of the precursors of cerebellar granule neurons toward the internal layers of cerebellum, during the morphogenesis of cerebellum. Moreover, if the expression of Cxcl3 is reduced in cerebellar granule neuron precursors, this highly enhances the frequency of the medulloblastoma, the tumor of cerebellum. In fact, the reduced expression of Cxcl3 forces the cerebellar granule neuron precursors to remain at the surface of the cerebellum, where they highly proliferate under the stimulus of Sonic hedgehog, becoming target of transforming insults. Remarkably, the treatment with CXCL3 completely prevents the growth of medulloblastoma lesions in a Shh-type mouse model of medulloblastoma. Thus, CXCL3 is a target for medulloblastoma therapy. Cxcl3 is directly regulated transcriptionally by BTG2
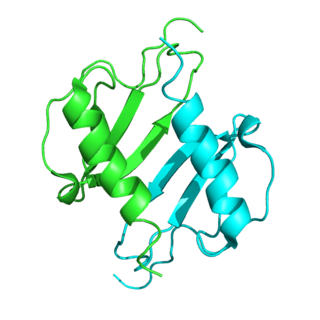
C-X-C motif chemokine 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CXCL5 gene.

Chemokine ligand 13 (CXCL13), also known as B lymphocyte chemoattractant (BLC) or B cell-attracting chemokine 1 (BCA-1), is a protein ligand that in humans is encoded by the CXCL13 gene.
CXC chemokine receptors are integral membrane proteins that specifically bind and respond to cytokines of the CXC chemokine family. They represent one subfamily of chemokine receptors, a large family of G protein-linked receptors that are known as seven transmembrane (7-TM) proteins, since they span the cell membrane seven times. There are currently six known CXC chemokine receptors in mammals, named CXCR1 through CXCR6.

Chemokine ligand 7 (CXCL7) is a human gene.

Chemokine receptor CXCR3 is a Gαi protein-coupled receptor in the CXC chemokine receptor family. Other names for CXCR3 are G protein-coupled receptor 9 (GPR9) and CD183. There are three isoforms of CXCR3 in humans: CXCR3-A, CXCR3-B and chemokine receptor 3-alternative (CXCR3-alt). CXCR3-A binds to the CXC chemokines CXCL9 (MIG), CXCL10 (IP-10), and CXCL11 (I-TAC) whereas CXCR3-B can also bind to CXCL4 in addition to CXCL9, CXCL10, and CXCL11.

Interleukin 8 receptor, beta is a chemokine receptor. IL8RB is also known as CXCR2, and CXCR2 is now the IUPHAR Committee on Receptor Nomenclature and Drug classification-recommended name.

C-C chemokine receptor type 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCR1 gene.

Atypical chemokine receptor 3 also known as C-X-C chemokine receptor type 7 (CXCR-7) and G-protein coupled receptor 159 (GPR159) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACKR3 gene.


















