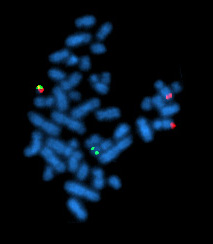
The Philadelphia chromosome or Philadelphia translocation (Ph) is a specific genetic abnormality in chromosome 22 of leukemia cancer cells. This chromosome is defective and unusually short because of reciprocal translocation, t(9;22)(q34;q11), of genetic material between chromosome 9 and chromosome 22, and contains a fusion gene called BCR-ABL1. This gene is the ABL1 gene of chromosome 9 juxtaposed onto the breakpoint cluster region BCR gene of chromosome 22, coding for a hybrid protein: a tyrosine kinase signaling protein that is "always on", causing the cell to divide uncontrollably by interrupting the stability of the genome and impairing various signaling pathways governing the cell cycle.

Macrophage Inflammatory Proteins (MIP) belong to the family of chemotactic cytokines known as chemokines. In humans, there are two major forms, MIP-1α and MIP-1β that are now officially named CCL3 and CCL4, respectively. However, other names can sometimes be encountered, especially in older literature, as LD78α, AT 464.1 and GOS19-1 for human CCL3 and AT 744, Act-2, LAG-1, HC21 and G-26 for human CCL4. Other macrophage inflammatory proteins include MIP-2, MIP-3 and MIP-5.
Chemokine ligand 1 (CCL1) is also known as small inducible cytokine A1 and I-309 in humans. CCL1 is a small glycoprotein that belongs to the CC chemokine family.

Chemokine ligand 20 (CCL20) or liver activation regulated chemokine (LARC) or Macrophage Inflammatory Protein-3 (MIP3A) is a small cytokine belonging to the CC chemokine family. It is strongly chemotactic for lymphocytes and weakly attracts neutrophils. CCL20 is implicated in the formation and function of mucosal lymphoid tissues via chemoattraction of lymphocytes and dendritic cells towards the epithelial cells surrounding these tissues. CCL20 elicits its effects on its target cells by binding and activating the chemokine receptor CCR6.

Chemokine ligand 18 (CCL18) is a small cytokine belonging to the CC chemokine family. The functions of CCL18 have been well studied in laboratory settings, however the physiological effects of the molecule in living organisms have been difficult to characterize because there is no similar protein in rodents that can be studied. The receptor for CCL18 has been identified in humans only recently, which will help scientists understand the molecule's role in the body.

Chemokine ligand 21 (CCL21) is a small cytokine belonging to the CC chemokine family. This chemokine is also known as 6Ckine, exodus-2, and secondary lymphoid-tissue chemokine (SLC). CCL21 elicits its effects by binding to a cell surface chemokine receptor known as CCR7. The main function of CCL21 is to guide CCR7 expressing leukocytes to the secondary lymphoid organs, such as lymph nodes and Peyer´s patches.

C-C motif chemokine 22 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCL22 gene.

Chemokine ligand 19 (CCL19) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCL19 gene.

The "C" sub-family of chemokine receptors contains only one member: XCR1, the receptor for XCL1 and XCL2.
CC chemokine receptors are integral membrane proteins that specifically bind and respond to cytokines of the CC chemokine family. They represent one subfamily of chemokine receptors, a large family of G protein-linked receptors that are known as seven transmembrane (7-TM) proteins since they span the cell membrane seven times. To date, ten true members of the CC chemokine receptor subfamily have been described. These are named CCR1 to CCR10 according to the IUIS/WHO Subcommittee on Chemokine Nomenclature.

C-C chemokine receptor type 2 (CCR2 or CD192 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCR2 gene. CCR2 is a CC chemokine receptor.

Interleukin 8 receptor, alpha is a chemokine receptor. This name and the corresponding gene symbol IL8RA have been replaced by the HGNC approved name C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 1 and the approved symbol CXCR1. It has also been designated as CD181. The IUPHAR Committee on Receptor Nomenclature and Drug Classification use the HGNC recommended name, CXCR1.

C-C chemokine receptor type 7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCR7 gene. Two ligands have been identified for this receptor: the chemokines ligand 19 (CCL19/ELC) and ligand 21 (CCL21). The ligands have similar affinity for the receptor, though CCL19 has been shown to induce internalisation of CCR7 and desensitisation of the cell to CCL19/CCL21 signals. CCR7 is a transmembrane protein with 7 transmembrane domains, which is coupled with heterotrimeric G proteins, which transduce the signal downstream through various signalling cascades. The main function of the receptor is to guide immune cells to immune organs by detecting specific chemokines, which these tissues secrete.

C-C chemokine receptor type 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCR1 gene.

Chemokine receptor 6 also known as CCR6 is a CC chemokine receptor protein which in humans is encoded by the CCR6 gene. CCR6 has also recently been designated CD196. The gene is located on the long arm of Chromosome 6 (6q27) on the Watson (plus) strand. It is 139,737 bases long and encodes a protein of 374 amino acids.

C-C chemokine receptor type 10 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCR10 gene.

C-C chemokine receptor type 9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCR9 gene. This gene is mapped to the chemokine receptor gene cluster region. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described.

G protein coupled receptor 132, also termed G2A, is classified as a member of the proton sensing G protein coupled receptor (GPR) subfamily. Like other members of this subfamily, i.e. GPR4, GPR68 (OGR1), and GPR65 (TDAG8), G2A is a G protein coupled receptor that resides in the cell surface membrane, senses changes in extracellular pH, and can alter cellular function as a consequence of these changes. Subsequently, G2A was suggested to be a receptor for lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC). However, the roles of G2A as a pH-sensor or LPC receptor are disputed. Rather, current studies suggest that it is a receptor for certain metabolites of the polyunsaturated fatty acid, linoleic acid.

Chemokine-binding protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCBP2 gene.
Lenzilumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that targets colony stimulating factor 2 (CSF2)/granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF).













