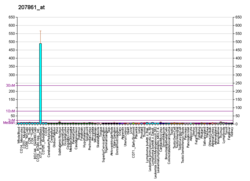
C-C motif chemokine 22 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCL22 gene. [4] [5] [6]
Contents
The protein encoded by this gene is secreted by dendritic cells and macrophages, and elicits its effects on its target cells by interacting with cell surface chemokine receptors such as CCR4. [7] The gene for CCL22 is located in human chromosome 16 in a cluster with other chemokines called CX3CL1 and CCL17. [8] [9]