Related Research Articles

Intel Corporation, stylized as intel, is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is the developer of the x86 series of microprocessors, the processors found in most personal computers (PCs). Incorporated in Delaware, Intel ranked No. 45 in the 2020 Fortune 500 list of the largest United States corporations by total revenue for nearly a decade, from 2007 to 2016 fiscal years.

A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or a small number of integrated circuits. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circuitry required to perform the functions of a computer's central processing unit. The integrated circuit is capable of interpreting and executing program instructions and performing arithmetic operations. The microprocessor is a multipurpose, clock-driven, register-based, digital integrated circuit that accepts binary data as input, processes it according to instructions stored in its memory, and provides results as output. Microprocessors contain both combinational logic and sequential digital logic, and operate on numbers and symbols represented in the binary number system.

Semiconductor device fabrication is the process used to manufacture semiconductor devices, typically the metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) devices used in the integrated circuit (IC) chips such as modern computer processors, microcontrollers, and memory chips such as NAND flash and DRAM that are present in everyday electrical and electronic devices. It is a multiple-step sequence of photolithographic and chemical processing steps during which electronic circuits are gradually created on a wafer made of pure semiconducting material. Silicon is almost always used, but various compound semiconductors are used for specialized applications.

The StrongARM is a family of computer microprocessors developed by Digital Equipment Corporation and manufactured in the late 1990s which implemented the ARM v4 instruction set architecture. It was later sold to Intel in 1997, who continued to manufacture it before replacing it with the XScale in the early 2000s.
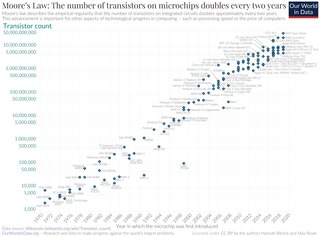
Moore's law is the observation that the number of transistors in a dense integrated circuit (IC) doubles about every two years. Moore's law is an observation and projection of a historical trend. Rather than a law of physics, it is an empirical relationship linked to gains from experience in production.
N-type metal-oxide-semiconductor logic uses n-type (-) MOSFETs to implement logic gates and other digital circuits. These nMOS transistors operate by creating an inversion layer in a p-type transistor body. This inversion layer, called the n-channel, can conduct electrons between n-type "source" and "drain" terminals. The n-channel is created by applying voltage to the third terminal, called the gate. Like other MOSFETs, nMOS transistors have four modes of operation: cut-off, triode, saturation, and velocity saturation.
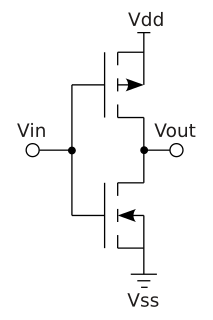
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor, also known as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (COS-MOS), is a type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type MOSFETs for logic functions. CMOS technology is used for constructing integrated circuit (IC) chips, including microprocessors, microcontrollers, memory chips, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for analog circuits such as image sensors, data converters, RF circuits, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication.
Electronic design automation (EDA), also referred to as electronic computer-aided design (ECAD), is a category of software tools for designing electronic systems such as integrated circuits and printed circuit boards. The tools work together in a design flow that chip designers use to design and analyze entire semiconductor chips. Since a modern semiconductor chip can have billions of components, EDA tools are essential for their design; this article in particular describes EDA specifically with respect to integrated circuits (ICs).

Masatoshi Shima is a Japanese electronics engineer. He was one of the architects of the world's first microprocessor, the Intel 4004. In 1968, Shima worked for Busicom in Japan, and did the logic design for a specialized CPU to be translated into three-chip custom chips. In 1969, he worked with Intel's Ted Hoff and Stanley Mazor to reduce the three-chip Busicom proposal into a one-chip architecture. In 1970, that architecture was transformed into a silicon chip, the Intel 4004, by Federico Faggin, with Shima's assistance in logic design.
JTAG is an industry standard for verifying designs and testing printed circuit boards after manufacture.
The foundry model is a microelectronics engineering and manufacturing business model consisting of a semiconductor fabrication plant, or foundry, and an integrated circuit design operation, each belonging to separate companies or subsidiaries.

ASML Holding N.V. is a Dutch multinational corporation founded in 1984 and specializing in the development and manufacturing of photolithography systems. Currently it is the largest supplier of photolithography systems primarily for the semiconductor industry and the sole supplier of extreme ultraviolet lithography (EUV) photolithography machines in the world. ASML employs more than 31,000 people from 120 nationalities, relies on a vast network of more than 4,000 suppliers and has offices in the United States, Belgium, France, Germany, Ireland, Israel, Italy, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, mainland China, Hong Kong, Japan, Malaysia, Singapore, South Korea, and Taiwan.

Integrated circuit design, or IC design, is a sub-field of electronics engineering, encompassing the particular logic and circuit design techniques required to design integrated circuits, or ICs. ICs consist of miniaturized electronic components built into an electrical network on a monolithic semiconductor substrate by photolithography.

In the microelectronics industry, a semiconductor fabrication plant is a factory where devices such as integrated circuits are manufactured.
In engineering, a process is a series of interrelated tasks that, together, transform inputs into a given output. These tasks may be carried out by people, nature or machines using various resources; an engineering process must be considered in the context of the agents carrying out the tasks and the resource attributes involved. Systems engineering normative documents and those related to Maturity Models are typically based on processes, for example, systems engineering processes of the EIA-632 and processes involved in the Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI) institutionalization and improvement approach. Constraints imposed on the tasks and resources required to implement them are essential for executing the tasks mentioned.

A multigate device, multi-gate MOSFET or multi-gate field-effect transistor (MuGFET) refers to a metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) that has more than one gate into a single device. The multiple gates may be controlled by a single gate electrode, wherein the multiple gate surfaces act electrically as a single gate, or by independent gate electrodes. A multigate device employing independent gate electrodes is sometimes called a multiple-independent-gate field-effect transistor (MIGFET). The most widely used multi-gate devices are the FinFET and the GAAFET, which are non-planar transistors, or 3D transistors.

Read-only memory (ROM) is a type of non-volatile memory used in computers and other electronic devices. Data stored in ROM cannot be electronically modified after the manufacture of the memory device. Read-only memory is useful for storing software that is rarely changed during the life of the system, also known as firmware. Software applications for programmable devices can be distributed as plug-in cartridges containing ROM.
A chip shortage, also referred to as semiconductor shortage or chip famine, is a phenomenon in the integrated circuit (chip) industry when demand for silicon chips outstrips supply.

Production planning is the planning of production and manufacturing modules in a company or industry. It utilizes the resource allocation of activities of employees, materials and production capacity, in order to serve different customers.
References
- McDonald, C. J. Copy EXACTLY! "A paradigm shift in technology transfer method". Advanced Semiconductor Manufacturing Conference and Workshop, IEEE/SEMI, 1997 Cambridge, MA. IEEE, 414–417.