
Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the common cold, while more lethal varieties can cause SARS, MERS and COVID-19. In cows and pigs they cause diarrhea, while in mice they cause hepatitis and encephalomyelitis.

Varicella zoster virus (VZV), also known as human herpesvirus 3 or Human alphaherpesvirus 3 (taxonomically), is one of nine known herpes viruses that can infect humans. It causes chickenpox (varicella) commonly affecting children and young adults, and shingles in adults but rarely in children. As a late complication of VZV infection, Ramsay Hunt syndrome type 2 may develop in rare cases. VZV infections are species-specific to humans. The virus can survive in external environments for a few hours.

Rubella virus (RuV) is the pathogenic agent of the disease rubella, transmitted only between humans via the respiratory route, and is the main cause of congenital rubella syndrome when infection occurs during the first weeks of pregnancy.
Avian infectious bronchitis (IB) is an acute and highly contagious respiratory disease of chickens. The disease is caused by avian infectious bronchitis virus (IBV), a coronavirus, and characterized by respiratory signs including gasping, coughing, sneezing, tracheal rales, and nasal discharge. In young chickens, severe respiratory distress may occur. In layers, respiratory distress, nephritis, decrease in egg production, and loss of internal and external egg quality are reported.
Avian coronavirus is a species of virus from the genus Gammacoronavirus that infects birds; since 2018, all gammacoronaviruses which infect birds have been classified as this single species. The strain of avian coronavirus previously known as infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) is the only coronavirus that infects chickens. It causes avian infectious bronchitis, a highly infectious disease that affects the respiratory tract, gut, kidney and reproductive system. IBV affects the performance of both meat-producing and egg-producing chickens and is responsible for substantial economic loss within the poultry industry. The strain of avian coronavirus previously classified as Turkey coronavirus causes gastrointestinal disease in turkeys.
Aviadenoviruses are adenoviruses that affect birds—particularly chickens, ducks, geese, turkeys and pheasants. There are 15 species in this genus. Viruses in this genus cause specific disease syndromes such as Quail Bronchitis (QB), Egg Drop Syndrome (EDS), Haemorrhagic Enteritis (HE), Pheasant Marble Spleen Disease (MSD), and Inclusion Body Hepatitis (IBH). Avian adenoviruses have a worldwide distribution and it is common to find multiple species on a single farm. The most common serogroups are serogroup 1, 2 and 3.

Astroviruses (Astroviridae) are a type of virus that was first discovered in 1975 using electron microscopes following an outbreak of diarrhea in humans. In addition to humans, astroviruses have now been isolated from numerous mammalian animal species and from avian species such as ducks, chickens, and turkey poults. Astroviruses are 28–35 nm diameter, icosahedral viruses that have a characteristic five- or six-pointed star-like surface structure when viewed by electron microscopy. Along with the Picornaviridae and the Caliciviridae, the Astroviridae comprise a third family of nonenveloped viruses whose genome is composed of plus-sense, single-stranded RNA. Astrovirus has a non-segmented, single stranded, positive sense RNA genome within a non-enveloped icosahedral capsid. Human astroviruses have been shown in numerous studies to be an important cause of gastroenteritis in young children worldwide. In animals, Astroviruses also cause infection of the gastrointestinal tract but may also result in encephalitis, hepatitis (avian) and nephritis (avian).

Duck plague is a worldwide disease caused by Anatid alphaherpesvirus 1 (AnHV-1) of the family Herpesviridae that causes acute disease with high mortality rates in flocks of ducks, geese, and swans. It is spread both vertically and horizontally—through contaminated water and direct contact. Migratory waterfowl are a major factor in the spread of this disease as they are often asymptomatic carriers of disease. The incubation period is three to seven days. Birds as young as one week old can be infected. DEV is not zoonotic.

The Goose Guangdong virus refers to the strain A/Goose/Guangdong/1/96 (Gs/Gd)-like H5N1 HPAI viruses. It is a strain of the Influenzavirus A subtype H5N1 virus that was first detected in a goose in Guangdong in 1996. It is an HPAI virus, meaning that it can kill a very high percentage of chickens in a flock in mere days. It is believed to be the immediate precursor of the current dominant strain of HPAI A(H5N1) that evolved from 1999 to 2002 creating the Z genotype that is spreading globally and is epizootic and panzootic, killing tens of millions of birds and spurring the culling of hundreds of millions of others to stem its spread.

Veterinary virology is the study of viruses in non-human animals. It is an important branch of veterinary medicine.
Avian metapneumovirus (aMPV), also known as turkey rhinotracheitis or swollen head syndrome, causes a variety of disease syndromes in birds, depending on the bird species and virus type.
Amur virus (AMRV) is a zoonotic negative-sense single-stranded RNA virus. It may be a member of the genus Orthohantavirus, but it has not be definitively classified as a species and may only be a strain. It has been identified as a causative agent of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome.
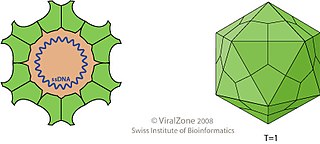
Circovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Circoviridae. Birds and pigs serve as natural hosts, though dogs have been shown to be infected as well. It is a single stranded DNA virus (ssDNA). There are 49 species in this genus. Some members of this genus cause disease: PCV-1 is non pathogenic, while PCV-2 causes postweaning multisystemic wasting syndrome (PMWS).
Bat mastadenovirus A, formerly Bat adenovirus TJM, is a species of the genus Mastadenovirus of the family Adenoviridae. It is a double stranded DNA virus with no RNA sequence. The designation TJM refers to the strain as there are several species of Bat adenoviruses in three groups 1, 2, and 3.
Acciptrid herpesvirus 1 (AcHV-1) is an unaccepted species of virus suggested to belong to the order Herpesvirales and family Herpesviridae. It was isolated from a bald eagle.
Anhembi orthobunyavirus, also called Anhembi virus (AMBV), is a species of virus. It was initially considered a strain of Wyeomyia virus, belonging serologically to the Bunyamwera serogroup of bunyaviruses. In 2018 it was made its own species. It was isolated from the rodent - Proechimys iheringi - and a mosquito - Phoniomyia pilicauda - in São Paulo, Brazil.

Egg drop syndrome '76 is a viral disease that affects birds, notably chickens, ducks, geese and swans. It is characterised by a sudden drop in production of eggs as well as its eggshell quality in apparent healthy laying birds.
Duck circovirus (DuCV) is a type of virus found in ducks. Strains of the virus have predominantly been found in China, though strains have also been isolated from ducks in Germany and the United States.

Quaranjavirus is a genus of enveloped RNA viruses, one of seven genera in the virus family Orthomyxoviridae. The genome is single-stranded, negative-sense segmented RNA, generally with six segments. The genus contains two species: Johnston Atoll virus and Quaranfil virus; it has been proposed to contain species or strains including Cygnet River virus, Lake Chad virus, Tyulek virus and Wellfleet Bay virus. Quaranjaviruses predominantly infect arthropods and birds; As of March 2015, Quaranfil quaranjavirus is the only member of the genus to have been shown to infect humans. The Quaranfil and Johnston Atoll viruses are transmitted between vertebrates by ticks, resembling members of Thogotovirus, another genus of Orthomyxoviridae.

Avian metaavulavirus 2, formerly Avian paramyxovirus 2, is a species of virus belonging to the family Paramyxoviridae and genus Metaavulavirus. The virus is a negative strand RNA virus containing a monopartite genome. Avian metaavulavirus 2 is one of nine species belonging to the genus Metaavulavirus. The most common serotype of Avulavirinae is serotype 1, the cause of Newcastle disease (ND). Avian metaavulavirus 2 has been known to cause disease, specifically mild respiratory infections in domestic poultry, including turkeys and chickens, and has many economic effects on egg production and poultry industries. The virus was first isolated from a strain in Yucaipa, California in 1956. Since then, other isolates of the virus have been isolated worldwide.










