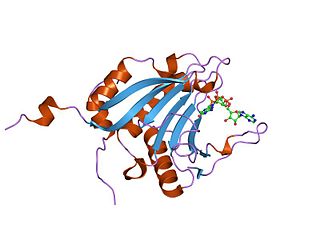
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF4EBP1 gene.

Polyadenylate-binding protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PABPC1 gene. The protein PABP1 binds mRNA and facilitates a variety of functions such as transport into and out of the nucleus, degradation, translation, and stability. There are two separate PABP1 proteins, one which is located in the nucleus (PABPN1) and the other which is found in the cytoplasm (PABPC1). The location of PABP1 affects the role of that protein and its function with RNA.

Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E, also known as eIF4E, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF4E gene.

Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4 gamma 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF4G2 gene.

Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 subunit E (eIF3e) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF3E gene.

Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4 gamma 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF4G1 gene.

Translation initiation factor eIF-2B subunit beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF2B2 gene.

Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 subunit A (eIF3a) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF3A gene. It is one of the subunits of Eukaryotic initiation factor 3 (eIF3) a multiprotein complex playing major roles in translation initiation in eukaryotes.

Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2-alpha kinase 3, also known as protein kinase R (PKR)-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the EIF2AK3 gene.

Translation initiation factor eIF-2B subunit alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF2B1 gene.

MAP kinase-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MKNK1 gene.

Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 subunit I (eIF3i) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF3I gene.

Eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-I is a 46 kDa cytosolic protein that, in humans, is encoded by the EIF4A1 gene, which is located on chromosome 17. It is the most prevalent member of the eIF4A family of ATP-dependant RNA helicases, and plays a critical role in the initiation of cap-dependent eukaryotic protein translation as a component of the eIF4F translation initiation complex. eIF4A1 unwinds the secondary structure of RNA within the 5'-UTR of mRNA, a critical step necessary for the recruitment of the 43S preinitiation complex, and thus the translation of protein in eukaryotes. It was first characterized in 1982 by Grifo, et al., who purified it from rabbit reticulocyte lysate.

Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF4B gene.

Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 subunit H (eIF3h) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF3H gene.

Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 subunit F (eIF3f) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF3F gene.

Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 subunit D (eIF3d) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF3D gene.

Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E type 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF4E2 gene. It belongs to the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E family.

Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF4EBP2 gene.
The eukaryotic initiation factor-4A (eIF4A) family consists of 3 closely related proteins EIF4A1, EIF4A2, and EIF4A3. These factors are required for the binding of mRNA to 40S ribosomal subunits. In addition these proteins are helicases that function to unwind double-stranded RNA.
























