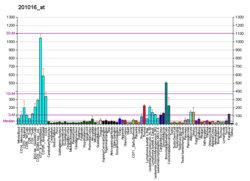
| EIF1AX | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | EIF1AX , EIF1A, EIF1AP1, EIF4C, eIF-1A, eIF-4C, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 1A, X-linked, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 1A X-linked | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 300186; MGI: 95298; HomoloGene: 20364; GeneCards: EIF1AX; OMA:EIF1AX - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 1A, X-chromosomal (eIF1A) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF1AX gene. [5] [6] [7] This gene encodes an essential eukaryotic translation initiation factor. The protein is a component of the 43S pre-initiation complex (PIC), which mediates the recruitment of the small 40S ribosomal subunit to the 5' cap of messenger RNAs. [7]