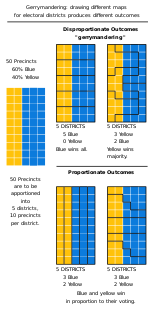
Gerrymandering is a practice intended to establish a political advantage for a particular party or group by manipulating district boundaries.
Proportional representation (PR) characterizes electoral systems in which divisions in an electorate are reflected proportionately in the elected body—each citizen voter being represented proportionately as by Evaluative Proportional Representation located in Section 5.5.5, or by each party being represented proportionately. If n% of the electorate support a particular political party as their favorite, then roughly n% of seats will be won by that party. The essence of such systems is that all votes contribute to the result—not just a plurality, or a bare majority. The most prevalent forms of proportional representation all require the use of multiple-member voting districts, as it is not possible to fill a single seat in a proportional manner. In fact, the implementations of PR that achieve the highest levels of proportionality tend to include districts with large numbers of seats.

The Electoral College is a body of electors established by the United States Constitution, constituted every four years for the sole purpose of electing the president and vice president of the United States. The Electoral College consists of 538 electors, and an absolute majority of 270 electoral votes is required to win an election. Pursuant to Article II, Section 1, Clause 2, the legislature of each state determines the manner by which its electors are chosen. Each state's number of electors is equal to the combined total of the state's membership in the Senate and House of Representatives; currently there are 100 senators and 435 representatives. Additionally, the Twenty-third Amendment provides that the District of Columbia (D.C.) is entitled to a number of electors no greater than that of the least populous state.
Elections Canada is an independent, non-partisan agency reporting directly to the Parliament of Canada. Its ongoing responsibility is to ensure that Canadians can exercise their choices in federal elections and referendums through an open and impartial process. Elections Canada is the sole agency responsible for administering Canadian federal elections.
An electoral district, also known as an election district, legislative district, voting district, constituency, riding, ward, division, (election) precinct, electoral area, or electorate, is a territorial subdivision for electing members to a legislative body. Generally, only voters (constituents) who reside within the district are permitted to vote in an election held there. From a single district, a single member or multiple members might be chosen. Members might be chosen by a first-past-the-post system or a proportional representative system, or another voting method entirely. Members might be chosen through a direct election under universal suffrage, an indirect election, or another form of suffrage.
This is a list of past arrangements of Canada's electoral districts. Each district sends one member to the House of Commons of Canada. In 1999 and 2003, the Legislative Assembly of Ontario was elected using the same districts within that province. 96 of Ontario's 107 provincial electoral districts, roughly those outside Northern Ontario, remain coterminous with their federal counterparts.

An electoral district in Canada, also known as a "constituency" or a "riding", is a geographical constituency upon which Canada's representative democracy is based. It is officially known in Canadian French as a circonscription, but frequently called a comté (county).

For the purpose of electing members of the Victorian Legislative Assembly, one of the two houses of the Parliament of the Australian State of Victoria, the State is divided into 88 single-member electoral districts, commonly referred to as "seats" or "electorates". The Legislative Assembly has had 88 electorates since the 1985 election, increased from 81 previously.
This is a list of current and former electoral divisions for the Legislative Assembly of Queensland, the state legislature for Queensland, Australia.
A ward is a local authority area, typically used for electoral purposes. Wards are usually named after neighbourhoods, thoroughfares, parishes, landmarks, geographical features and in some cases historical figures connected to the area. It is common in the United States for wards to simply be numbered.
The wards and electoral divisions in the United Kingdom are electoral districts at sub-national level represented by one or more councillors. The ward is the primary unit of English electoral geography for civil parishes and borough and district councils, electoral ward is the unit used by Welsh principal councils, while the electoral division is the unit used by English county councils and some unitary authorities. Each ward/division has an average electorate of about 5,500 people, but ward-population counts can vary substantially. As at the end of 2014 there were 9,456 electoral wards/divisions in the UK.
Logan is an electoral district in southern Queensland, Australia.
A State Electoral District is an electorate within the Lower House or Legislative Assembly of Australian states and territories. Most state electoral districts send a single member to a state or territory's parliament using the preferential method of voting. The area of a state electoral district is dependent upon the Electoral Acts in the various states and vary in area between them. At present, there are 409 state electoral districts in Australia.
Electoral reform is change in electoral systems to improve how public desires are expressed in election results. That can include reforms of:
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.






