
Romanesque architecture is an architectural style of medieval Europe characterized by semi-circular arches. There is no consensus for the beginning date of the Romanesque style, with proposals ranging from the 6th to the 11th century, this later date being the most commonly held. In the 12th century it developed into the Gothic style, marked by pointed arches. Examples of Romanesque architecture can be found across the continent, making it the first pan-European architectural style since Imperial Roman architecture. The Romanesque style in England and Sicily is traditionally referred to as Norman architecture.

Soissons is a commune in the northern French department of Aisne, in the region of Hauts-de-France. Located on the river Aisne, about 100 kilometres (62 mi) northeast of Paris, it is one of the most ancient towns of France, and is probably the ancient capital of the Suessiones. Soissons is also the see of an ancient Roman Catholic diocese, whose establishment dates from about 300, and it was the location of a number of church synods called "Council of Soissons".

A crypt is a stone chamber beneath the floor of a church or other building. It typically contains coffins, sarcophagi, or religious relics.

Anglo-Saxon architecture was a period in the history of architecture in England from the mid-5th century until the Norman Conquest of 1066. Anglo-Saxon secular buildings in Britain were generally simple, constructed mainly using timber with thatch for roofing. No universally accepted example survives above ground. Generally preferring not to settle within the old Roman cities, the Anglo-Saxons built small towns near their centres of agriculture, at fords in rivers or sited to serve as ports. In each town, a main hall was in the centre, provided with a central hearth.

Rose window is often used as a generic term applied to a circular window, but is especially used for those found in Gothic cathedrals and churches. The windows are divided into segments by stone mullions and tracery. The term rose window was not used before the 17th century and comes from the English flower name rose.

In Christian architecture the baptistery or baptistry is the separate centrally planned structure surrounding the baptismal font. The baptistery may be incorporated within the body of a church or cathedral, and provided with an altar as a chapel. In the early Church, the catechumens were instructed and the sacrament of baptism was administered in the baptistery.

Pre-Romanesque art and architecture is the period in European art from either the emergence of the Merovingian kingdom in about 500 AD or from the Carolingian Renaissance in the late 8th century, to the beginning of the 11th century Romanesque period. The term is generally used in English only for architecture and monumental sculpture, but here all the arts of the period are briefly described.

Saint-Pierre de Montmartre is one of the oldest surviving churches in Paris, second to the Abbey of Saint-Germain-des-Pres, but the lesser known of the two main churches in Montmartre, the other being the more famous 19th-century Sacré-Cœur Basilica, just above it. Saint-Pierre de Montmartre, begun in 1133, was the church of the prestigious Montmartre Abbey, destroyed in the French Revolution.

Jouarre is a commune in the Seine-et-Marne department in the Île-de-France region in north-central France.

French architecture consists of numerous architectural styles that either originated in France or elsewhere and were developed within the territories of France.
The opus gallicum was a technique of construction whereby precise holes were created in stone masonry for the insertion of wooden beams to create a wooden infrastructure. The technique was so named because, though its presence is attested in protohistoric times, its use was common enough in Gaul to merit mention in Julius Caesar's Commentarii de Bello Gallico and was frequently employed in the Merovingian era. The technique was imported by the Normans into the Molise, where it was used extensively in the raising of castles in a short time. Gaulish masons are even known to have brought the technique from Merovingian Francia to Anglo-Saxon England during the 7th and 8th centuries and employed it in church architecture.

Fréjus Cathedral is a Roman Catholic church located in the town of Fréjus in the Var department of Provence, southeast France, and dedicated to Saint Leontius of Fréjus.
The architecture of Provence includes a rich collection of monuments from the Roman era, Cistercian monasteries from the Romanesque period, medieval castles and fortifications, as well as numerous hilltop villages and fine churches. Provence was a very poor region after the 18th century, but in the 20th century it had an economic revival and became the site of one of the most influential buildings of the 20th century, the Unité d'Habitation of the architect Le Corbusier in Marseille.

Jouarre Abbey is a Benedictine abbey in Jouarre in the département of Seine-et-Marne.

The Abbey Church of Saint Peter and Saint Paul, Monkwearmouth–Jarrow, known simply as Monkwearmouth–Jarrow Abbey, was a Benedictine double monastery in the Kingdom of Northumbria, England.

Agilberta, also known as Aguilberta of Jouarre and Gilberta of Jouarre, is a Benedictine French saint, venerated in both the Roman Catholic Church and Antiochian Orthodox Church. She was a nun and the second abbess of the Jouarre Abbey, in the département of Seine-et-Marne. Agilberta was a relative of Ebrigisil and Ado, who founded Jouarre in 660. Her brother, Agilbert, was bishop of Paris. Agilberta's sister, Balda, was Jouarre's third abbess.
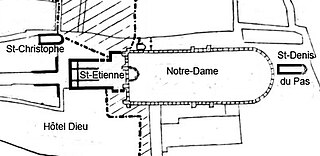
The Basilica and Cathedral of Saint-Étienne in Paris, on the Île de la Cité, was an early Christian church that preceded Notre-Dame de Paris. It was built in the 4th or 5th century, directly in front of the location of the modern cathedral, and just 250 meters from the royal palace. It became one of the wealthiest and most prestigious churches in France. Nothing remains above the ground of the original cathedral. It was demolished beginning in about 1163, when construction began on Notre-Dame de Paris. Vestiges of the foundations remain beneath the pavement of the square in front of Notre-Dame and beneath the west front of the cathedral. The church was built and rebuilt over the years in the Merovingian, Carolingian and Romanesque architectural styles.

























