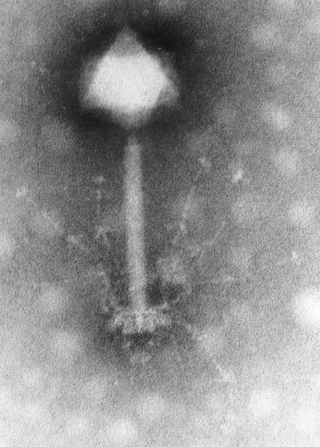
Myoviridae was a family of bacteriophages in the order Caudovirales. The family Myoviridae and order Caudovirales have now been abolished, with the term myovirus now used to refer to the morphology of viruses in this former family. Bacteria and archaea serve as natural hosts. There were 625 species in this family, assigned to eight subfamilies and 217 genera.
Uetakevirus is a genus of viruses in the order Caudovirales, in the family Podoviridae. Bacteria serve as natural hosts. There are three species in this genus. These phages are temperate and infect Salmonella and Escherichia coli.
Twortvirus is a genus of viruses in the order Caudovirales, in the family Herelleviridae, in the subfamily Twortvirinae. Bacteria serve as natural hosts. There is only one species in this genus: Staphylococcus virus Twort.
Tequatrovirus is a genus of viruses in subfamily Tevenvirinae of family Straboviridae. Gram-negative bacteria serve as the natural host, with transmission achieved through passive diffusion. There are 84 species in this genus.
Felixounavirus is a genus of viruses in the order Caudovirales, in the family Myoviridae. Bacteria serve as natural hosts, with transmission achieved through passive diffusion. There are currently 16 species in this genus, including the type species Salmonella virus FelixO1.
Hapunavirus is a genus of viruses in the class Caudoviricetes, not assigned to a subfamily. Bacteria serve as the natural host, with transmission achieved through passive diffusion. There are two species in this genus. Hapunavirus was classified in the family Myoviridae.
Bixzunavirus is a genus of viruses in the subfamily Ceeclamvirinae. Bacteria serve as natural hosts, with transmission achieved through passive diffusion. There are eight species in this genus. Bixzunavirus were previously classified under the order Caudovirales, in the family Myoviridae.
Muvirus is a genus of viruses in the order Caudovirales, in the family Myoviridae. Bacteria serve as natural hosts, with transmission achieved through passive diffusion. There are two species in this genus.
Pbunavirus is a genus of viruses in the order Caudovirales, in the family Myoviridae. Bacteria serve as natural hosts. There are 27 species in this genus.
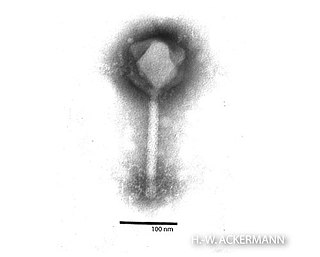
Phikzvirus is a genus of viruses in the order Caudovirales, in the family Chimalliviridae. Bacteria serve as natural hosts. There are three species in this genus.
Rosenblumvirus is a genus of viruses in the order Caudovirales, in the family Rountreeviridae, in the subfamily Rakietenvirinae. Gram positive bacteria serve as natural hosts, with transmission achieved through passive diffusion. There are 12 species in this genus.
Salasvirus is a genus of viruses in the order Caudovirales, in the family Salasmaviridae, in the subfamily Picovirinae. Bacteria serve as natural hosts. There are four species in this genus.
Fromanvirus is a genus of viruses in the order Caudovirales, in the family Siphoviridae. Bacteria serve as natural hosts, with transmission achieved through passive diffusion. There are 59 species in this genus.
Ravinvirus is a genus of viruses in the order Caudovirales, in the family Siphoviridae. Bacteria serve as natural hosts, with transmission achieved through passive diffusion. There is only one species in this genus: Escherichia virus N15.
Lomovskayavirus is a genus of viruses in the order Caudovirales, in the family Siphoviridae. Bacteria serve as natural hosts. There are two species in this genus.
Psimunavirus is a genus of viruses in the family Siphoviridae. Bacteria and archaea serve as the natural host, with transmission achieved through passive diffusion. There is only one species in this genus: Psimunavirus psiM2.
Spbetavirus is a genus of viruses in the order Caudovirales, in the family Siphoviridae. Bacteria serve as natural hosts. There is only one species in this genus: Bacillus virus SPbeta.
Tequintavirus is a genus of viruses in the order Caudovirales, in the family Demerecviridae. Bacteria serve as the natural host, with transmission achieved through passive diffusion. There are currently 22 species in this genus, including the type species Escherichia virus T5.
Tunavirus is a genus of viruses in the order Caudovirales, in the family Drexlerviridae. Bacteria serve as natural hosts. There are currently 14 species in this genus, including the type species Escherichia virus T1.
Yuavirus is a genus of viruses in the family Siphoviridae, unassigned to a sub-family. Bacteria serve as the natural host, with transmission achieved through passive diffusion. There are six species in this genus.

