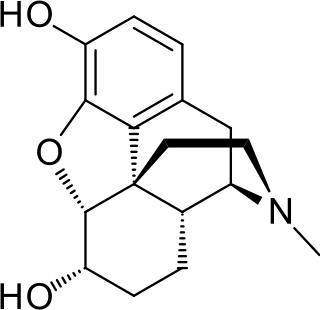
Hydrocodone, sold under the brand name Hysingla among others, is an opioid used to treat severe pain of a prolonged duration, if other measures are not sufficient. It also used as a cough suppressant in adults. It is taken by mouth. Typically it is sold as the combinations acetaminophen/hydrocodone or ibuprofen/hydrocodone. By itself it is sold in a long acting formulation.

Morphine is a pain medication of the opiate family which is found naturally in a number of plants and animals. It acts directly on the central nervous system (CNS) to decrease the feeling of pain. It can be taken for both acute pain and chronic pain. It is frequently used for pain from myocardial infarction and during labor. It can be given by mouth, by injection into a muscle, by injection under the skin, intravenously, injection into the space around the spinal cord, or rectally. Maximum effect is reached after about 20 minutes when given intravenously and after 60 minutes when given by mouth, while duration of effect is 3–7 hours. Long-acting formulations also exist.
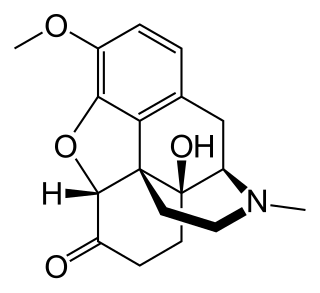
Oxycodone, sold under brand name OxyContin among others, is an opioid medication used for treatment of moderate to severe pain. It is usually taken by mouth, and is available in immediate release and controlled release formulations. Onset of pain relief typically begins within 15 minutes and lasts for up to six hours with the immediate release formulation. In the United Kingdom, it is available by injection. Combination products are also available with paracetamol (acetaminophen) or aspirin.

Hydromorphone, also known as dihydromorphinone, and sold under the brand name Dilaudid among others, is an opioid used to treat moderate to severe pain. Long term use is typically only recommended for pain due to cancer. It may be used by mouth or by injection into a vein, muscle, or under the skin. Effects generally begin within half an hour and last for up to five hours.

The Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It represents action in line with treaty commitments under the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, the Convention on Psychotropic Substances, and the United Nations Convention Against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances.

Opioid use disorder is a problematic pattern of opioid use that causes significant impairment or distress. Symptoms of the disorder include a strong desire to use opioids, increased tolerance to opioids, failure to fulfill obligations, trouble reducing use, and withdrawal syndrome with discontinuation. Opioid withdrawal symptoms may include nausea, muscle aches, diarrhea, trouble sleeping, or a low mood. Addiction and dependence are components of a substance use disorder. Complications may include opioid overdose, suicide, HIV/AIDS, hepatitis C, marriage problems, or unemployment.
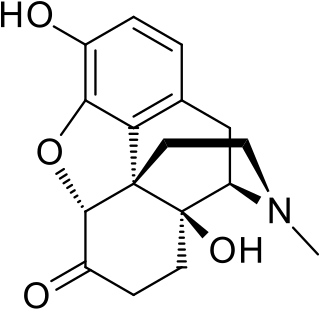
Oxymorphone, sold under the brand names Numorphan among others, is a powerful semi-synthetic opioid analgesic (painkiller). Pain relief after injection begins after about 5–10 minutes and 15–30 minutes after rectal administration, and lasts about 3–4 hours for immediate-release tablets and 12 hours for extended-release tablets.

Dihydrocodeine is a semi-synthetic opioid analgesic prescribed for pain or severe dyspnea, or as an antitussive, either alone or compounded with paracetamol (acetaminophen) or aspirin. It was developed in Germany in 1908 and first marketed in 1911.
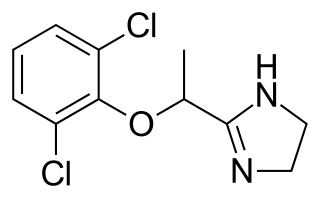
Lofexidine, sold under the brand name Lucemyra among others, is a medication historically used to treat high blood pressure, but more commonly used to help with the physical symptoms of opioid withdrawal. It is taken by mouth. It is an α2A adrenergic receptor agonist. It was approved for use by the Food and Drug Administration in the United States in 2018.

Nicocodeine is an opioid analgesic and cough suppressant, an ester of codeine closely related to dihydrocodeine and the codeine analogue of nicomorphine. It is not commonly used in most countries, but has activity similar to other opiates. Nicocodeine and nicomorphine were introduced in 1957 by Lannacher Heilmittel of Austria. Nicocodeine is metabolised in the liver by demethylation to produce nicomorphine, also known as 6-nicotinoylmorphine, and subsequently further metabolised to morphine. Side effects are similar to those of other opiates and include itching, nausea and respiratory depression. Related opioid analogues such as nicomorphine and nicodicodeine were first synthesized. The definitive synthesis, which involves treating anhydrous codeine base with nicotinic anhydride at 130 °C, was published by Pongratz and Zirm in Monatshefte für Chemie in 1957, simultaneously with the two analogues in an article about amides and esters of various organic acids.

Acetyldihydrocodeine is an opiate derivative discovered in Germany in 1914 and was used as a cough suppressant and analgesic. It is not commonly used, but has activity similar to other opiates. Acetyldihydrocodeine is a very close relative derivative of Thebacon, where only the 6-7 double bond is unsaturated. Acetyldihydrocodeine can be described as the 6-acetyl derivative of dihydrocodeine and is metabolised in the liver by demethylation and deacetylation to produce dihydromorphine.

Diacetyldihydromorphine is a potent opiate derivative developed in Germany in 1929 which is rarely used in some countries for the treatment of severe pain such as that caused by terminal cancer, as another form of diamorphine. Diacetyldihydromorphine is fast-acting and longer-lasting than diamorphine, with a duration of action of around 4-7 hours.
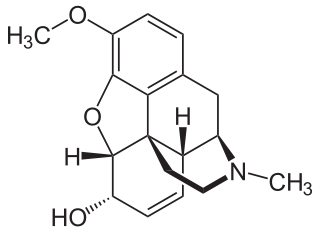
Codeine is an opiate used to treat pain, as a cough medicine, and for diarrhea. It is typically used to treat mild to moderate degrees of pain. Greater benefit may occur when combined with paracetamol (acetaminophen) or a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) such as aspirin or ibuprofen. Evidence does not support its use for acute cough suppression in children or adults. In Europe it is not recommended as a cough medicine in those under twelve years of age. It is generally taken by mouth. It typically starts working after half an hour with maximum effect at two hours. Its effects last for about four to six hours.
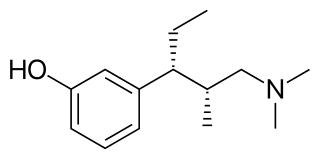
Tapentadol is a centrally acting opioid analgesic of the benzenoid class with a dual mode of action as an agonist of the μ-opioid receptor and as a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (NRI). Analgesia occurs within 32 minutes of oral administration, and lasts for 4–6 hours.

Allylprodine is an opioid analgesic that is an analog of prodine. It was discovered by Hoffman-La Roche in 1957 during research into the related drug pethidine. Derivatives were tested to prove the theory that phenolic & non-phenolic opioids bind at different sites of the opiate receptor.

Meprodine is an opioid analgesic that is an analogue of pethidine (meperidine). It is closely related to the drug prodine, the only difference being that meprodine has an ethyl group rather than a methyl at the 3-position of the piperidine ring.

Benzethidine is a 4-phenylpiperidine derivative that is related to the clinically used opioid analgesic drug pethidine.
In the United States, prescription monitoring programs (PMPs) or prescription drug monitoring programs (PDMPs) are state-run programs which collect and distribute data about the prescription and dispensation of federally controlled substances and, as the individual states deem appropriate, other potentially addictive or abusable prescription drugs. PMPs help to prevent adverse drug-related events through opioid overdoses, drug diversion, and substance abuse by decreasing the amount and/or frequency of opioid prescribing.

Buprenorphine/naloxone, sold under the brand name Suboxone among others, is a combination medication that includes buprenorphine and naloxone. In combination with counselling, it is used to treat opioid use disorder. It decreases withdrawal symptoms for about 24 hours. Buprenorphine/naloxone is available for use in two different forms, under the tongue or in the cheek.