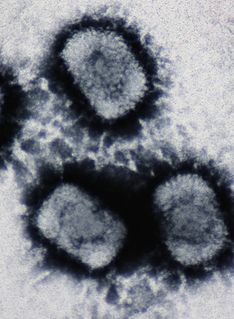
A DNA virus is a virus that has a genome made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) that is replicated by a DNA polymerase. They can be divided between those that have two strands of DNA in their genome, called double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) viruses, and those that have one strand of DNA in their genome, called single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) viruses. dsDNA viruses primarily belong to two realms: Duplodnaviria and Varidnaviria, and ssDNA viruses are almost exclusively assigned to the realm Monodnaviria, which also includes some dsDNA viruses. Additionally, many DNA viruses are unassigned to higher taxa. Reverse transcribing viruses, which have a DNA genome that is replicated through an RNA intermediate by a reverse transcriptase, are classified into the kingdom Pararnavirae in the realm Riboviria.

A retrovirus is a type of virus that inserts a DNA copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades, thus changing the genome of that cell. Once inside the host cell's cytoplasm, the virus uses its own reverse transcriptase enzyme to produce DNA from its RNA genome, the reverse of the usual pattern, thus retro (backwards). The new DNA is then incorporated into the host cell genome by an integrase enzyme, at which point the retroviral DNA is referred to as a provirus. The host cell then treats the viral DNA as part of its own genome, transcribing and translating the viral genes along with the cell's own genes, producing the proteins required to assemble new copies of the virus.

A reverse transcriptase (RT) is an enzyme used to generate complementary DNA (cDNA) from an RNA template, a process termed reverse transcription. Reverse transcriptases are used by viruses such as HIV and hepatitis B to replicate their genomes, by retrotransposon mobile genetic elements to proliferate within the host genome, and by eukaryotic cells to extend the telomeres at the ends of their linear chromosomes. Contrary to a widely held belief, the process does not violate the flows of genetic information as described by the classical central dogma, as transfers of information from RNA to DNA are explicitly held possible.

Parvoviruses are a family of animal viruses that constitute the family Parvoviridae. They have linear, single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) genomes that typically contain two genes encoding for a replication initiator protein, called NS1, and the protein the viral capsid is made of. The coding portion of the genome is flanked by telomeres at each end that form into hairpin loops that are important during replication. Parvovirus virions are small compared to most viruses, at 23–28 nanometers in diameter, and contain the genome enclosed in an icosahedral capsid that has a rugged surface.

Hepadnaviridae is a family of viruses. Humans, apes, and birds serve as natural hosts. There are currently 18 species in this family, divided among 5 genera. Its best-known member is hepatitis B virus. Diseases associated with this family include: liver infections, such as hepatitis, hepatocellular carcinomas, and cirrhosis. It is the sole accepted family in the order Blubervirales.

Picornaviruses are a group of related nonenveloped RNA viruses which infect vertebrates including fish, mammals, and birds. They are viruses that represent a large family of small, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA viruses with a 30 nm icosahedral capsid. The viruses in this family can cause a range of diseases including the common cold, poliomyelitis, meningitis, hepatitis, and paralysis.
Microviridae is a family of bacteriophages with a single-stranded DNA genome. The name of this family is derived from the ancient Greek word μικρός (mikrós), meaning "small". This refers to the size of their genomes, which are among the smallest of the DNA viruses. Enterobacteria, intracellular parasitic bacteria, and spiroplasma serve as natural hosts. There are 22 species in this family, divided among seven genera and two subfamilies.

Geminiviridae is a family of plant viruses that encode their genetic information on a circular genome of single-stranded (ss) DNA. There are 520 species in this family, assigned to 14 genera. Diseases associated with this family include: bright yellow mosaic, yellow mosaic, yellow mottle, leaf curling, stunting, streaks, reduced yields. They have single-stranded circular DNA genomes encoding genes that diverge in both directions from a virion strand origin of replication. According to the Baltimore classification they are considered class II viruses. It is the largest known family of single stranded DNA viruses.
Pseudoviridae is a family of viruses, which includes three genera.

Tombusviridae is a family of single-stranded positive sense RNA plant viruses. There are three subfamilies, 17 genera, and 95 species in this family. The name is derived from Tomato bushy stunt virus (TBSV).

Φ6 is the best-studied bacteriophage of the virus family Cystoviridae. It infects Pseudomonas bacteria. It has a three-part, segmented, double-stranded RNA genome, totalling ~13.5 kb in length. Φ6 and its relatives have a lipid membrane around their nucleocapsid, a rare trait among bacteriophages. It is a lytic phage, though under certain circumstances has been observed to display a delay in lysis which may be described as a "carrier state".
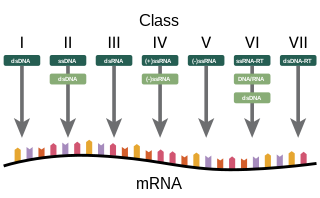
Baltimore classification is a system used to classify viruses based on their manner of messenger RNA (mRNA) synthesis. By organizing viruses based on their manner of mRNA production, it is possible to study viruses that behave similarly as a distinct group. Seven Baltimore groups are described that take into consideration whether the viral genome is made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) or ribonucleic acid (RNA), whether the genome is single- or double-stranded, and whether the sense of a single-stranded RNA genome is positive or negative.
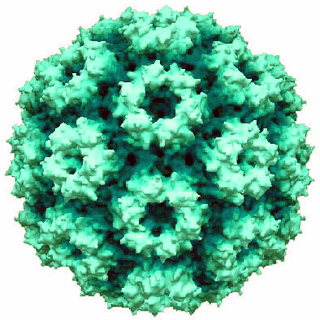
Cowpea chlorotic mottle virus, known by the abbreviation CCMV, is a virus that specifically infects the cowpea plant, or black-eyed pea. The leaves of infected plants develop yellow spots, hence the name "chlorotic". Similar to its "brother" virus, Cowpea mosaic virus (CPMV), CCMV is produced in high yield in plants. In the natural host, viral particles can be produced at 1–2 mg per gram of infected leaf tissue. Belonging to the bromovirus genus, cowpea chlorotic mottle virus (CCMV) is a small spherical plant virus. Other members of this genus include the brome mosaic virus (BMV) and the broad bean mottle virus (BBMV).

Iridoviridae is a family of viruses with double-stranded DNA genomes. Amphibians, fish, and invertebrates such as arthropods serve as natural hosts. There are currently 22 species in this family, divided among two subfamilies and seven genera.

Corticovirus is a genus of viruses in the family Corticoviridae. Corticoviruses are bacteriophages; that is, their natural hosts are bacteria. The genus contains two species. The name is derived from Latin cortex, corticis. However, prophages closely related to PM2 are abundant in the genomes of aquatic bacteria, suggesting that the ecological importance of corticoviruses might be underestimated. Bacteriophage PM2 was first described in 1968 after isolation from seawater sampled from the coast of Chile.

Ff phages is a group of almost identical filamentous phage including phages f1, fd, M13 and ZJ/2, which infect bacteria bearing the F fertility factor. The virion is a flexible filament measuring about 6 by 900 nm, comprising a cylindrical protein tube protecting a single-stranded circular DNA molecule at its core. The phage codes for only 11 gene products, and is one of the simplest viruses known. It has been widely used to study fundamental aspects of molecular biology. George Smith and Greg Winter used f1 and fd for their work on phage display for which they were awarded a share of the 2018 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Early experiments on Ff phages used M13 to identify gene functions, and M13 was also developed as a cloning vehicle, so the name M13 is sometimes used as an informal synonym for the whole group of Ff phages.

Positive-strand RNA viruses are a group of related viruses that have positive-sense, single-stranded genomes made of ribonucleic acid. The positive-sense genome can act as messenger RNA (mRNA) and can be directly translated into viral proteins by the host cell's ribosomes. Positive-strand RNA viruses encode an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) which is used during replication of the genome to synthesize a negative-sense antigenome that is then used as a template to create a new positive-sense viral genome.

Avian metaavulavirus 2, formerly Avian paramyxovirus 2, is a species of virus belonging to the family Paramyxoviridae and genus Metaavulavirus. The virus is a negative strand RNA virus containing a monopartite genome. Avian metaavulavirus 2 is one of nine species belonging to the genus Metaavulavirus. The most common serotype of Avulavirinae is serotype 1, the cause of Newcastle disease (ND). Avian metaavulavirus 2 has been known to cause disease, specifically mild respiratory infections in domestic poultry, including turkeys and chickens, and has many economic effects on egg production and poultry industries. The virus was first isolated from a strain in Yucaipa, California in 1956. Since then, other isolates of the virus have been isolated worldwide.

Monodnaviria is a realm of viruses that includes all single-stranded DNA viruses that encode an endonuclease of the HUH superfamily that initiates rolling circle replication of the circular viral genome. Viruses descended from such viruses are also included in the realm, including certain linear single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) viruses and circular double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) viruses. These atypical members typically replicate through means other than rolling circle replication.
Rolling hairpin replication (RHR) is a unidirectional, strand displacement form of DNA replication used by parvoviruses, a group of viruses that constitute the family Parvoviridae. Parvoviruses have linear, single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) genomes in which the coding portion of the genome is flanked by telomeres at each end that form hairpin loops. During RHR, these hairpin loops repeatedly unfold and refold to change the direction of DNA replication so that replication progresses in a continuous manner back and forth across the genome. RHR is initiated and terminated by an endonuclease encoded by parvoviruses that is variously called NS1 or Rep, and RHR is similar to rolling circle replication, which is used by ssDNA viruses that have circular genomes.
















