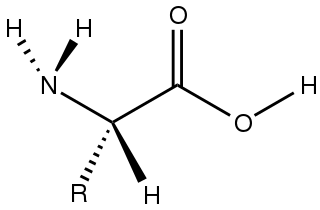
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha amino acids appear in the genetic code.
Proline (symbol Pro or P) is an organic acid classed as a proteinogenic amino acid (used in the biosynthesis of proteins), although it does not contain the amino group -NH
2 but is rather a secondary amine. The secondary amine nitrogen is in the protonated form (NH2+) under biological conditions, while the carboxyl group is in the deprotonated −COO− form. The "side chain" from the α carbon connects to the nitrogen forming a pyrrolidine loop, classifying it as a aliphatic amino acid. It is non-essential in humans, meaning the body can synthesize it from the non-essential amino acid L-glutamate. It is encoded by all the codons starting with CC (CCU, CCC, CCA, and CCG).

Glutamic acid is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can synthesize enough for its use. It is also the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate nervous system. It serves as the precursor for the synthesis of the inhibitory gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in GABA-ergic neurons.

Histidine (symbol His or H) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated –NH3+ form under biological conditions), a carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated –COO− form under biological conditions), and an imidazole side chain (which is partially protonated), classifying it as a positively charged amino acid at physiological pH. Initially thought essential only for infants, it has now been shown in longer-term studies to be essential for adults also. It is encoded by the codons CAU and CAC.

γ-Aminobutyric acid, or GABA, is the chief inhibitory neurotransmitter in the developmentally mature mammalian central nervous system. Its principal role is reducing neuronal excitability throughout the nervous system.

N-methyl-D-aspartic acid or N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) is an amino acid derivative that acts as a specific agonist at the NMDA receptor mimicking the action of glutamate, the neurotransmitter which normally acts at that receptor. Unlike glutamate, NMDA only binds to and regulates the NMDA receptor and has no effect on other glutamate receptors. NMDA receptors are particularly important when they become overactive during, for example, withdrawal from alcohol as this causes symptoms such as agitation and, sometimes, epileptiform seizures.
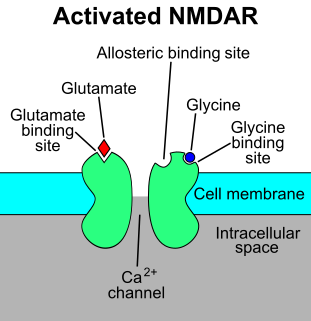
The N-methyl-D-aspartatereceptor (also known as the NMDA receptor or NMDAR), is a glutamate receptor and ion channel found in neurons. The NMDA receptor is one of three types of ionotropic glutamate receptors, the other two being AMPA and kainate receptors. Depending on its subunit composition, its ligands are glutamate and glycine (or D-serine). However, the binding of the ligands is typically not sufficient to open the channel as it may be blocked by Mg2+ ions which are only removed when the neuron is sufficiently depolarized. Thus, the channel acts as a “coincidence detector” and only once both of these conditions are met, the channel opens and it allows positively charged ions (cations) to flow through the cell membrane. The NMDA receptor is thought to be very important for controlling synaptic plasticity and mediating learning and memory functions.

Phenethylamine (PEA) is an organic compound, natural monoamine alkaloid, and trace amine, which acts as a central nervous system stimulant in humans. In the brain, phenethylamine regulates monoamine neurotransmission by binding to trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) and inhibiting vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2) in monoamine neurons. To a lesser extent, it also acts as a neurotransmitter in the human central nervous system. In mammals, phenethylamine is produced from the amino acid L-phenylalanine by the enzyme aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase via enzymatic decarboxylation. In addition to its presence in mammals, phenethylamine is found in many other organisms and foods, such as chocolate, especially after microbial fermentation.

In organic chemistry, a carbamate is a category of organic compounds with the general formula R2NC(O)OR and structure >N−C(=O)−O−, which are formally derived from carbamic acid. The term includes organic compounds, formally obtained by replacing one or more of the hydrogen atoms by other organic functional groups; as well as salts with the carbamate anion H2NCOO−.

Tautomers are structural isomers of chemical compounds that readily interconvert. The chemical reaction interconverting the two is called tautomerization. This conversion commonly results from the relocation of a hydrogen atom within the compound. The phenomenon of tautomerization is called tautomerism, also called desmotropism. Tautomerism is for example relevant to the behavior of amino acids and nucleic acids, two of the fundamental building blocks of life.
GABAB receptors (GABABR) are G-protein coupled receptors for gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), therefore making them metabotropic receptors, that are linked via G-proteins to potassium channels. The changing potassium concentrations hyperpolarize the cell at the end of an action potential. The reversal potential of the GABAB-mediated IPSP is –100 mV, which is much more hyperpolarized than the GABAA IPSP. GABAB receptors are found in the central nervous system and the autonomic division of the peripheral nervous system.

Cyanamide is an organic compound with the formula CN2H2. This white solid is widely used in agriculture and the production of pharmaceuticals and other organic compounds. It is also used as an alcohol-deterrent drug. The molecule features a nitrile group attached to an amino group. Derivatives of this compound are also referred to as cyanamides, the most common being calcium cyanamide (CaCN2).
Carbamic acid, which might also be called aminoformic acid or aminocarboxylic acid, is the chemical compound with the formula H2NCOOH. It can be obtained by the reaction of ammonia NH3 and carbon dioxide CO2 at very low temperatures, which also yields an equal amount of ammonium carbamate [NH4]+[NH2CO2]−. The compound is stable only up to about 250 K (−23 °C); at higher temperatures it decomposes into those two gases. The solid apparently consists of dimers, with the two molecules connected by hydrogen bonds between the two carboxyl groups –COOH.
Argiotoxins represent a class of polyamine toxins isolated from the orb-weaver spider.

Metabotropic glutamate receptor 3 (mGluR3) is an inhibitory Gi/G0-coupled G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) generally localized to presynaptic sites of neurons in classical circuits. However, in higher cortical circuits in primates, mGluR3 are localized post-synaptically, where they strengthen rather than weaken synaptic connectivity. In humans, mGluR3 is encoded by the GRM3 gene. Deficits in mGluR3 signaling have been linked to impaired cognition in humans, and to increased risk of schizophrenia, consistent with their expanding role in cortical evolution.

LY-307,452 is a drug used in neuroscience research, which was among the first compounds found that acts as a selective antagonist for the group II metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR2/3), and was useful in early studies of this receptor family, although it has largely been replaced by newer drugs such as LY-341,495. Its molecular formula is C21H25NO4

HYDIA is a drug that is used in neuroscience research, which acts as a potent and selective antagonist for the group II metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR2/3). It has been useful in the mapping of the group II mGluR receptor proteins and their molecular modeling. HYDIA is similar in structure to group II mGluR agonists such as eglumegad and LY-404,039, but the addition of the 3-hydroxy group reverses the activity to a competitive antagonist. Other derivatives such as the 3-benzyloxy ether are more potent antagonists than HYDIA itself.
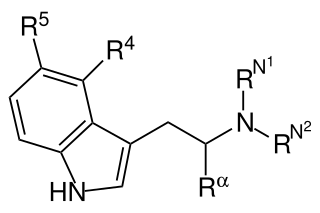
Substituted tryptamines, or serotonin analogues, are organic compounds which may be thought of as being derived from tryptamine itself. The molecular structures of all tryptamines contain an indole ring, joined to an amino (NH2) group via an ethyl (−CH2–CH2−) sidechain. In substituted tryptamines, the indole ring, sidechain, and/or amino group are modified by substituting another group for one of the hydrogen (H) atoms.

Kaitocephalin is a non-selective ionotropic glutamate receptor antagonist, meaning it blocks the action of the neurotransmitter glutamate. It is produced by the fungus Eupenicillium shearii. Although similar molecules have been produced synthetically, kaitocephalin is the only known naturally occurring glutamate receptor antagonist. There is some evidence that kaitocephalin can protect the brain and central nervous system, so it is said to have neuroprotective properties. Kaitocephalin protects neurons by inhibiting excitotoxicity, a mechanism which causes cell death by overloading neurons with glutamate. Because of this, it is of interest as a potential scaffold for drug development. Drugs based on kaitocephalin may be useful in treating neurological conditions, including Alzheimer's, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and stroke.

Phenylglycine is the organic compound with the formula C6H5CH(NH2)CO2H. It is a non-proteinogenic alpha amino acid related to alanine, but with a phenyl group in place of the methyl group. It is a white solid. The compound exhibits some biological activity.



















