
Makati, officially the City of Makati, is a highly urbanized city in the National Capital Region of the Philippines, known for being one of the leading financial centers in the country. As of 2013, the city has the highest concentration of multinational and local corporations in the Philippines. Major banks, corporations, department stores as well as foreign embassies are based in Makati. Makati is also known for being a major cultural and entertainment hub in Metro Manila. According to the 2020 census, it had a population of 629,616 people, making it the 47th most populous city in the country and 8th most populous in Metro Manila. Makati is one of the most densely populated city proper areas globally, ranking 8th worldwide and 2nd in the Philippines, after Manila, with a population density of 28,975 inhabitants per square kilometer.

Paco, formerly known as Dilao, is a district of Manila, Philippines, located south of the Pasig River and San Miguel, west of Santa Ana, southwest of Pandacan, north of Malate, northwest of San Andres Bukid, and east of Ermita. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 79,839 people.

Malate is a district of Manila, Philippines. Together with the district of Ermita, it serves as Manila's center for commerce and tourism.
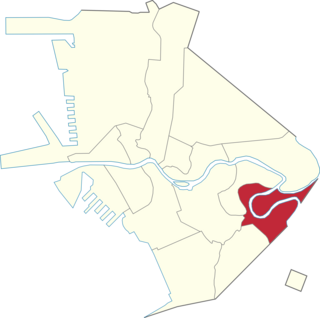
Santa Ana is a district in the City of Manila, Philippines. It is located on the city's southeast, bordering the cities of Mandaluyong and Makati in the east, the city districts of Paco and Pandacan in the west, and Santa Mesa in the north. It is part of the 6th congressional district of Manila, with thirty-five barangays. Based on the 2020 national census, the Philippine Statistics Authority reports that the district has a population of 203,598.

Namayan, also called Sapa and sometimes Lamayan, was an independent polity on the banks of the Pasig River in the Philippines. It is believed to have achieved its peak in 1175, and to have gone into decline sometime in the 13th century, although it continued to be inhabited until the arrival of European colonizers in the 1570s.

Manila, also known as Tondo until 1859, was a province of the Philippines that encompassed the former pre-Hispanic polities of Tondo, Maynila, and Namayan. In 1898, it comprised the city of Manila and 23 other municipalities. In 1901, the province was dissolved, with the city of Manila absorbing six of its smaller neighboring municipalities. The remaining part was merged with the adjacent district of Morong to form the province of Rizal.

Pablo Ocampo Street, also known simply as Ocampo Street and formerly and still referred to as Vito Cruz Street, is an inner-city main road in Manila, Philippines. It runs west–east for about 3.448 kilometers (2.142 mi), connecting the southern districts of Malate and San Andres southeast to the adjacent city of Makati.

Pedro Gil Street is an east-west inner city street and a tertiary national road in south-central Manila, Philippines. It is 3.65 kilometers (2.27 mi) long and spans the entire length of Ermita, Malate, Paco, and Santa Ana. The street is served by the Pedro Gil LRT Station along Taft Avenue and the Paco railway station along Quirino Avenue. It also continues towards the central Metro Manila cities of Mandaluyong and San Juan across the Pasig River as New Panaderos and General Kalentong Streets.

President Elpidio Quirino Avenue, more commonly known as Quirino Avenue, is a 6-10 lane divided highway in Manila, Philippines. It runs for 3.6 kilometers (2.2 mi) in a northeast–southwest direction from Nagtahan Bridge across Santa Mesa in the north to Roxas Boulevard in Malate in the south. It passes through the Paco and Pandacan districts and serves as a truck route between the Port Area and the South Luzon Expressway. North of Nagtahan Bridge, the road continues as Nagtahan Street. It is designated as part of Circumferential Road 2. It is named after Elpidio Quirino, the sixth President of the Philippines.

J. P. Rizal Avenue, also known as J. P. Rizal Street, is a major local avenue in Makati and Taguig, Metro Manila, Philippines. It is a contour collector road on the south bank of the Pasig River that runs east–west from Pateros Bridge at the Taguig–Pateros boundary to its intersection with Zobel Roxas, Delpan, and Tejeron Streets at the Makati–Manila boundary. It is a component of Radial Road 4 (R-4). The avenue was named after the Philippines' national hero, Dr. José P. Rizal.

Kalayaan Avenue is a major east–west route in Makati and Taguig, Metro Manila, Philippines. For most of its length, it runs parallel to Jose P. Rizal Avenue to the north from East Rembo near Fort Bonifacio to Barangay Singkamas by the border with Santa Ana, Manila. It is interrupted by Bel-Air Village between Rockwell Drive and Epifanio de los Santos Avenue (EDSA). The avenue east of EDSA is designated as a component of National Route 190 of the Philippine highway network.
Slums are traditionally described as dense urban settlements, usually displaying characteristics such as crowded and compact housing units, informal delivery of utilities, and unofficial recognition by local government. In the Philippines, residents of slum areas are commonly referred to as "squatters" and have historically been subject to relocation or forced demolition. With a steadily growing metropolitan area, Metro Manila is subject to a densifying population of slum dwellers—a 2014 article states that Manila has an estimated 4 million people living in slums, out of a total population of 21.3 million.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Metro Manila:

The following is an alphabetical list of articles related to the Philippine capital region of Metro Manila.

The President Sergio Osmeña Sr. Highway, also known as the South Superhighway, is a 4.595-kilometer (2.855 mi) major highway that links Quirino Avenue in Paco, Manila to Epifanio de los Santos Avenue (EDSA) and South Luzon Expressway (SLEX) at the Magallanes Interchange in Makati.

Greater Manila, officially the City of Greater Manila and sometimes referred to as the Greater Manila Area (GMA), was a chartered city that existed during the Japanese occupation of the Philippines in World War II, from 1942 to 1945. Governed by the Commonwealth of the Philippines, it served as a model for the present-day Metro Manila and the administrative functions of the governor of Metro Manila—both established three decades later during the administration of President Ferdinand Marcos. It was a merger of Manila, Quezon City, and the then-Rizal towns of Caloocan, Makati, Mandaluyong, Parañaque, Pasay, and San Juan, all present parts of Metro Manila.

Manila's 2nd congressional district is one of the six congressional districts of the Philippines in the city of Manila. It has been represented in the House of Representatives of the Philippines since 1916 and earlier in the Philippine Assembly from 1907 to 1916. The district consists of barangays 147 to 267 in the eastern part of the Manila district of Tondo, east of Dagupan Street, Estero de Vitas and Estero de Sunog Apog bordering Navotas and southern Caloocan. It is currently represented in the 19th Congress by Rolando M. Valeriano of the National Unity Party (NUP) and Asenso Manileño.

Manila's 5th congressional district is one of the six congressional districts of the Philippines in the city of Manila. It has been represented in the House of Representatives of the Philippines since 1987. The district consists of barangays 649 to 828 in the south Manila districts of Ermita, Intramuros, Malate, Port Area, San Andres and south Paco bordering the adjacent cities of Makati and Pasay. It is currently represented in the 19th Congress by William Irwin C. Tieng of Asenso Manileño and Lakas–CMD.




















