
Phenylpropanolamine (PPA), sold under many brand names, is a sympathomimetic agent which is used as a decongestant and appetite suppressant. It was previously commonly used in prescription and over-the-counter cough and cold preparations. The medication is taken by mouth.

Phenylephrine, sold under the brand names Neosynephrine and Sudafed PE among numerous others, is a medication used as a decongestant for uncomplicated nasal congestion, used to dilate the pupil, used to increase blood pressure, and used to relieve hemorrhoids. It can be taken by mouth, as a nasal spray, given by injection into a vein or muscle, applied to the skin, or as a rectal suppository.

Isoprenaline, also known as isoproterenol and sold under the brand name Isuprel among others, is a sympathomimetic medication which is used in the treatment of acute bradycardia, heart block, and rarely for asthma, among other indications. It is used by injection into a vein, muscle, fat, or the heart, by inhalation, and in the past under the tongue or into the rectum.

Metaraminol, also known as metaradrine and sold under the brand names Aramine and Pressonex among others, is a sympathomimetic medication which is used in the prevention and treatment of hypotension, particularly as a complication of anesthesia. It is given by intramuscular or intravenous administration.

Corbadrine, sold under the brand name Neo-Cobefrine and also known as levonordefrin and α-methylnorepinephrine, is a catecholamine sympathomimetic used as a topical nasal decongestant and vasoconstrictor in dentistry in the United States. It is usually used in a pre-mixed solution with local anesthetics, such as mepivacaine.
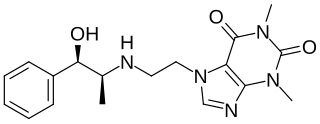
Cafedrine, sold under the brand name Akrinor among others, is a chemical linkage of norephedrine and theophylline and is a cardiac stimulant and antihypotensive agent used to increase blood pressure in people with hypotension. It has been marketed in Europe, South Africa, and Indonesia.
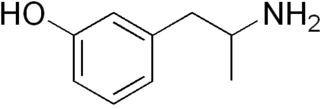
Gepefrine, also known as 3-hydroxyamphetamine or α-methyl-meta-tyramine and sold under the brand names Pressionorm and Wintonin, is a sympathomimetic medication used as an antihypotensive agent which has been marketed in Germany.

Mephentermine, sold under the brand name Wyamine among others, is a sympathomimetic medication which was previously used in the treatment of low blood pressure but is mostly no longer marketed. It is used by injection into a vein or muscle, by inhalation, and by mouth.

Norfenefrine, also known as meta-octopamine or norphenylephrine and sold under the brand name Novadral among others, is a sympathomimetic medication which is used in the treatment of hypotension. Along with its structural isomer p-octopamine and the tyramines, norfenefrine is a naturally occurring endogenous trace amine and plays a role as a minor neurotransmitter in the brain.

Oxyfedrine, sold under the brand names Ildamen and Myofedrin among others, is a sympathomimetic agent and coronary vasodilator which is used in the treatment of coronary heart disease, angina pectoris, and acute myocardial infarction. It is taken by mouth or intravenously.
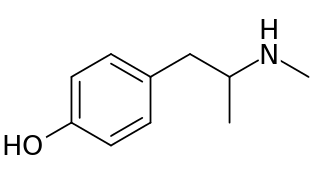
Pholedrine, also known as 4-hydroxy-N-methylamphetamine and sold under the brand names Paredrinol, Pulsotyl, and Veritol among others, is a sympathomimetic drug used in topical eye drops to dilate the pupil. It can be used to diagnose Horner's syndrome.

Metaterol, also known as isofenefrine, isopropylnoradrianol, and 3,β-dihydroxy-N-isopropylphenethylamine, is a sympathomimetic and bronchodilator of the phenethylamine family that was never marketed. It is structurally related to norfenefrine, phenylephrine, and etilefrine.

Cinnamedrine, also known as N-cinnamylephedrine, is a sympathomimetic drug with similar effects relative to those of ephedrine. It also has some local anesthetic activity. Cinnamedrine was previously used, in combination with analgesics, as an antispasmodic to treat dysmenorrhea in the over-the-counter drug Midol in the 1980s. There is a case series of the drug being abused as a psychostimulant.

Butidrine, sold under the brand names Betabloc, Butidrate, and Recetan among others, is a beta blocker related to pronethalol and propranolol that was developed in the 1960s. It is not cardioselective. It has membrane stabilizing activity but no intrinsic sympathomimetic activity. Similarly to certain other beta blockers, butidrine additionally possesses local anesthetic properties.
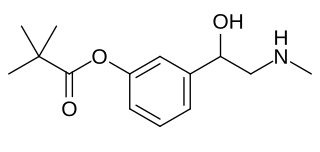
Pivenfrine, also known as pivalylphenylephrine or phenylephrine pivalate, is a sympathomimetic and mydriatic agent which was never marketed. It is the 3-pivalyl ester of phenylephrine. Pivenfrine has much greater lipophilicity than phenylephrine. Higher lipophilicity is known to greatly improve corneal permeability, as in dipivefrine. Another related compound is etilefrine pivalate.

Racefemine, sold under the brand names Dysmalgine and Evalgin, is a uterine spasmolytic and muscle relaxant of the amphetamine family. It is the racemic threo form of dextrofemine. The drug acts as a β-adrenergic receptor agonist and sympathomimetic. It appears to no longer be marketed. Other tocolytics with similar chemical structures as phenethylamines or amphetamines include bedoradrine, buphenine, fenoterol, hexoprenaline, isoxsuprine, ritodrine, and terbutaline.

Bufenadrine, also known as 2-tert-butyldiphenhydramine, is a drug described as an antiemetic, antihistamine, anticholinergic, and antiparkinsonian agent which was never marketed. It is the 2-tert-butyl analogue of diphenhydramine. The drug was found to produce stereoselective hepatotoxicity in animals and this led to the discontinuation of its development. Bufenadrine was first described in the literature by 1967. Its INNTooltip International Nonproprietary Name suffix "-drine" is generally for sympathomimetics but bufenadrine itself is not actually a sympathomimetic or related agent.

Norbudrine, also known as norbutrine or as N-cyclobutylnoradrenaline, is a drug of the phenethylamine and catecholamine families described as a sympathomimetic and bronchodilator which was never marketed. It is the N-cyclobutyl analogue of norepinephrine (noradrenaline). The drug was first described in the literature by 1966.

Trecadrine is a drug that was originally developed as an anti-ulcer agent but was found to act as a β3-adrenergic receptor agonist with potential anti-obesity and anti-diabetic properties. It is selective for the β3-adrenergic receptor, lacking activity at the β1- and β2-adrenergic receptors. The drug is orally active. Structurally, trecadrine is a substituted β-hydroxyamphetamine and derivative of β-hydroxy-N-methylamphetamine with a tricyclic moiety attached at the amine.

Clorprenaline, also known as isoprophenamine and known as clorprenaline hydrochloride in the case of the hydrochloride salt, is a sympathomimetic and bronchodilator medication which is marketed in Japan. It acts as a β-adrenergic receptor agonist or as a β-sympathomimetic. Brand names of clorprenaline in Japan are numerous and include Asnormal, Bazarl, Bronchon, Clopinerin, Conselt, Cosmoline, Fusca, Kalutein, Pentadoll, Restanolon, and Troberin. The drug was first described in the literature by 1956.




















